
1 # Poisson‘s equation之求解 - 有限差分法 2 3 import numpy 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 6 7 class PoissonEq(object): 8 9 def __init__(self, nx=150, ny=100, a=3, b=2): 10 self.__nx = nx # x轴子区间划分数 11 self.__ny = ny # y轴子区间划分数 12 self.__Lx = a # x轴椭圆半长 13 self.__Ly = b # y轴椭圆半长 14 self.__epsilon = 1 # 真空介电常数取值 15 16 assert a > b, "a must larger than b" 17 18 self.__hx = 2 * a / nx 19 self.__hy = 2 * b / ny 20 self.__ht = min([self.__hx, self.__hy]) ** 3 21 22 self.__X, self.__Y = self.__build_gridPoints() 23 self.__Ax, self.__Ay = self.__build_2ndOrdMat() 24 self.__V = self.__get_V() 25 26 self.__OuterLoc = self.__X ** 2 / a ** 2 + self.__Y ** 2 / b ** 2 >= 1 27 self.__InnerLoc = self.__X ** 2 / a ** 2 + self.__Y ** 2 / b ** 2 <= 1 28 self.__Angle = numpy.angle(self.__X + 1j * self.__Y) 29 30 31 def get_solu(self, maxIter=1000000, varepsilon=1.e-9): 32 ‘‘‘ 33 数值求解 34 maxIter: 最大迭代次数 35 varepsilon: 收敛判据 36 ‘‘‘ 37 U0 = self.__get_initial_U() 38 self.__fill_boundary_U(U0) 39 for i in range(maxIter): 40 t = i * self.__ht 41 Uk = self.__calc_Uk(t, U0) 42 43 # print(i, numpy.linalg.norm(Uk - U0, numpy.inf)) 44 if self.__isConverged(U0, Uk, varepsilon): 45 break 46 47 U0 = Uk 48 else: 49 raise Exception(">>> Not converged after {} iterations!<<<".format(maxIter)) 50 51 return numpy.ma.array(self.__X, mask=~self.__InnerLoc), numpy.ma.array(self.__Y, mask=~self.__InnerLoc), numpy.ma.array(Uk, mask=~self.__InnerLoc) 52 53 54 def get_Efield(self, U): 55 ‘‘‘ 56 获取电场 57 ‘‘‘ 58 Ey, Ex = numpy.gradient(U, self.__hy, self.__hx) 59 return numpy.linspace(-self.__Lx, self.__Lx, self.__nx + 1), numpy.linspace(-self.__Ly, self.__Ly, self.__ny + 1), -Ex, -Ey 60 61 62 def __isConverged(self, U0, Uk, varepsilon): 63 normVal = numpy.linalg.norm(Uk - U0, numpy.inf) 64 if normVal < varepsilon: 65 return True 66 return False 67 68 69 def __calc_Uk(self, t, U0): 70 K1 = self.__calc_F(U0) 71 Uk = U0 + K1 * self.__ht 72 self.__fill_boundary_U(Uk) 73 return Uk 74 75 76 def __calc_F(self, U): 77 term0 = numpy.matmul(U, self.__Ax) / self.__hx ** 2 78 term1 = numpy.matmul(self.__Ay, U) / self.__hy ** 2 79 term2 = self.__V / self.__epsilon 80 FVal = term0 + term1 + term2 81 return FVal 82 83 84 def __fill_boundary_U(self, U): 85 ‘‘‘ 86 填充边界条件 87 ‘‘‘ 88 U[self.__OuterLoc] = numpy.cos(self.__Angle[self.__OuterLoc]) 89 90 91 def __get_initial_U(self): 92 ‘‘‘ 93 获取初始条件 94 ‘‘‘ 95 U0 = numpy.zeros(self.__X.shape) 96 return U0 97 98 99 def __get_V(self): 100 ‘‘‘ 101 获取电荷密度 102 ‘‘‘ 103 c = numpy.math.sqrt(self.__Lx ** 2 - self.__Ly ** 2) 104 term0 = -100 * ((self.__X - c) ** 2 + self.__Y ** 2) 105 term1 = -100 * ((self.__X + c) ** 2 + self.__Y ** 2) 106 V = 100 * numpy.exp(term0) - 100 * numpy.exp(term1) 107 return V 108 109 110 def __build_2ndOrdMat(self): 111 ‘‘‘ 112 构造2阶微分算子的矩阵形式 113 ‘‘‘ 114 Ax = self.__build_AMat(self.__nx + 1) 115 Ay = self.__build_AMat(self.__ny + 1) 116 return Ax, Ay 117 118 119 def __build_AMat(self, n): 120 term0 = numpy.identity(n) * -2 121 term1 = numpy.eye(n, n, 1) 122 term2 = numpy.eye(n, n, -1) 123 AMat = term0 + term1 + term2 124 return AMat 125 126 127 def __build_gridPoints(self): 128 ‘‘‘ 129 构造网格节点 130 ‘‘‘ 131 X = numpy.linspace(-self.__Lx, self.__Lx, self.__nx + 1) 132 Y = numpy.linspace(-self.__Ly, self.__Ly, self.__ny + 1) 133 X, Y = numpy.meshgrid(X, Y) 134 return X, Y 135 136 137 class PoissonPlot(object): 138 139 @staticmethod 140 def plot_fig(poiObj): 141 maxIter = 1000000 142 varepsilon = 1.e-9 143 144 X, Y, U = poiObj.get_solu(maxIter, varepsilon) 145 X1, Y1, Ex, Ey = poiObj.get_Efield(U) 146 147 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4)) 148 ax1 = plt.subplot() 149 150 cs1 = ax1.contour(X, Y, U, levels=50, cmap="jet") 151 ax1.streamplot(X1, Y1, Ex, Ey, density=1, linewidth=1, color="black") 152 fig.colorbar(cs1) 153 fig.tight_layout() 154 fig.savefig("plot_fig.png", dpi=100) 155 156 157 if __name__ == "__main__": 158 nx = 150 159 ny = 100 160 a = 1.5 161 b = 1 162 poiObj = PoissonEq(nx, ny, a, b) 163 164 PoissonPlot.plot_fig(poiObj)
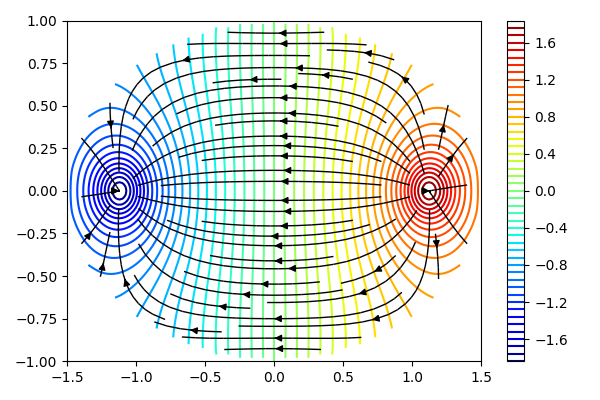 注意, 图中等高线代表等势线, 流线代表电场走向.
注意, 图中等高线代表等势线, 流线代表电场走向.2D Poisson's Equation - Finite Difference
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xxhbdk/p/14534909.html