CREATE TABLE `t` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`k` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into t(id, k) values(1,1),(2,2);

begin;
select * from t;
+--------+----+
| id | c |
+--------+----+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
+--------+----+
update t set c=0 where id=c;
select * from t;
+--------+----+
| id | c |
+--------+----+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
+--------+----+
上文中update无法修改的问题,为什么会产生这种情况?
CREATE TABLE `geek` (
`a` int(11) NOT NULL,
`b` int(11) NOT NULL,
`c` int(11) NOT NULL,
`d` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`,`b`),
KEY `c` (`c`),
KEY `ca` (`c`,`a`),
KEY `cb` (`c`,`b`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
select * from geek where c=N order by a limit 1;
select * from geek where c=N order by b limit 1;
非主键索引的叶子节点上会挂着主键,因此:
由上可以得出,索引c可以等价于ca,保留较小的索引,去除索引ca
-- 非主键索引重建
alter table T drop index k;
alter table T add index(k);
-- 主键索引重建方式1
alter table T drop primary key;
1075 - Incorrect table definition; there can be only one auto column and it must be defined as a key
alter table T add primary key(id);
-- 主键索引重建方式2
alter table T engine=InnoDB;
-- 第一种,直接执行
delete from T limit 10000;
-- 第二种,在一个连接中循环执行 20 次
delete from T limit 500;
-- 第三种,在 20 个连接中同时执行
delete from T limit 500
mysql> show index from t;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| t | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 93536 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| t | 1 | a | 1 | a | A | 93536 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
mysql> explain select * from t where a is null;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | ref | a | a | 5 | const | 1 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+
1 row in set
mysql> explain select * from t where a is not null;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | ALL | a | NULL | NULL | NULL | 93536 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+-------------+
1 row in set
is null使用了索引,is not null未使用索引。那么,是否可以得出结论:is null走索引,is not null不走索引呢?
对于二级索引来说,索引列的值可能为NULL,对于索引列值为NULL的二级索引记录来说,它们被放在B+树的最左边。由此,可以看出SQL中的NULL值认为是列中最小的值。因此,is null使用了索引,is not null由于需要查询所有值,最终还需要回表到主键索引,因此,直接使用全部扫描。
上述现象的本质还是优化器对索引成本的估算,如果上述案例中a is NULL的数量达到一定的程度,回表成本增加,可能就会被优化器放弃,改走全部扫描。
同理,!=、not in是否走索引,都是同样的原理。
在不同的 MySQL 引擎中,count(*) 有不同的实现方式。
不同count的用法对比:
CREATE TABLE `t` (
`id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
`city` VARCHAR (16) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR (16) NOT NULL,
`age` INT (11) NOT NULL,
`addr` VARCHAR (128) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `city` (`city`)
) ENGINE = INNODB;
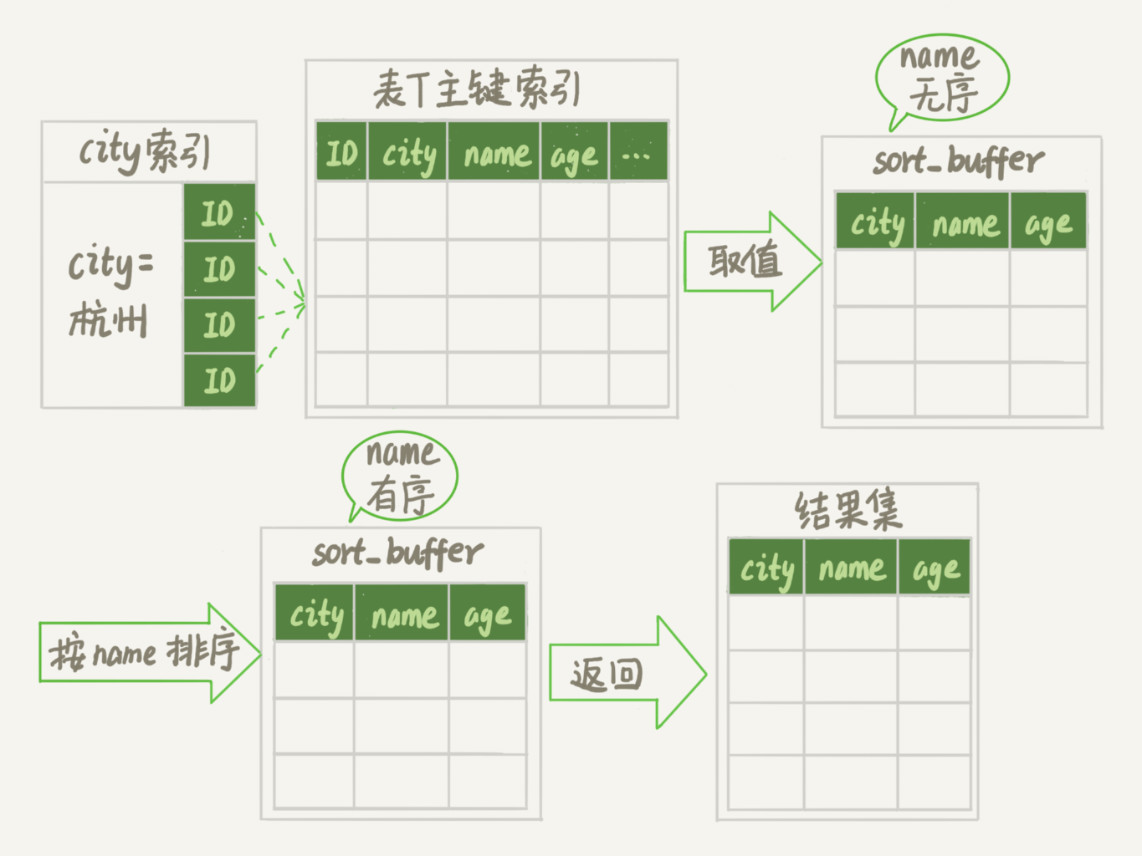
select city,name,age from t where city=‘杭州‘ order by name limit 1000;
-- MySQL中用于控制排序行数据长度的一个参数,如果单行的长度超过这个值,改用rowid排序
SET max_length_for_sort_data = 16;
| 全字段排序 | rowid 排序 |
|---|---|
 |
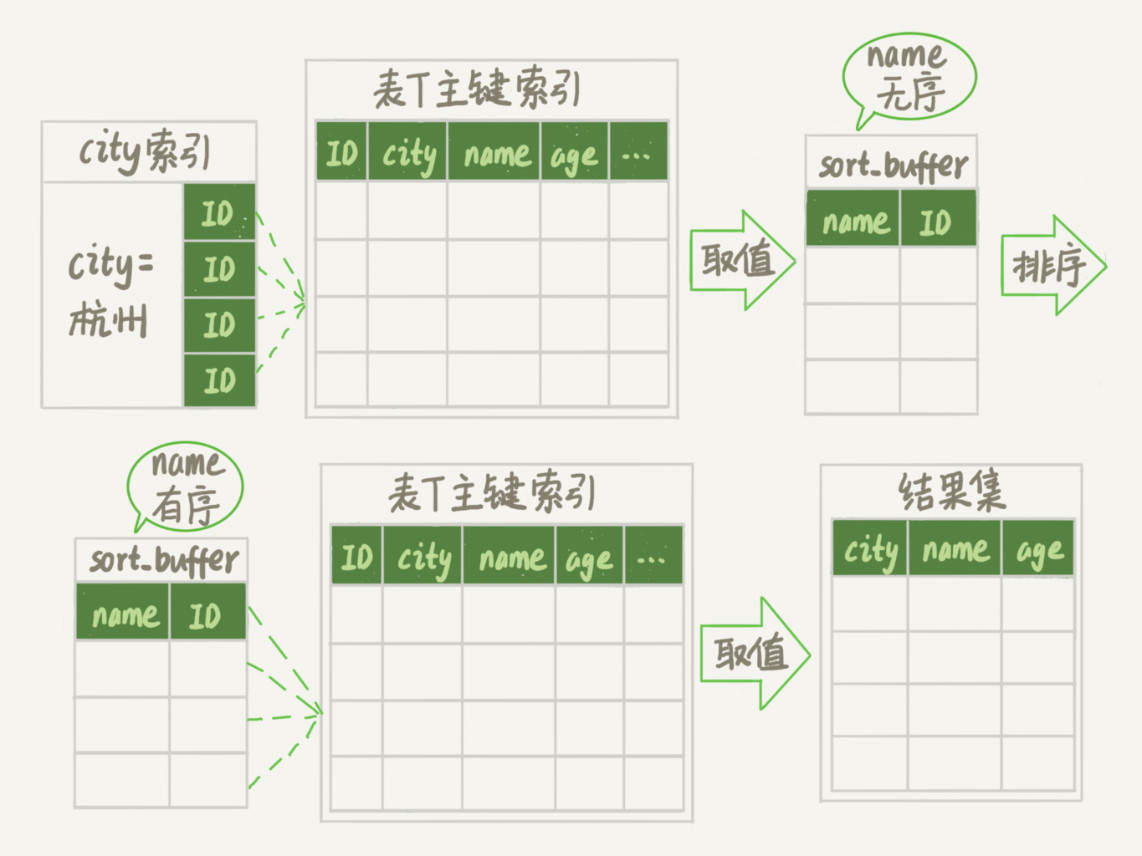 |
max_length_for_sort_data让优化器选择rowid排序算法,默认16,当要查询的单条数据全文本长度大于16采用rowid排序优化方案:使数据本身有序
alter table t add index city_user(city, name);
-- 利用索引中相同city下name有序性
select city,name,age from t where city=‘杭州‘ order by name limit 1000;
-- 进一步优化,使用覆盖索引,减少回表
alter table t add index city_user_age(city, name, age);
-- city多值情况下,又该如何处理? sql拆分
select * from t where city in (‘杭州‘," 苏州 ") order by name limit 100;
CREATE TABLE t1 (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
a INT,
b INT,
INDEX (a)
);
select id%10 as m,count(*) as c from t2 group by m;
首先分析下group by语句的执行计划,如下:
-- 此处使用MySQL 8.0+,已取消group by隐式排序,否则Exta中还会多一个Using filesort
mysql> explain select id%10 as m,count(*) from t group by m;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | index | PRIMARY,a | a | 5 | NULL | 998529 | 100 | Using index; Using temporary |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+--------+----------+------------------------------+
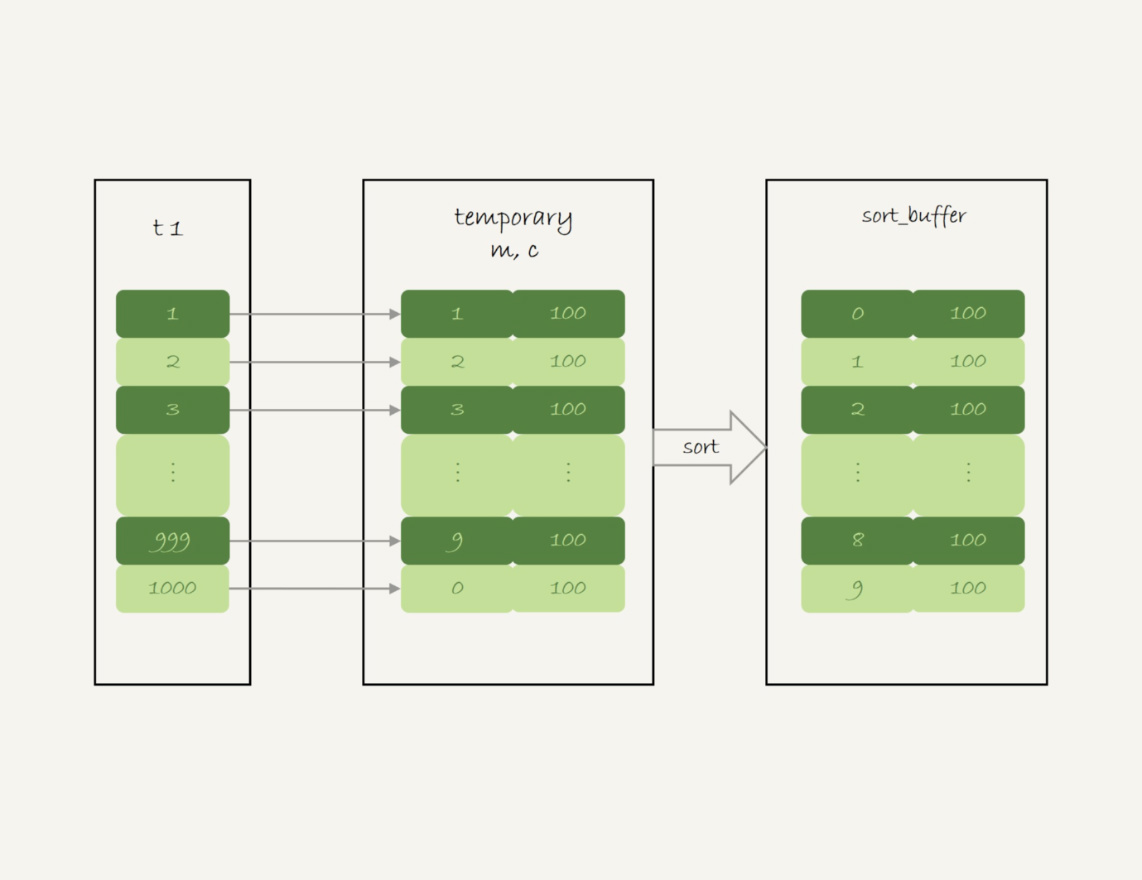
只用到了主键id字段,可以使用覆盖索引,因此选择了索引a,不用回表
获取主键id,id%10后放入临时表,如果存在,计数列加1
MySQL 8.0前group by支持隐式排序,无排序需求时,建议加上order by null
如何优化?
适合创建索引,直接加索引
-- 此处举例中分组字段是不存在,新增一个,并创建索引
-- 实际场景中可能会有已有分组字段,但未加索引,加上索引即可
mysql> alter table t1 add column z int generated always as(id % 100), add index(z);
-- 使用索引字段进行分组排序
mysql> explain select z as m,count(*) from t1 group by z ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | index | z | z | 5 | NULL | 1000 | 100 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
索引是有序的,顺序扫描,依次累加,统计完一个再统计下一个,不需要暂存中间结果,也不需要额外排序。如果需要倒序排列,Backward index scan,从后扫描索引即可
多个分组字段,建议使用联合索引
不适合创建索引,数据量不大,走内存临时表即可。如果数据量较大,使用SQL_BIG_RESULT告诉优化器,放弃内存临时表,直接磁盘临时表
mysql> explain select SQL_BIG_RESULT id%10 as m,count(*) from t1 group by m ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | index | PRIMARY,a,z | a | 5 | NULL | 1000 | 100 | Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-----+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
通过执行计划可以看出实际并未使用临时表,为什么呢?
因此,磁盘临时表是B+树存储,存储效率不高,从磁盘空间考虑,直接使用数组存储,流程如下:
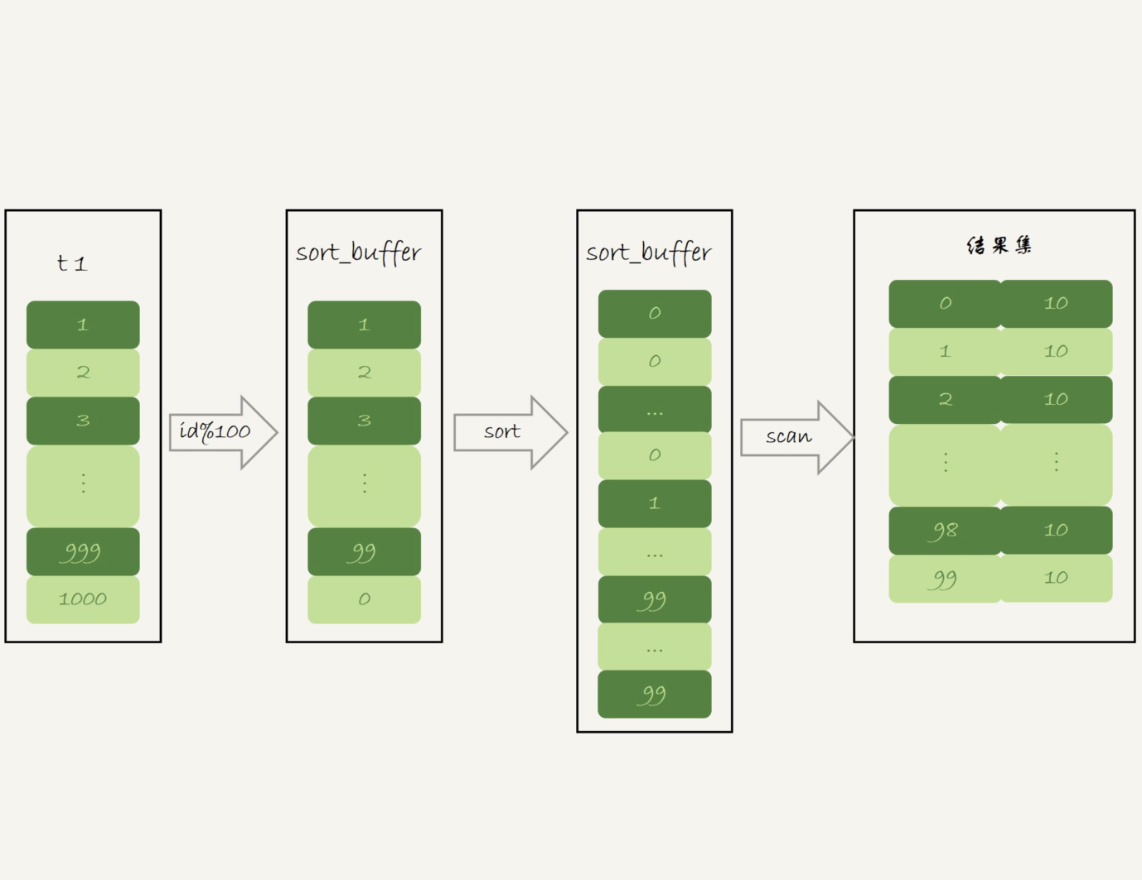
直接把分组值m放在sort_buffer中,空间不足使用磁盘临时文件辅助排序,这样就得到一个有序数组。在有序数组上计算相同值出现的次数就比较简单了,和在索引上统计计数一样,逐个累加计数即可。
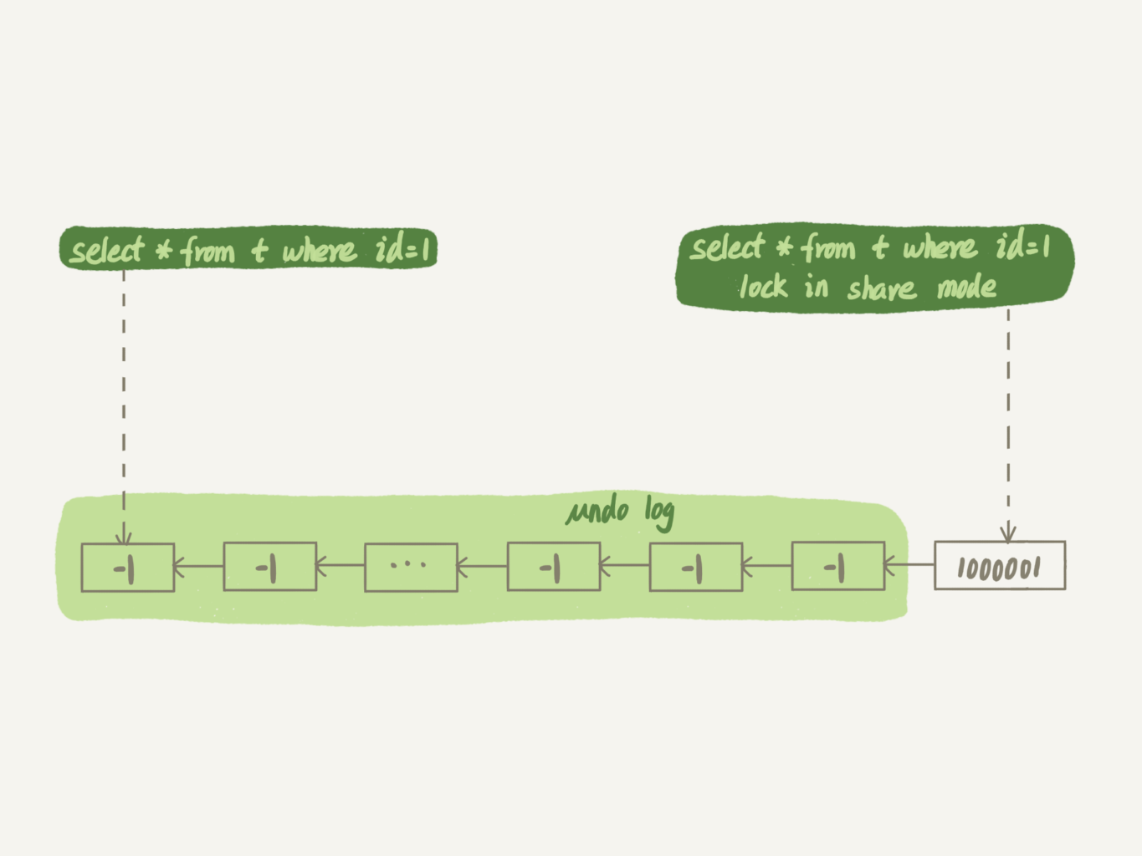
| session A | session B |
|---|---|
| start transaction with consistent snapshot; | |
| update t set c=c+1 where id=1;//执行100万次 | |
| select * from t where id=1; | |
| select * from t where id=1 lock in share mode; |
-- 创建表t
CREATE TABLE `t` (
`id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
`b` VARCHAR (10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `b` (`b`)
) ENGINE = INNODB;
-- 值超出字段长度,字符串截断后传递给执行引擎,可能匹配上大量数据,最终导致大量回表二次验证b=‘1234567890abcd‘
explain select * from t where b=‘1234567890abcd‘;
-- 类型隐式转换,扫描全部索引树
explain select * from t where b=1235
业务上有这样的需求,A、B 两个用户,如果互相关注,则成为好友。
-- 创建关注表
CREATE TABLE `like` (
`id` INT (11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
`liker_id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uk_user_id_liker_id` (`user_id`, `liker_id`)
) ENGINE = INNODB;
-- 创建好友表
CREATE TABLE `friend` (
`id` INT (11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`friend_1_id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
`friend_2_id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uk_friend` (
`friend_1_id`,
`friend_2_id`
)
) ENGINE = INNODB;
| session1(A关注B,A=1,B=2) | session2(B关注A,A=1,B=2) |
|---|---|
| begin; | |
| select * from user_like where user_id=2 and liker_id=1;(Empty set) | begin; |
| insert into user_like(user_id,liker_id) values(1,2); | |
| select * from user_like where user_id=1 and liker_id=2;(Empty set) | |
| insert into user_like(user_id,liker_id) values(2,1); | |
| commit; | |
| commit; |
A、B两个用户同时关注对方,即使session2中select先于session1中insert操作,session2也无法感知其未提交的数据。从而两个session执行完后建立了双向关注,但未建立好友关系。如何解决?
方案1:按照规则,使AB互关映射到同一条数据上,通过行锁冲突+on duplicate key实现好友关系的建立
-- 增加互关关系字段
ALTER TABLE `user_like`
ADD COLUMN `relation_ship` int NOT NULL AFTER `liker_id`;
-- 按照用户编号正序排列,不关A关注B,还是B关注A,都会命中同一条数据,用relation_ship标识两者之间的关系
-- A关注B,若A=1、B=2
insert into user_like(user_id,liker_id,relation_ship) values(1,2,1) on duplicate key update relation_ship = relation_ship|1;
-- A关注B,若A=2、B=1
insert into user_like(user_id,liker_id,relation_ship) values(1,2,2) on duplicate key update relation_ship = relation_ship|2;
-- 查询AB之前的关系
select relation_ship from user_like where user_id=1 and liker_id=2;
-- 以上两条insert执行后,上一步查询的relation_ship=1|2=3,可执行好友插入
insert ignore into user_friend(friend_1_id, friend_2_id) values(1,2);
(user_id=A and relation_ship<>2) or (liker_id=A and relation_ship=3)方案2:新的事务中或者异步调用好友关系建立服务
begin;
-- 验证双向关系是否存在,即存在两条数据
select couny(*) from user_like where user_id in (1,2) and liker_id in (1,2);
-- 双向关系存在,插入两条双向好友关系
insert ignore into user_friend (friend_1_id,friend_2_id) select
user_id,liker_id from user_like where user_id in (1,2) and liker_id in (1,2);
CREATE TABLE `t` (
`id` INT (11) NOT NULL,
`a` INT (11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE = INNODB;
insert into t values(1,2);
| session A | session B |
|---|---|
| begin; | |
| select * from t where id=1; | |
| update t set a=3 where id=1; | |
| update t set a=3 where id=1; | |
| select * from t where id=1; | |
| update t set a=4 where id=1; | |
| select * from t where id=1; |
session A中后两次select返回结果是什么?
有疑问的在于第二次,由于session B中已经把a修改为了3,session A中update是当前读,就看是否可以感知a已变更为3。MySQL 8.0.11中已感知不会执行修改操作,第二次读取的快照读还是(1,2)。有说法是update中当前读读取的只是where条件中的列,无法感知a是否变更,执行了修改操作,第二次读取结果为(1,3)
方案1:随机函数排序
-- 不建议采用:排序耗费资源
select * from t order by rand() limit n;
方案2:随机主键
-- 查询主键取值区间
select max(id),min(id) into @M,@N from t ;
-- 随机一个主键区间的值
set @X=floor((@M-@N+1)*rand() + @N);
-- 随机的主键值可能不存在,使用范围查找
select * from t where id >= @X limit 1;
缺点:
方案3:随机行数
-- 获取总行数
select count(*) into @C from t;
-- 设置随机显示数量
set @N = 1;
-- 计算起始行数
set @Y = floor(@C * rand())-@N+1;
-- 拼接sql
set @sql = concat("select * from t limit ", @Y, ",", @N);
-- 预处理语句
prepare stmt from @sql;
-- 执行语句
execute stmt;
-- prepare、execute、deallocate统称为prepare statement,称为预处理语句,deallocate用于释放资源
deallocate prepare stmt;
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`c` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
create table t2 like t1;
create table t3 like t2;
-- 初始化三张表的数据
insert into ...
-- 以下查询需要加哪些索引来优化?
SELECT
*
FROM
t1
JOIN t2 ON (t1.a = t2.a)
JOIN t3 ON (t2.b = t3.b)
WHERE
t1.c >= X
AND t2.c >= Y
AND t3.c >= Z;
索引原则,尽量使用BKA算法,小表作为驱动表,假设第一个驱动表为:
同时,还需要在第一个驱动表的字段 c 上创建索引
自增主键可能不连续,可能原因如下:
MySQL 5.1.22 版本开始引入的参数 innodb_autoinc_lock_mode(默认1,语句结束后释放自增锁),控制了自增值申请时的锁范围。
默认值是 1。
从并发性能的角度考虑,建议将其设置为 2,同时将 binlog_format 设置为 row
误删数据分类:
sql_safe_updates=on关闭批量修改或删除,增加SQL审计CREATE TABLE `t` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`c` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`d` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `c` (`c`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into t values(null, 1,1);
insert into t values(null, 2,2);
insert into t values(null, 3,3);
insert into t values(null, 4,4);
create table t2 like t
-- 语句1:不走索引,加锁范围:所有行锁和间隙锁
mysql> explain insert into t2(c,d) select c,d from t;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | INSERT | t3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 100 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
-- 语句2:强制走索引c,倒序取第一条,加锁范围:(3,4]、(4,supremum]
mysql> explain insert into t2(c,d) (select c+1, d from t force index(c) order by c desc limit 1);
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------+
| 1 | INSERT | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | index | NULL | c | 5 | NULL | 1 | 100 | Backward index scan |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------+
-- 语句3:从表t查询数据,再插入到自身,需要暂存中间数据,使用了临时表,在临时表上limit,
-- 加锁范围:所有行锁和间隙锁(8.0.11上和语句2一样,锁范围未发生变化)
mysql> explain insert into t(c,d) (select c+1, d from t force index(c) order by c desc limit 1);
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------+
| 1 | INSERT | t | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | index | NULL | c | 5 | NULL | 1 | 100 | Backward index scan; Using temporary |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------+
-- 假设语句3,先把数据放入临时表,再进行limit,会扫描所有行,如何优化?
create temporary table temp_t(c int,d int) engine=memory;
insert into temp_t (select c+1, d from t force index(c) order by c desc limit 1);
insert into t select * from temp_t;
drop table temp_t;
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/sheung/p/14628063.html