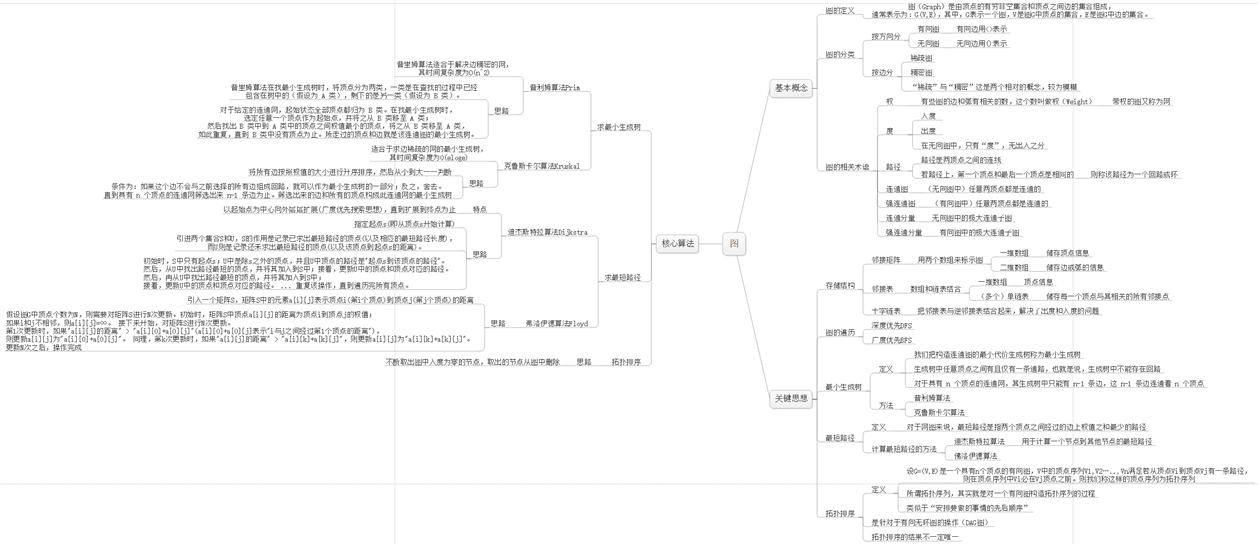
图的遍历是指,从给定图中任意指定的顶点(称为初始点)出发,按照某种搜索方法沿着图的边访问图中的所有顶点,使每个顶点仅被访问一次,这个过程称为图的遍历。遍历过程中得到的顶点序列称为图遍历序列。
图的遍历过程中,根据搜索方法的不同,又可以划分为两种搜索策略:
(1)深度优先搜索(DFS,Depth First Search)
(2)广度优先搜索(BFS,Breadth First Search)
(仅介绍无向图)
#include <stdio.h>
int e[100][100], book[100], n, sum = 0;
void dfs(int cur) {
int i;
printf("%d ", cur);
sum++;
// 边界
if (sum == n) {
return;
}
// 尝试每一步
for (i = 1; i <=n; i++) {
if (e[cur][i] == 1 && book[i] == 0) {
book[i] = 1;
dfs(i);
}
}
}
int main(void) {
int i, j, m, a, b;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (i == j) e[i][j] = 0;
else e[i][j] = 9;
// 二位数组是沿着主对角线对称,即无向图
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
e[a][b] = 1;
e[b][a] = 1;
}
book[1] = 1;
dfs(1);
printf("\n");
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
printf("%5d ", e[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int e[100][100], book[100] = {0}, n, sum = 0;
int i, j, m, a, b, cur;
// 初始化队列
struct node {
int n;
} que[100];
int head = 0;
int tail = 0;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (i == j) e[i][j] = 0;
else e[i][j] = 9;
// 二位数组是沿着主对角线对称,即无向图
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
e[a][b] = 1;
e[b][a] = 1;
}
book[1] = 1;
que[tail].n = 1;
tail++;
while (head < tail) {
cur = que[head].n;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (e[cur][i] == 1 && book[i] == 0) {
book[i] = 1;
que[tail].n = i;
tail++;
}
if (tail > n) {
break;
}
}
head++;
}
for (i = 0; i < tail; i++)
printf("%d ", que[i].n);
return 0;
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/sleep-early/p/m.html