总线-设备-驱动 又称为 设备驱动模型。
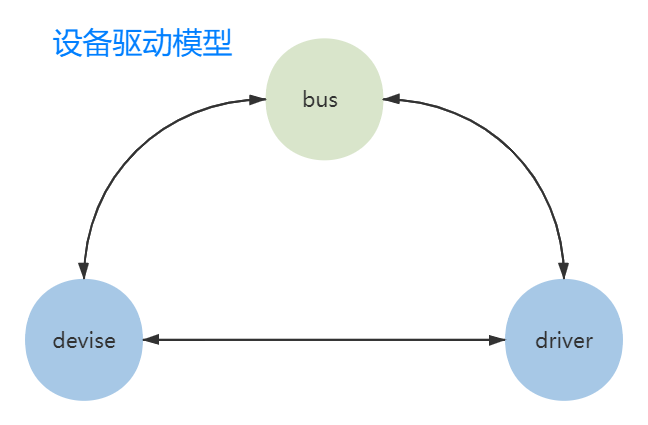
总线(bus):负责管理挂载对应总线的设备以及驱动;
设备(device):挂载在某个总线的物理设备;
驱动(driver):与特定设备相关的软件,负责初始化该设备以及提供一些操作该设备的操作方式;
类(class):对于具有相同功能的设备,归结到一种类别,进行分类管理;
以下只说 总线-设备-驱动 模式下的操作
总线:
总线:
总线驱动:
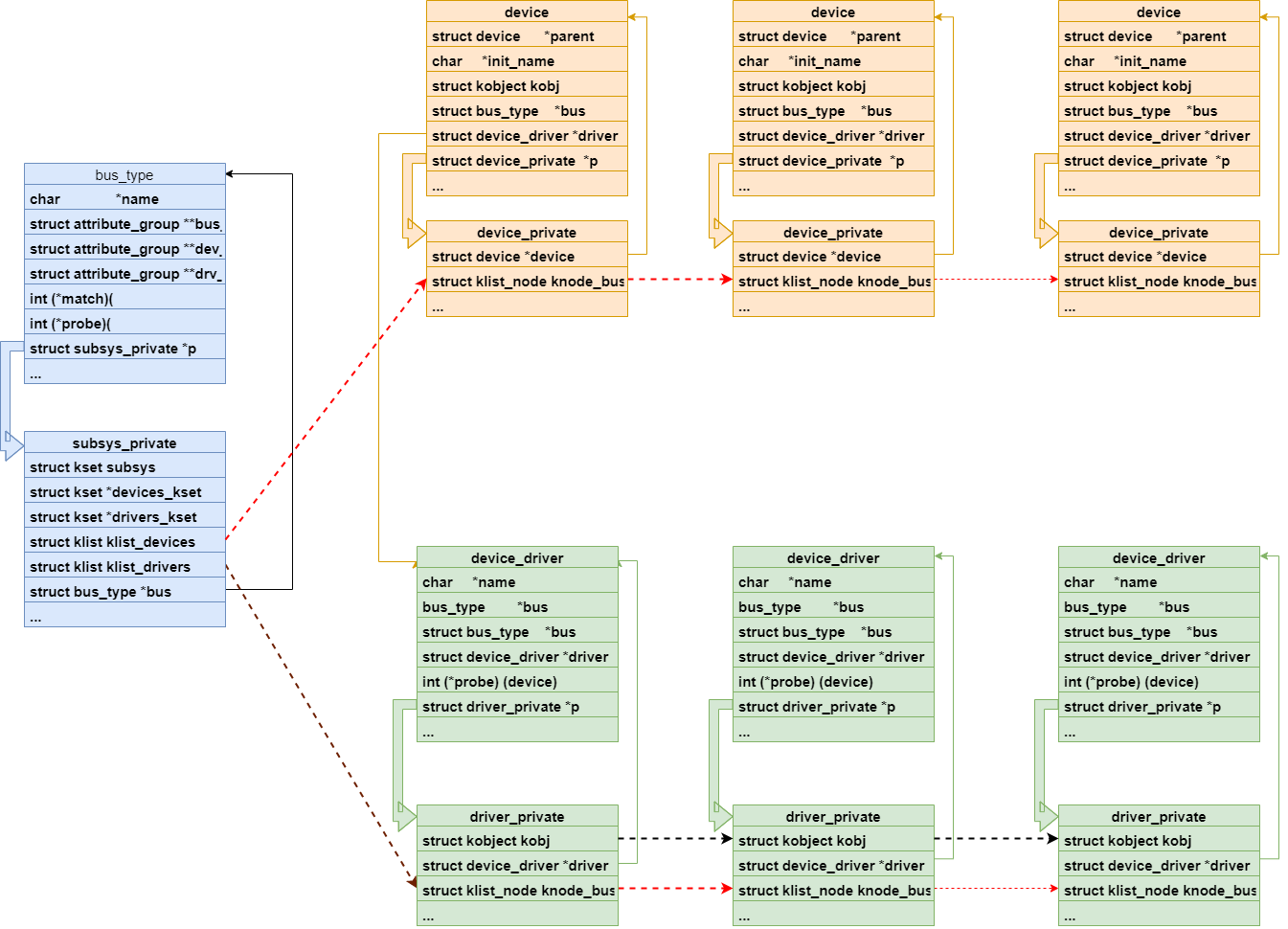
总线结构体:
struct bus_type {
const char *name;
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct subsys_private *p;
};
在实际的驱动开发中,Linux 已经为我们编写好了大部分的总线驱动。
但是内核也提供了注册总线的 API。
bus_register():
int bus_register(struct bus_type *bus);。
bus_unregister():
int bus_unregister(struct bus_type *bus);。
当我们成功注册总线时,会在 /sys/bus/ 目录下创建一个新目录,目录名为我们新注册的总线名。
在 /sys/devices 目录记录了系统中所有的设备。
/sys 下的所有设备文件和 /sys/dev 下的所有设备节点都是链接文件,实际上都指向了对应的设备文件。
device 结构体:
struct device
{
const char *init_name;
struct device *parent;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct device_driver *driver;
void *platform_data;
void *driver_data;
struct device_node *of_node;
dev_t devt;
struct class *class;
void (*release)(struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */
struct device_private *p;
};
在前面的字符设备驱动编写中,我们使用到了 device_create() 函数和 device_destroy() 函数来创建和删除设备。
现在介绍向总线注册和注销设备。
向总线注册设备:
int device_register(struct device *dev);。
向总线注销设备:
int device_unregister(struct device *dev);。
driver 结构体:
struct device_driver
{
const char *name;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
struct driver_private *p;
};
向总线注册驱动:
int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv);。
向总线注销驱动:
int driver_unregister(struct device_driver *drv);。
数据结构该系统:
注册流程图:
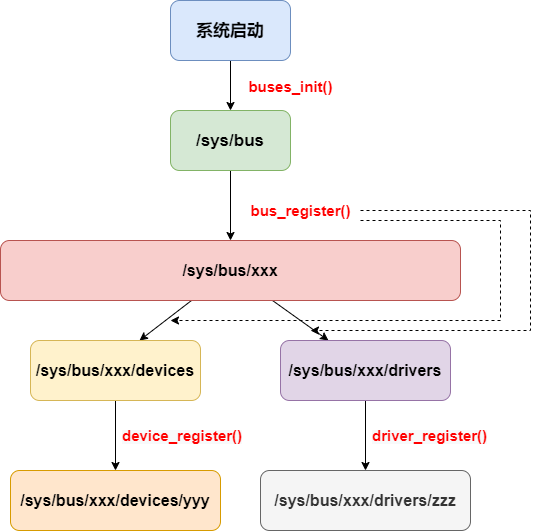
系统启动之后会调用buses_init函数创建/sys/bus文件目录,这部分系统在开机时已经帮我们准备好了, 接下去就是通过总线注册函数bus_register进行总线注册,注册完总线后在总线的目录下生成devices文件夹和drivers文件夹, 最后分别通过device_register以及driver_register函数注册相对应的设备和驱动。
attribute 结构体:
struct attribute {
const char *name;
umode_t mode;
};
bus_type、device、device_driver 结构体中都包含了一种数据类型 struct attribute_group,它是多个 attribute 文件的集合, 利用它进行初始化,可以避免一个个注册 attribute。
struct attribute_group 结构体:
struct attribute_group
{
const char *name;
umode_t (*is_visible)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *, int);
struct attribute **attrs;
struct bin_attribute **bin_attrs;
};
Linux 提供注册和注销设备属性文件的 API。我们可以通过这些 API 直接在用户层进行查询和修改。
struct device_attribute 结构体:
struct device_attribute
{
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count);
};
#define DEVICE_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
extern int device_create_file(struct device *device, const struct device_attribute *entry);
extern void device_remove_file(struct device *dev, const struct device_attribute *attr);
Linux 提供注册和注销驱动属性文件的 API。我们可以通过这些 API 直接在用户层进行查询和修改。
struct driver_attribute 结构体:
struct driver_attribute
{
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct device_driver *driver, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct device_driver *driver, const char *buf, size_t count);};
#define DRIVER_ATTR_RW(_name) struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RW(_name)
#define DRIVER_ATTR_RO(_name) struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RO(_name)
#define DRIVER_ATTR_WO(_name) struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR_WO(_name)
extern int __must_check driver_create_file(struct device_driver *driver, const struct driver_attribute *attr);
extern void driver_remove_file(struct device_driver *driver, const struct driver_attribute *attr);
struct bus_attribute 结构体:
struct bus_attribute
{
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct bus_type *bus, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct bus_type *bus, const char *buf, size_t count);
};
#define BUS_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) struct bus_attribute bus_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
extern int __must_check bus_create_file(struct bus_type *, struct bus_attribute *);
extern void bus_remove_file(struct bus_type *, struct bus_attribute *);
下章笔记就是记录平台设备。本次匹配规则就参考 平台设备驱动 源码。
最先比较 platform_device.driver_override 和 platform_driver.driver.name。
可以设置 platform_device 的 driver_override,强制选择某个 platform_driver。
其次比较 platform_device.name 和 platform_driver.id_table[i].name。
platform_driver.id_table 是 platform_device_id 指针,表示该 drv 支持若干个 device,它里面列出了各个 device 的 {.name, .driver_data},其中的 name 表示该 drv 支持的设备的名字,driver_data是些提供给该 device 的私有数据。
最后比较 platform_device.name 和 platform_driver.driver.name。
由于 platform_driver.id_table 可能为空,所以,接下来就可以使用 platform_driver.driver.name 来匹配。
platform_device_register
platform_device_add
device_add
bus_add_device // 放入链表
bus_probe_device // probe 枚举设备,即找到匹配的(dev, drv)
device_initial_probe
__device_attach
bus_for_each_drv(...,__device_attach_driver,...)
__device_attach_driver
driver_match_device(drv, dev) // 是否匹配
driver_probe_device // 调用 drv 的 probe
platform_driver_register
__platform_driver_register
driver_register
bus_add_driver // 放入链表
driver_attach(drv)
bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
__driver_attach
driver_match_device(drv, dev) // 是否匹配
driver_probe_device // 调用 drv 的 probe
总线、设备、驱动都基于驱动模型上实现,方便插入。
模块三步骤:
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/lizhuming/p/14596239.html