一、函数
1、定义
将命令序列按格式写在一起,可方便重复使用命令序列
//方式一
function 函数名 {
命令序列
}
//方式二
函数名() {
命令序列
}
2、函数返回值
return表示退出函数并返回一个退出值,脚本中可以用$?变量显示该值
2.1 使用原则
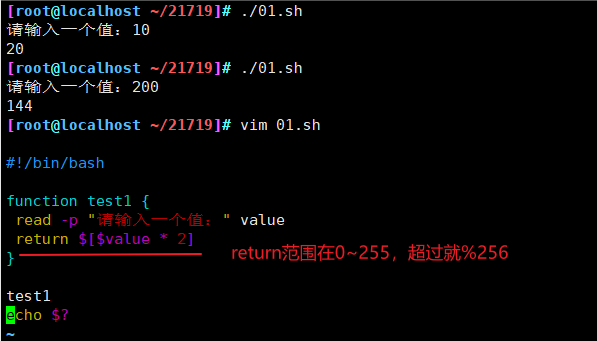
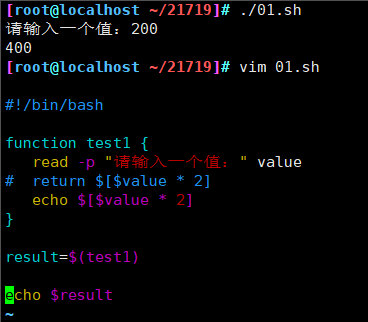
#!/bin/bash
function test1 {
read -p "请输入一个值:" value
# return $[$value * 2]
echo $[$value * 2]
}
result=$(test1)
#echo $result
echo $[$result * 2]
二、函数传参
1、函数变量的作用范围
函数在Shell脚本中仅在当前Shell环境中有效,
Shell脚本中变量默认全局有效,
将变量限定在函数内部使用local命令
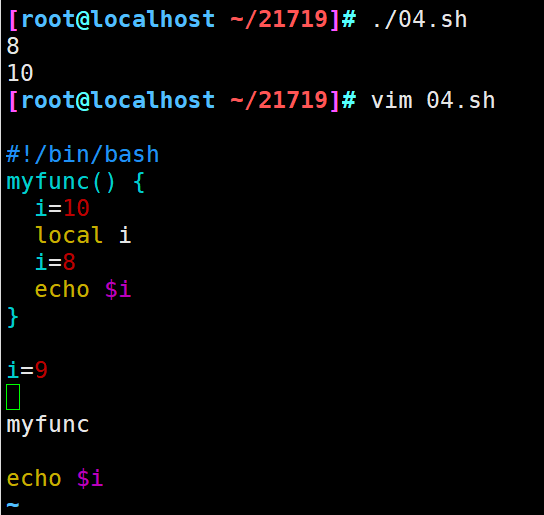
#!/bin/bash
myfunc() {
i=10
local i
i=8
echo $i
}
i=9
myfunc
echo $i
三、递归
函数调用自己本身的函数
1、阶乘
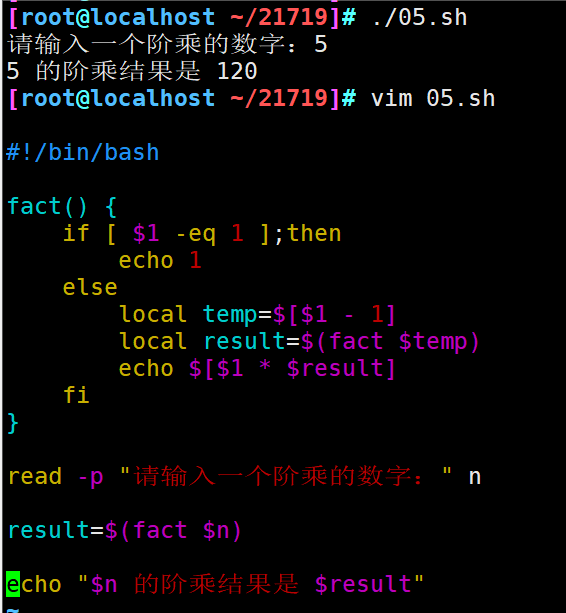
#!/bin/bash
fact() {
if [ $1 -eq 1 ];then
echo 1
else
local temp=$[$1 - 1]
local result=$(fact $temp)
echo $[$1 * $result]
fi
}
read -p "请输入一个阶乘的数字:" n
result=$(fact $n)
echo "$n 的阶乘结果是 $result"
四、递归目录
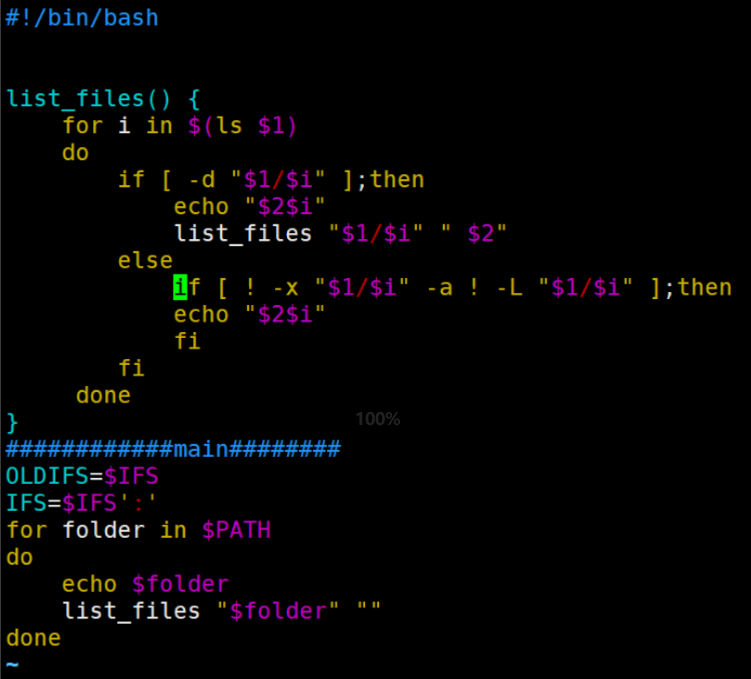
#!/bin/bash
list_files() {
for i in $(ls $1)
do
if [ -d "$1/$i" ];then
echo "$2$i"
list_files "$1/$i" " $2"
else
if [ ! -x "$1/$i" -a ! -L "$1/$i" ];then
echo "$2$i"
fi
fi
done
}
############main########
OLDIFS=$IFS
IFS=$IFS‘:‘
for folder in $PATH
do
echo $folder
list_files "$folder" ""
done
IFS=$OLDIFS
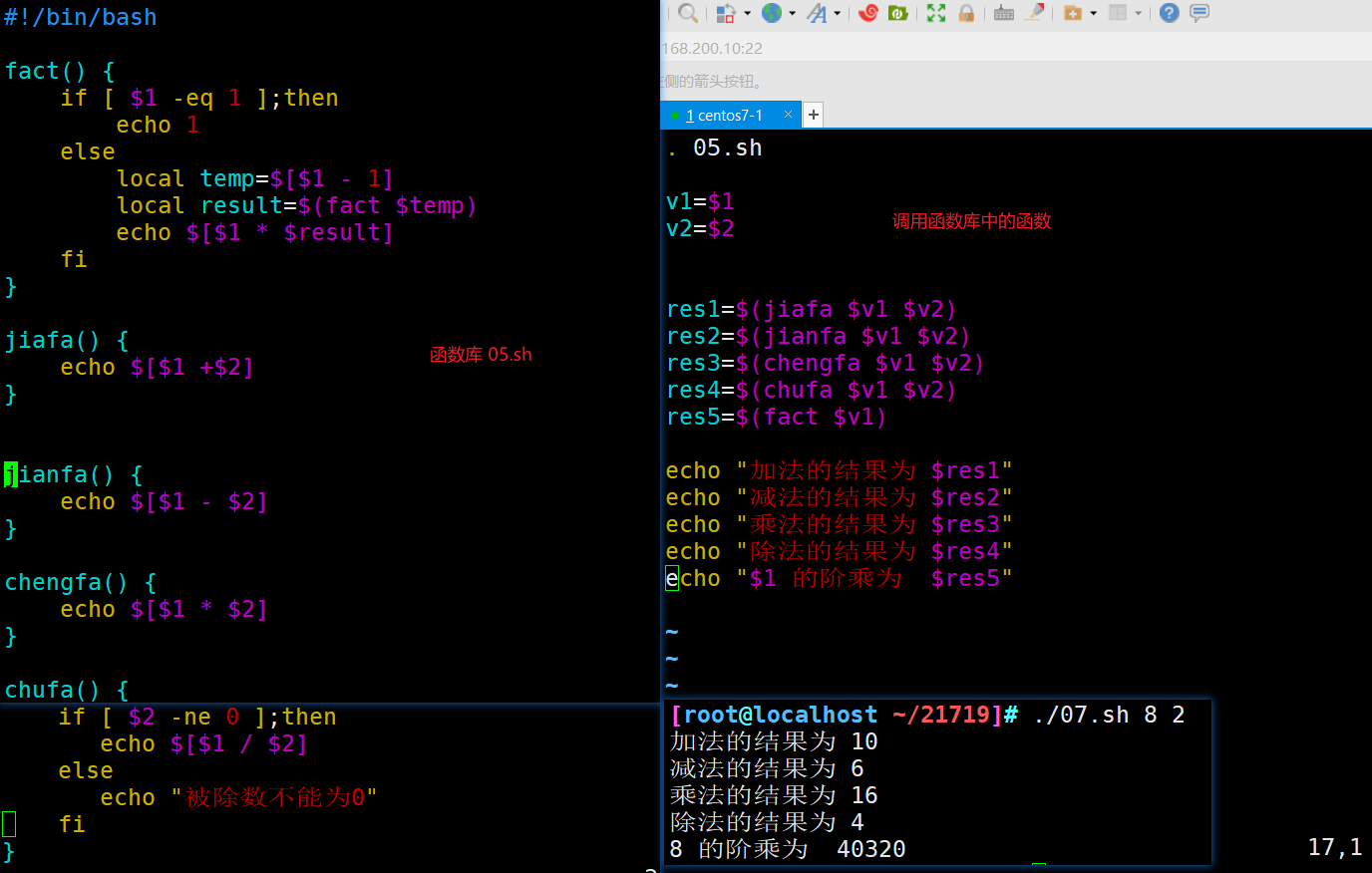
五、创建库
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/htfhtf/p/15101719.html