创建/销毁线程需要消耗系统资源,线程池可以复用已创建的线程。
控制并发的数量。并发数量过多,可能会导致资源消耗过多,从而造成服务器崩溃。(主要原因)
可以对线程做统一管理。
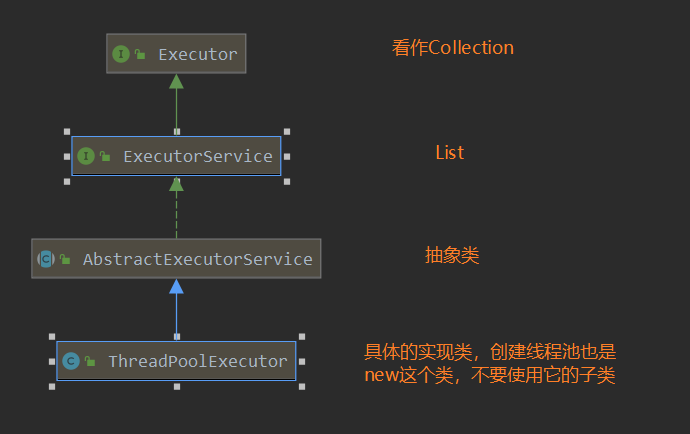
使用ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法创建
public class ThreadPoolTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 8, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS
, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5)
, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
pool.execute(
() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
);
}
}
使用Executors这个工具类来实现
JDK工具类为我们提供了四种常用的线程池,其实它们的底层源码都是调用ThreadPoolExecutor来实现的,传递的线程池参数不同罢了。
工程中我们都是使用第一种方法来创建线程池,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的?险(OOM)
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
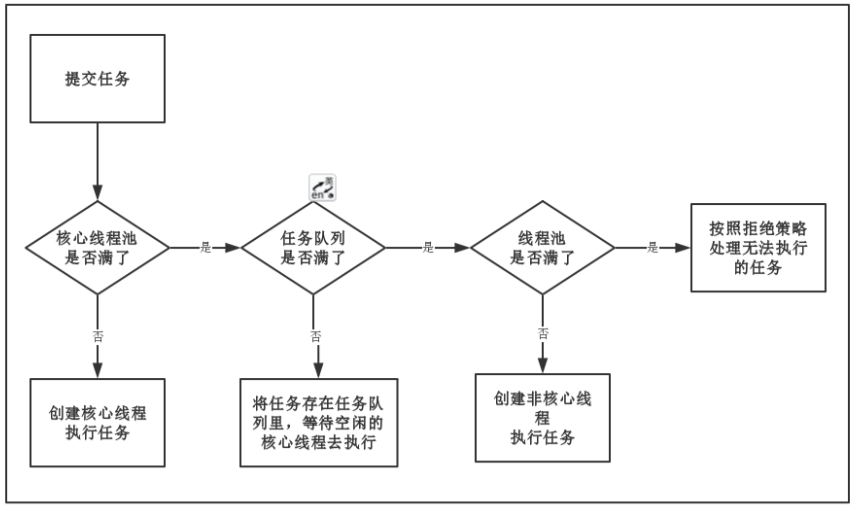
线程池调度的核心是execute方法,总结完就是上图
// JDK 1.8
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
// 1.当前线程数小于corePoolSize,则调用addWorker创建核心线程执行任务
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 2.如果不小于corePoolSize,则将任务添加到workQueue队列。
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
// 2.1 如果isRunning返回false(状态检查),则remove这个任务,然后执行拒绝策略。
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
// 2.2 线程池处于running状态,但是没有线程,则创建线程
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 3.如果放入workQueue失败,则创建非核心线程执行任务,
// 如果这时创建非核心线程失败(当前线程总数不小于maximumPoolSize时),就会执行拒绝策略。
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
这个对线程调度的源码没有深入分析,如addWord函数,拒绝策略是怎么实现的等。以后会再专门写一篇文章,可以参考《并发编程之美》的源码分析。
这也可以看到线程池的又一优点:灵活。
JavaGuide
还没仔细研究,粗略看了下,怎么很不错,值得参考
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/sang-bit/p/14706295.html