
实际代码
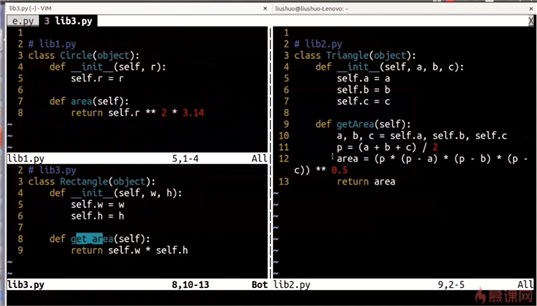
# lib1.py
class Circle(object):
def __init__(self, r):
self.r = r
def area(self):
return self.r **2* 3.14
#lib2.py
class Triangle(object):
def __init__(self, a,b,c):
self.a = a
self.b = b
self.c = c
def getArea(self):
a,b,c = self.a, self.b, self.c
p = (a+b+c)/2
area = (p * (p-a)* (p - b)* (p-c))** 0.5
return area
#lib3.py
class Rectangle(object):
def __init__ (self,w,h):
self.w = w
self.h = h
def get_area(self):
return self.w * self.h
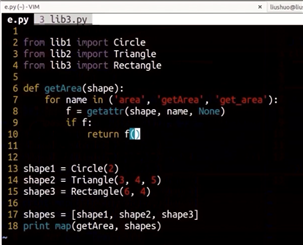
# from lib1 import circle
# from lib2 import Triangle
# from lib3 import Rectangle
def getArea(shape):
for name in( ‘area‘, ‘getArea‘, ‘get_area‘ ):
f = getattr(shape,name,None)
if f:
return f()
# continue
shape1 = Circle(2)
shape2 = Triangle(3,4,5)
shape3 = Rectangle(6,4)
shapes = [shape1, shape2, shape3]
print(list(map(getArea, shapes)))
# for i in shapes:
# print(getArea(i))
输出:[12.56, 6.0, 24]
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/heris/p/11665984.html