1、获得图片路径列表给x,获得标签列表给y.
2、将数据集装载到dataset。
3、打乱,用map()函数读取图片数据。
(1) images and labels ? ?? = [1. ??????, 2. ??????, 3. ??????, … ] ? ?? = [4,9,1, … ] (2)tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X,Y)) (3).shuffle().map(????????).batch()
4、map()函数如下:
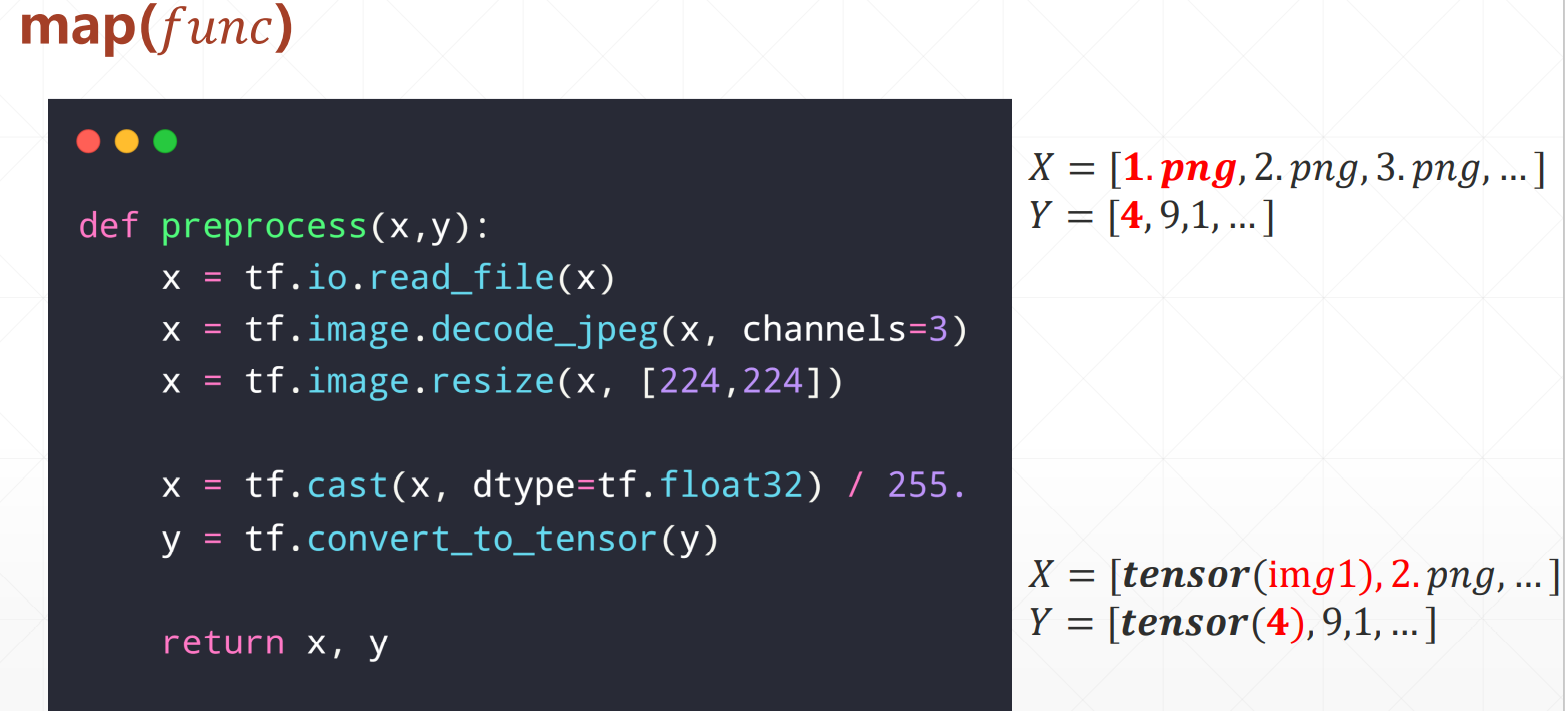
5、数据集步骤:
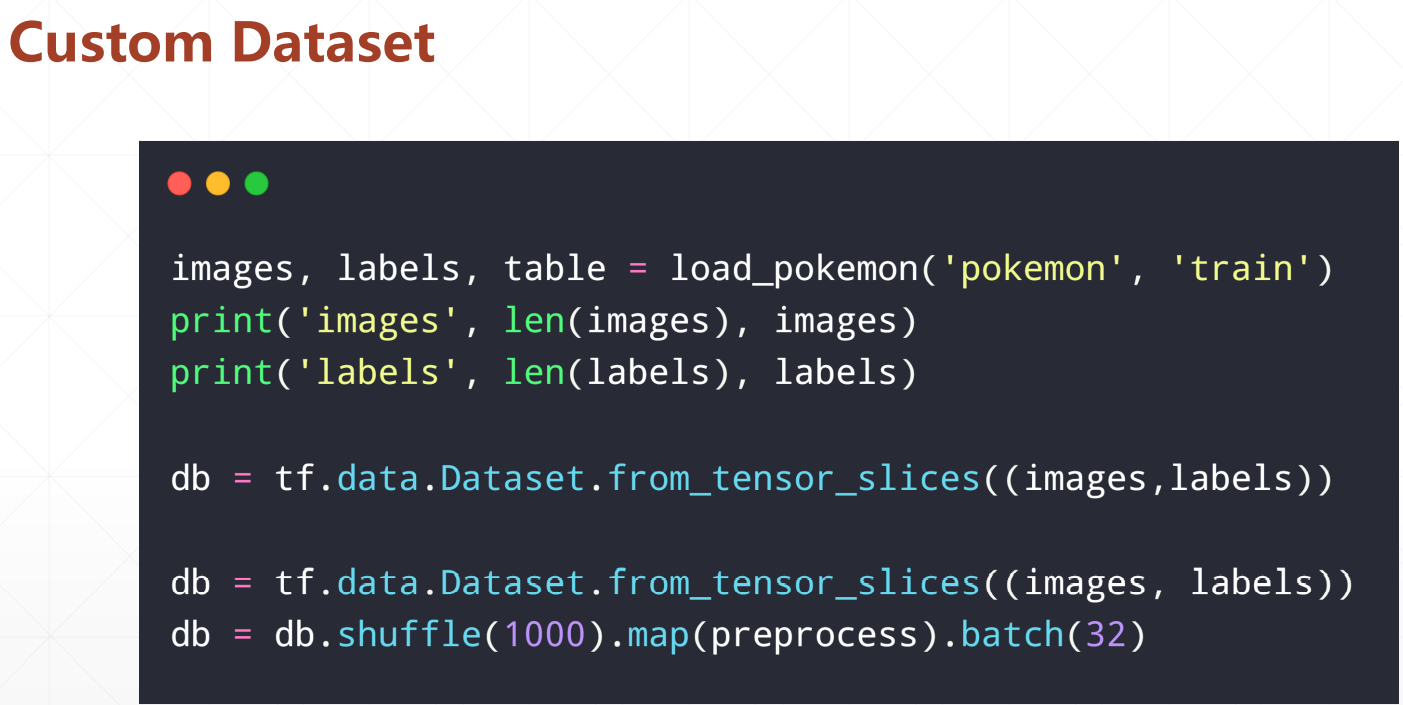
6、数据预处理步骤:


import os, glob import random, csv import tensorflow as tf def load_csv(root, filename, name2label): # root:数据集根目录 # filename:csv文件名 # name2label:类别名编码表 if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(root, filename)): images = [] for name in name2label.keys(): # ‘pokemon\\mewtwo\\00001.png images += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, ‘*.png‘)) images += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, ‘*.jpg‘)) images += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, ‘*.jpeg‘)) # 1167, ‘pokemon\\bulbasaur\\00000000.png‘ print(len(images), images) random.shuffle(images) with open(os.path.join(root, filename), mode=‘w‘, newline=‘‘) as f: writer = csv.writer(f) for img in images: # ‘pokemon\\bulbasaur\\00000000.png‘ name = img.split(os.sep)[-2] label = name2label[name] # ‘pokemon\\bulbasaur\\00000000.png‘, 0 writer.writerow([img, label]) print(‘written into csv file:‘, filename) # read from csv file images, labels = [], [] with open(os.path.join(root, filename)) as f: reader = csv.reader(f) for row in reader: # ‘pokemon\\bulbasaur\\00000000.png‘, 0 img, label = row label = int(label) images.append(img) labels.append(label) assert len(images) == len(labels) return images, labels def load_pokemon(root, mode=‘train‘): # 创建数字编码表 name2label = {} # "sq...":0 for name in sorted(os.listdir(os.path.join(root))): if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join(root, name)): continue # 给每个类别编码一个数字 name2label[name] = len(name2label.keys()) # 读取Label信息 # [file1,file2,], [3,1] images, labels = load_csv(root, ‘images.csv‘, name2label) if mode == ‘train‘: # 60% images = images[:int(0.6 * len(images))] labels = labels[:int(0.6 * len(labels))] elif mode == ‘val‘: # 20% = 60%->80% images = images[int(0.6 * len(images)):int(0.8 * len(images))] labels = labels[int(0.6 * len(labels)):int(0.8 * len(labels))] else: # 20% = 80%->100% images = images[int(0.8 * len(images)):] labels = labels[int(0.8 * len(labels)):] return images, labels, name2label img_mean = tf.constant([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) img_std = tf.constant([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) def normalize(x, mean=img_mean, std=img_std): # x: [224, 224, 3] # mean: [224, 224, 3], std: [3] x = (x - mean)/std return x def denormalize(x, mean=img_mean, std=img_std): x = x * std + mean return x def preprocess(x,y): # x: 图片的路径,y:图片的数字编码 x = tf.io.read_file(x) x = tf.image.decode_jpeg(x, channels=3) # RGBA x = tf.image.resize(x, [244, 244]) # data augmentation, 0~255 # x = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(x) x= tf.image.random_flip_left_right(x) x = tf.image.random_crop(x, [224, 224, 3]) # x: [0,255]=> 0~1 x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255. # 0~1 => D(0,1) x = normalize(x) y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y) return x, y def main(): import time images, labels, table = load_pokemon(‘pokemon‘, ‘train‘) print(‘images‘, len(images), images) print(‘labels‘, len(labels), labels) print(table) # images: string path # labels: number db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images, labels)) db = db.shuffle(1000).map(preprocess).batch(32) writter = tf.summary.create_file_writer(‘logs‘) for step, (x,y) in enumerate(db): # x: [32, 224, 224, 3] # y: [32] with writter.as_default(): x = denormalize(x) tf.summary.image(‘img‘,x,step=step,max_outputs=9) time.sleep(5) if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: main()
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangxianrong/p/14729670.html