The QtGui.QInputDialog provides a simple convenience dialog to get a single value from the user. The input value can be a string, a number or an item from a list.
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example, we receive data from
a QtGui.QInputDialog dialog.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: October 2011
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.btn = QtGui.QPushButton(‘Dialog‘, self)
self.btn.move(20, 20)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.showDialog)
self.le = QtGui.QLineEdit(self)
self.le.move(130, 22)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 290, 150)
self.setWindowTitle(‘Input dialog‘)
self.show()
def showDialog(self):
text, ok = QtGui.QInputDialog.getText(self, ‘Input Dialog‘,
‘Enter your name:‘)
if ok:
self.le.setText(str(text))
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
main()
The example has a button and a line edit widget. The button shows the input dialog for getting text values. The entered text will be displayed in the line edit widget.
text, ok = QtGui.QInputDialog.getText(self, ‘Input Dialog‘,
‘Enter your name:‘)
This line displays the input dialog. The first string is a dialog title, the second one is a message within the dialog. The dialog returns the entered text and a boolean value. If we click the Ok button, the boolean value is true.
if ok:
self.le.setText(str(text))
The text that we have received from the dialog is set to the line edit widget.
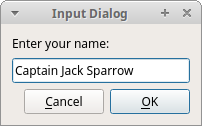 Figure: Input Dialog
Figure: Input Dialog
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hushaojun/p/4435703.html