http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3685
2 4 0 0 100 0 99 1 1 1 6 0 0 0 10 1 10 1 1 10 1 10 0
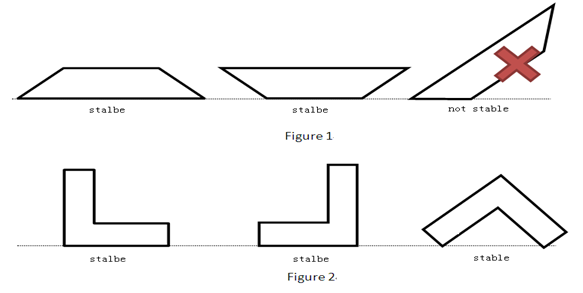
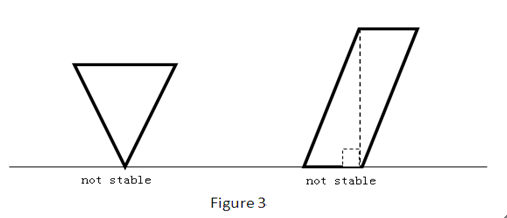
2 3HintThe sample test cases can be demonstrated by Figure 1 and Figure 2 in Description part.
题意:给一个多边形,问有几种稳定的摆放方式。。
思路:很简单。。。求出多边形的重心,然后由于不一定是凸多边形,所以再求下多边形凸包,枚举凸包的每一条边,看重心做垂足是否在边上,注意题目要求垂足在端点不算。。可以用点积看夹角是不是锐角来判断垂足位置。。
/**
* @author neko01
*/
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define min3(a,b,c) min(a,min(b,c))
#define max3(a,b,c) max(a,max(b,c))
#define pb push_back
#define mp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
#define clr(a) memset(a,0,sizeof a)
#define clr1(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof a)
#define dbg(a) printf("%d\n",a)
typedef pair<int,int> pp;
const double eps=1e-8;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int INF=0x7fffffff;
const LL inf=(((LL)1)<<61)+5;
int dcmp(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps) return 0;
if(x>0) return 1;
return -1;
}
struct point{
double x,y;
point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y) {}
};
point operator +(const point &a,const point &b){
return point(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y);
}
point operator -(const point &a,const point &b){
return point(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y);
}
point operator *(const point &a,const double &p){
return point(a.x*p,a.y*p);
}
point operator /(const point &a,const double &p){
return point(a.x/p,a.y/p);
}
bool operator < (const point &a,const point &b){
return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y);
}
bool operator == (const point &a,const point &b){
return dcmp(a.x-b.x)==0&&dcmp(a.y-b.y)==0;
}
double dot(point A,point B){
return A.x*B.x+A.y*B.y;
}
double cross(point A,point B){
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
double Length(point A){
return sqrt(dot(A,A));
}
bool OnSegment(point p,point a1,point a2) //判断点p是否在直线a1a2上
{
return dcmp(cross(a1-p,a2-p))==0&&dcmp(dot(a1-p,a2-p))<0; //线段包含端点时改成<=
}
point PolyGravity(point *p,int n) //求多边形重心
{
point ans=point(0,0);
double sumArea=0,area;
for(int i=2;i<n;i++)
{
area=cross(p[i-1]-p[0],p[i]-p[0]);
sumArea+=area;
ans.x+=(p[0].x+p[i-1].x+p[i].x)*area;
ans.y+=(p[0].y+p[i-1].y+p[i].y)*area;
}
return ans/(sumArea*3);
}
int graham(point *p,int n,point *ch) //凸包
{
sort(p,p+n);
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
while(m>1&&cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
int k=m;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
{
while(m>k&&cross(ch[m-1]-ch[m-2],p[i]-ch[m-2])<=0) m--;
ch[m++]=p[i];
}
if(n>1) m--;
return m;
}
point p[50005];
point ch[50005];
bool check(point P,point A,point B)
{
point v1=B-A,v2=P-A,v3=P-B;
if(dcmp(dot(v1,v2))<=0) return false;
if(dcmp(dot(v1,v3))>=0) return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n,t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
point g=PolyGravity(p,n);
int m=graham(p,n,ch),ans=0;
ch[m]=ch[0];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
if(OnSegment(g,ch[i],ch[i+1])||check(g,ch[i],ch[i+1]))
ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
hdu3685 Rotational Painting 求多边形重心和凸包
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/neko01/article/details/40678545