使用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。如孙悟空猴毛分身、鸣人影之分身、剑光分化、无限剑制
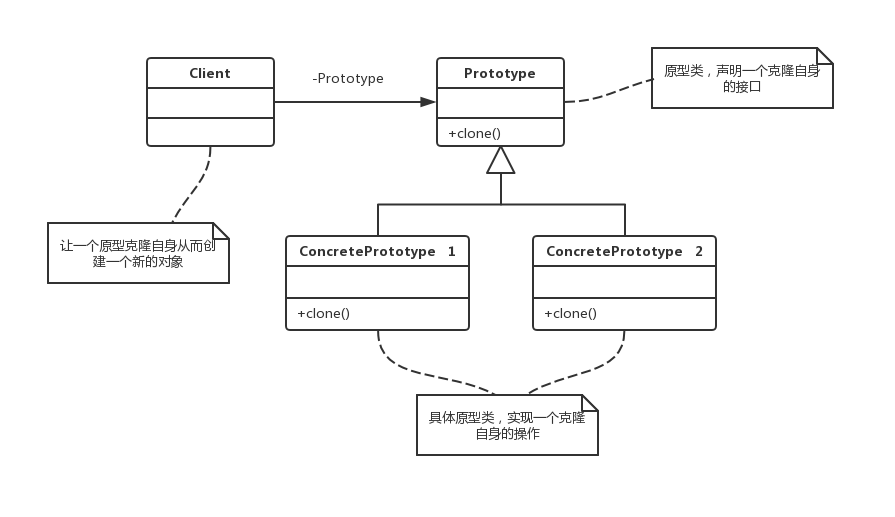
原型模式是一种创建型设计模式,允许一个对象再创建另外一个可定制的对象,无需知道如何创建的细节。
原型模式工作原理是:通过将一个原型对象传给那个要创建的对象,这个要创建的对象通过请求原型对象拷贝它们自己来实施创建对象,即对象Clone()
浅拷贝概念
深拷贝概念
写一个角色生成器、生成克隆角色
原型抽象类、具体类 —— 怪物、Ghost、Devil
// 抽象原型类 —— 怪物
UCLASS(Abstract)
class DESIGNPATTERNS_API UMonsterPrototype : public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// 克隆函数
virtual UMonsterPrototype* Clone() {
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Please implement this!"));
return nullptr;
}
// 展示信息
virtual void ShowInfo() {
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT(__FUNCTION__" %s [Health]%d, [Speed]%d"), *this->GetName() ,m_pHealth, m_pSpeed);
}
protected:
int32 m_pHealth = 100;
int32 m_pSpeed = 30;
};
// 具体产原型类 —— Ghost
UCLASS(Blueprintable, BlueprintType)
class DESIGNPATTERNS_API UGhost : public UMonsterPrototype
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// 重载克隆函数
virtual UMonsterPrototype* Clone() override {
UGhost* CloneIns = NewObject<UGhost>();
CloneIns->m_pHealth = m_pHealth;
CloneIns->m_pSpeed = m_pSpeed;
return CloneIns;
}
};
// 具体产原型类 —— Devil
UCLASS(Blueprintable, BlueprintType)
class DESIGNPATTERNS_API UDevil : public UMonsterPrototype
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// 初始化数值
UDevil() {
m_pHealth = 120;
m_pSpeed = 20;
}
// 重载克隆函数
virtual UMonsterPrototype* Clone() override {
UDevil* CloneIns = NewObject<UDevil>();
CloneIns->m_pHealth = m_pHealth;
CloneIns->m_pSpeed = m_pSpeed;
CloneIns->m_pAttack = m_pAttack;
return CloneIns;
}
// 展示信息
virtual void ShowInfo() override {
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT(__FUNCTION__" %s [Health]%d, [Speed]%d, [Attack] %d"), *this->GetName(), m_pHealth, m_pSpeed, m_pAttack);
}
protected:
int32 m_pAttack = 100;
};
创建工厂类 —— 怪物生成器
// 工厂类 —— 怪物生成器
UCLASS(Blueprintable, BlueprintType)
class DESIGNPATTERNS_API UMonsterSpawner : public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// 生成新怪物,使用模板,避免针对每种怪物都要写一遍
template <class T>
T* SpawnMonster() {
return NewObject<T>();
}
// 克隆怪物
UMonsterPrototype* SpawnMonster(UMonsterPrototype* pMonsterClass) {
return pMonsterClass->Clone();
}
};
调用测试
// 调用测试用的Actor
UCLASS()
class DESIGNPATTERNS_API AMonsterSpawnerActor : public AActor
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
void BeginPlay() override {
// 创建工厂
UMonsterSpawner* MonsterSpawner = NewObject<UMonsterSpawner>();
// 第一次创建 Ghost
UGhost* Ghost = MonsterSpawner->SpawnMonster<UGhost>();
// 克隆 Ghost
UGhost* Ghost_Copy1 = Cast<UGhost>(MonsterSpawner->SpawnMonster(Ghost));
Ghost->ShowInfo();
Ghost_Copy1->ShowInfo();
// 第一次创建 Devil
UDevil* Devil =MonsterSpawner->SpawnMonster<UDevil>();
// 克隆 Devil
UDevil* Devil_Copy1 = Cast<UDevil>(MonsterSpawner->SpawnMonster(Devil));
Devil->ShowInfo();
Devil_Copy1->ShowInfo();
}
};
调式输出
LogTemp: Warning: UMonsterPrototype::ShowInfo Ghost_0 [Health]100, [Speed]30
LogTemp: Warning: UMonsterPrototype::ShowInfo Ghost_1 [Health]100, [Speed]30
LogTemp: Warning: UDevil::ShowInfo Devil_0 [Health]120, [Speed]20, [Attack] 100
LogTemp: Warning: UDevil::ShowInfo Devil_1 [Health]120, [Speed]20, [Attack] 100
在数据建模时,同样可以运用原型模式
给对象声明一个prototype属性,该属性指定另外一个对象,如果访问的属性不在此对象内部,就去prototype指定的对象查找
{
"name": "goblin grunt",
"minHealth": 20,
"maxHealth": 30,
"resists": ["cold", "poison"],
"weaknesses": ["fire", "light"]
}
{
"name": "goblin wizard",
"prototype": "goblin grunt",
"spells": ["fire ball", "lighting bolt"]
}
{
"name": "goblin archer",
"prototype": "goblin grunt",
"attacks": ["short bow"]
}
【UE4 C++】 原型模式 Prototype Pattern
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/shiroe/p/14855200.html