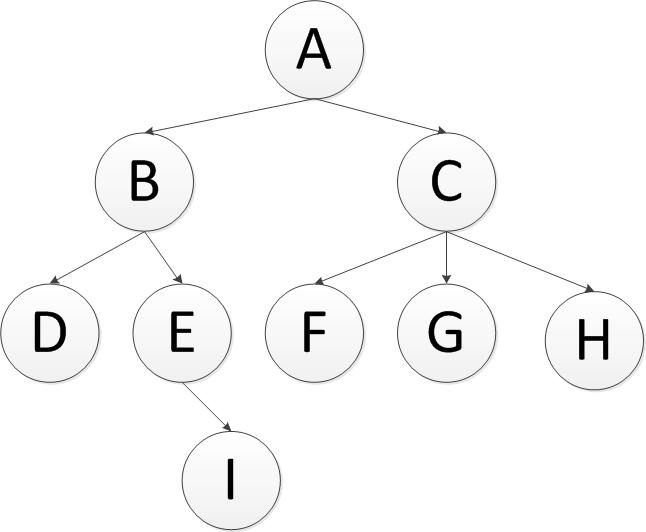
BFS其过程检验来说是对每一层节点依次访问,访问完一层进入下一层,而且每个节点只能访问一次。对于上面的例子来说,广度优先遍历的 结果是:A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I(假设每层节点从左到右访问)。
先往队列中插入左节点,再插右节点,这样出队就是先左节点后右节点了。
广度优先遍历树,需要用到队列(Queue)来存储节点对象,队列的特点就是先进先出。例如,上面这颗树的访问如下:
首先将A节点插入队列中,队列中有元素(A);
将A节点弹出,同时将A节点的左、右节点依次插入队列,B在队首,C在队尾,(B,C),此时得到A节点;
继续弹出队首元素,即弹出B,并将B的左、右节点插入队列,C在队首,E在队尾(C,D,E),此时得到B节点;
继续弹出,即弹出C,并将C节点的左、中、右节点依次插入队列,(D,E,F,G,H),此时得到C节点;
将D弹出,此时D没有子节点,队列中元素为(E,F,G,H),得到D节点;
。。。以此类推。。
2、深度优先
DFS,其过程简要来说是对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个节点只能访问一次。对于上面的例子来说深度优先遍历的结果就是:A,B,D,E,I,C,F,G,H.(假设先走子节点的的左侧)。
深度优先遍历各个节点,需要使用到栈(Stack)这种数据结构。stack的特点是是先进后出。整个遍历过程如下:
先往栈中压入右节点,再压左节点,这样出栈就是先左节点后右节点了。
首先将A节点压入栈中,stack(A);
将A节点弹出,同时将A的子节点C,B压入栈中,此时B在栈的顶部,stack(B,C);
将B节点弹出,同时将B的子节点E,D压入栈中,此时D在栈的顶部,stack(D,E,C);
将D节点弹出,没有子节点压入,此时E在栈的顶部,stack(E,C);
将E节点弹出,同时将E的子节点I压入,stack(I,C);
...依次往下,最终遍历完成。
1 package Demo; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.LinkedList; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.Queue; 7 import java.util.Stack; 8 9 public class T { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 Tree t = new Tree(); 13 Node root = new Node(1); 14 Node n1 = new Node(2); 15 Node n2 = new Node(3); 16 Node n3 = new Node(4); 17 Node n4 = new Node(5); 18 Node n5 = new Node(6); 19 20 root.left = n1; 21 root.right = n2; 22 n1.left = n3; 23 n1.right = n4; 24 n4.left = n5; 25 26 t.root = root; 27 28 int maxDepth = t.getMaxDepth(root); 29 System.out.println("最大深度:" + maxDepth); 30 int minDepth = t.getMinDepth(root); 31 System.out.println("最小深度:" + minDepth); 32 33 System.out.println("DFS算法--递归:"); 34 t.preOrder(root); 35 System.out.println("----------------"); 36 System.out.println("DFS算法--非递归:"); 37 t.newPreOrder(root); 38 System.out.println("----------------"); 39 System.out.println("BFS算法--非递归:"); 40 t.Order(root); 41 42 } 43 44 } 45 46 class Node { 47 int val; 48 Node left; 49 Node right; 50 51 public Node(int val) { 52 super(); 53 this.val = val; 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 public String toString() { 58 return val + ""; 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 class Tree { 64 Node root; 65 66 public Tree(Node root) { 67 this.root = root; 68 } 69 70 public Tree() { 71 super(); 72 } 73 74 // 最大深度 75 // 递归实现 76 // DFS 77 public int getMaxDepth(Node root) { 78 if (root == null) { 79 return 0; 80 } 81 82 int leftDepth = getMaxDepth(root.left) + 1; 83 int rightDepth = getMaxDepth(root.right) + 1; 84 85 return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth); 86 } 87 88 // 最小深度 89 // 递归实现 90 // DFS 91 public int getMinDepth(Node root) { 92 if (root == null) { 93 return 0; 94 } 95 96 int leftDepth = getMaxDepth(root.left) + 1; 97 int rightDepth = getMaxDepth(root.right) + 1; 98 99 return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth); 100 } 101 102 /* 103 * DFS、前序遍历、递归 104 */ 105 106 public void preOrder(Node root) { 107 108 if (root == null) { 109 return; 110 } 111 112 System.out.print(root.val + ""); 113 114 preOrder(root.left); 115 preOrder(root.right); 116 } 117 118 /* 119 * DFS、前序遍历,非递归 使用栈---先进后出 120 */ 121 public void newPreOrder(Node root) { 122 123 if (root == null) { 124 return; 125 } 126 127 Stack stack = new Stack(); 128 stack.push(root); 129 130 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 131 Node n = (Node) stack.pop(); 132 System.out.print(n.val + ""); 133 if (n.right != null) { 134 stack.push(n.right); 135 } 136 137 if (n.left != null) { 138 stack.push(n.left); 139 } 140 } 141 142 } 143 144 /* 145 * BFS、非递归 使用队列--先进先出 146 */ 147 148 public void Order(Node root) { 149 150 if (root == null) { 151 return; 152 } 153 154 Queue q = new LinkedList(); 155 156 q.add(root); 157 158 while (!q.isEmpty()) { 159 Node n = (Node) q.poll(); 160 System.out.print(n.val + ""); 161 162 if (n.left != null) { 163 q.add(n.left); 164 } 165 166 if (n.right != null) { 167 q.add(n.right); 168 } 169 170 } 171 172 } 173 174 }
运行结果:

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Leeyoung888/p/14638527.html