首先说一下什么是正互反矩阵,见下图,一看图其实就知道什么是正互反矩阵。
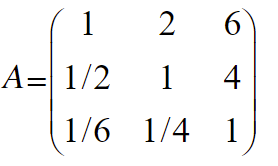
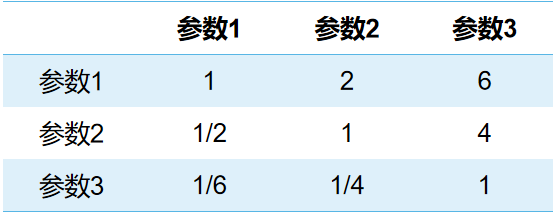
当我们现在有一堆参数,分了好几个层次,每个层次里面又有好多参数,那么每个层次的每个参数权重如何设定,这时候,会用到这种类型的矩阵。为方便理解,可以将矩阵A看成下面的表格
至于比较两个参数之间的重要程度的取值,自行寻找标准。下面是标准之一:1-9标度法
| 相对重要性 | 定义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 同等重要 | 两个目标同样重要 |
| 3 | 略微重要 | 经验或判断,认为一个目标比另一个略微重要 |
| 5 | 相当重要 | 经验或判断,认为一个目标比另一个重要 |
| 7 | 明显重要 | 深感一个目标比另一个重要,并且这种重要性已经有实践证明 |
| 9 | 绝对重要 | 强烈的感到一个目标比另一个重要的多 |
| 2,4,6,8 | 两个相邻判断的中间值 | 折中时采用 |
可以使用平常手算时的那种计算方式,通过|λE-A| = 0得到特征值,再代入(λE-A)中求解该特征值的特征向量。其中,我们只用到最大特征值、及其特向。
这种算法很精确,但是很麻烦,(如果你要是用Matlab当我没说。。。),由于参数之间的重要程度关系,都是由经验判断,主观性很强,所以对精度要求其实不高,大概即可,故有三种快速计算最大特征值及其特向的方法:根法、和法、幂法
public class MatrixUtil {
// 保留小数的位数
private final int BIT = 4;
/**
* 和法求解矩阵matrix的最大特征根、及其特征向量
*
* @param matrix
*/
public Map<String, Object> sumMethod(double[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length != matrix[0].length) {
throw new RuntimeException("必须是方阵");
}
// 保存结果用的
Map<String, Object> res = new HashMap<>();
// 判断矩阵w,目前与matrix一致,后面会对其进行修改
int rows = matrix.length, cols = matrix[0].length;
double[][] w = new double[rows][cols];
for(int row = 0; row < rows; ++row){
for (int col = 0; col < cols; ++col) {
w[row][col] = matrix[row][col];
}
}
// 矩阵的维度
final int DIM = matrix.length;
// 1、将矩阵的每一列进行归一化处理,得到判断矩阵w
normalizedColumn(w);
// 2、判断矩阵w的所有列进行相加,变成n x 1的矩阵后进行归一化处理
// 此时得到的n x 1矩阵就是matrix最大特征根的特征向量
double[][] t = mergeColumn(w);
normalizedColumn(t);
// 3、计算最大特征根
// 3.1 将原矩阵(m x m)与最大特向(m x 1)进行矩阵乘法(m x 1)
double[][] mx = matrixMult(matrix, t);
// 3.2 将mx和maxEigenVector这两个m x 1的列矩阵对应位置进行相除
for (int row = 0; row < DIM; ++row) {
mx[row][0] /= t[row][0];
}
// 3.3 将mx这一列矩阵的所有元素求和,最后取个均值就是最大特征根
double maxEigenValue = 0.0;
for (int row = 0; row < DIM; ++row) {
maxEigenValue += mx[row][0];
}
maxEigenValue /= DIM;
// 4、对特征值的小数进行保留
res.put("maxEigenvalue", toFixed(maxEigenValue));
// 5、对特征向量的小数进行保留
double[] maxEigenVector = convertData(t);
for (int i = 0; i < maxEigenVector.length; i++) {
maxEigenVector[i] = toFixed(maxEigenVector[i]);
}
// 6、通过上述过程可知,特征向量所有元素的和一定是1,但是经过小数保留后会存在误差,进行处理
correction(maxEigenVector);
res.put("maxEigenVector", maxEigenVector);
return res;
}
/**
* 矩阵乘法
*
* @param a 矩阵a
* @param b 矩阵b
*/
public double[][] matrixMult(double[][] a, double[][] b) {
int arows = a.length,
acols = a[0].length,
brows = b.length,
bcols = b[0].length;
// 判断两个矩阵是否能够进行相乘
if (acols != brows) {
throw new RuntimeException("矩阵a的列数与矩阵b的行数不等,无法进行矩阵相乘");
}
// 保存矩阵相乘的结果
double[][] res = new double[arows][bcols];
for (int i = 0; i < bcols; ++i) {
// j,k 定位行乘列
for (int j = 0; j < arows; ++j) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < acols; ++k) {
sum += a[j][k] * b[k][i];
}
res[j][i] = sum;
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 矩阵的列进行归一化,某元素在其所在列的比例
*
* @param matrix
*/
public void normalizedColumn(double[][] matrix) {
int rows = matrix.length,
cols = matrix[0].length,
row, col;
// 求出矩阵每一列之和
double[] temp = new double[cols];
for (col = 0; col < cols; ++col) {
for (row = 0; row < rows; ++row) {
temp[col] += matrix[row][col];
}
}
// 对matrix进行处理,得出每个元素在其所在列的占比
for (row = 0; row < rows; ++row) {
for (col = 0; col < cols; ++col) {
matrix[row][col] /= temp[col];
}
}
}
/**
* 合并矩阵的列,将m x n的矩阵变为m x 1的矩阵
*
* @param matrix
*/
public double[][] mergeColumn(double[][] matrix) {
int rows = matrix.length, cols = matrix[0].length;
double[][] res = new double[rows][1];
for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int col = 0; col < cols; ++col) {
sum += matrix[row][col];
}
res[row][0] = sum;
}
return res;
}
/**
* 保留指定个数的小数
*
* @param number 数字
*/
public double toFixed(double number) {
final double temp = Math.pow(10, BIT);
return Math.round(number * temp) / temp;
}
/**
* arr是一维的最大特征向量,
* 由于最大特征向量是一个n x 1的二维矩阵,会转换为一维数组
* 易知特向的每一个元素以及最大特征根是double类型,会对其保留BIT位的小数
* 存在四舍五入后,最大特征根的特向元素之和不为1的情况,可能会多或少Math.pow(10, -BIT)
* 这里做的处理:将这个误差给到权重最小的参数身上,保证所有参数的权重和为1
*
* @param arr
*/
public void correction(double[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
double bei = Math.pow(10, BIT);
double sum = 0.0;
for (double v : arr) {
sum = sum + v * bei;
}
// 四舍五入后没问题
if (sum == bei) return;
// 误差
double err = sum - bei;
// 定位到权重最小值的参数位置
int minRow = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
if (arr[i] < arr[minRow]) {
minRow = i;
}
}
arr[minRow] -= err / bei;
}
/**
* 二维数组转一维数组
*
* @param matrix
*/
public double[] convertData(double[][] matrix) {
int rows = matrix.length, cols = matrix[0].length;
int arrLen = rows * cols;
double[] res = new double[arrLen];
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < cols; ++col) {
res[index++] = matrix[row][col];
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[][] matrix = {
{1, 2, 6},
{0.5, 1, 4},
{1 / 6.0, 0.25, 1}
};
MatrixUtil matrixUtil = new MatrixUtil();
Map<String, Object> stringObjectMap = matrixUtil.sumMethod(matrix);
stringObjectMap.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k);
if(v instanceof double[])
System.out.println(Arrays.toString((double[]) v));
else
System.out.println(v);
});
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/silverbeats/p/15139387.html