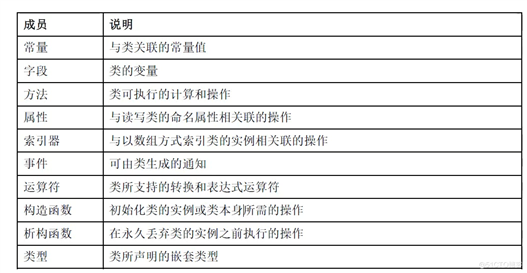
与类型关联的字段称为”静态字段",由static修饰
```c#
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 24;
stu.Score = i;
stuList.Add(stu);
}
int totalAge = 0;
int totalScore = 0;
foreach (var stu in stuList)
{
totalAge += stu.Age;
totalScore += stu.Score;
}
Student.AverageAge = totalAge / Student.Amount;
Student.AverageScore = totalScore / Student.Amount;
Student.ReportAmount();
Student.ReportAverageAge();
Student.ReportAveragSecore();
}}
class Student
{
public int Age;
public int Score;
public static int AverageAge;
public static int AverageScore;
public static int Amount;
public Student()
{
Student.Amount++;
}
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
public static void ReportAverageAge()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.AverageAge);
}
public static void ReportAveragSecore()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.AverageScore);
}}
}
实例只读字段
```c#
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student(1);
Console.WriteLine(stu1.ID);
}
}
class Student
{
public readonly int ID;
public int Age;
public int Score;
public Student(int id)
{
this.ID = id;
}
public static int AverageAge;
public static int AverageScore;
public static int Amount;
}
}
静态只读字段
```c#
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Red);
Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Green);
Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Blue);
}
}
class Color
{
public int Red;
public int Green;
public int Blue;
}
class Brush
{
public static readonly Color DefaultColor = new Color() { Red = 0,Green = 0,Blue = 0 };
}
}
## 2、属性
### (1)什么是属性只读属性——只有getter没有setter
}
private static int amount;
public static int Amount
{
get { return amount; }
set {
if (value>=0)
{
Student.amount = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Amount must greater than 0.");
}
}
}}
}
### (3) 属性与字段的关系
- 一般情况下,它们都用于表示实体(对象或类型)的状态
- 属性大多数情况下是字段的包装器(wrapper)
- 建议:永远使用属性(而不是字段)来暴露数据,即字段永远都是private或protected的
## 3、索引器
### (1)什么是索引器
- 索引器(indexer)是这样一种成员 :它使对象能够用与数组相同的方式(即使用下标)进行索引
### (2)索弓器的声明(indexer+Tab)
- 参见C#语言定义文档
- 注意:没有静态索引器
```c#
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu["Math"] = 90;
stu["Math"] = 100;
var mathScore = stu["Math"];
Console.WriteLine(mathScore);
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary<string, int> scoreDictionary = new Dictionary<string, int>();
public int? this[string subject]
{
get
{
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
return this.scoreDictionary[subject];
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
set
{
if (value.HasValue==false)
{
throw new Exception("Score cannot be null.");
}
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value;
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value.Value);
}
}
}
}
}原文:https://blog.51cto.com/u_15296868/3241834