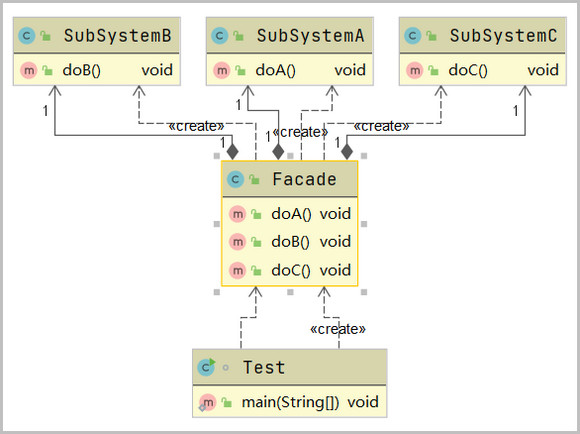
1、门面模式(Facade Pattern)又叫外观模式,提供了一个统一的接口,用来访问一群子系统中的接口。
2、特征,定义了一个高层接口,让子系统更容易使用。
3、属于《结构性模式》。
使用场景
1、子系统越来越复杂,增加门面模式提供简单接口。
2、构建多层系统结构,利用门面对象作为每层的入口,简化层间调用。
// 外观角色 Facade
public class Facade {
private SubSystemA a = new SubSystemA();
private SubSystemB b = new SubSystemB();
private SubSystemC c = new SubSystemC();
// 对外接口
public void doA() {
this.a.doA();
}
// 对外接口
public void doB() {
this.b.doB();
}
// 对外接口
public void doC() {
this.c.doC();
}
}
// 子系统
public class SubSystemA {
public void doA() {
System.out.println("doing A stuff");
}
}
// 子系统
public class SubSystemB {
public void doB() {
System.out.println("doing B stuff");
}
}
// 子系统
public class SubSystemC {
public void doC() {
System.out.println("doing C stuff");
}
}
// 客户
public static void main(String[] args) {
Facade facade = new Facade();
facade.doA();
facade.doB();
facade.doC();
}
商城积分兑换商品
//支付服务
public class PaymentService {
public boolean pay(GiftInfo giftInfo){
System.out.println("扣减" + giftInfo.getName() + " 积分成功");
return true;
}
}
//校验服务
public class QualifyService {
public boolean isAvailable(GiftInfo giftInfo){
System.out.println("校验" +giftInfo.getName() + "积分通过,库存通过。");
return true;
}
}
//物流服务
public class ShippingService {
public String delivery(GiftInfo giftInfo){
System.out.println(giftInfo.getName() + "进入物流系统");
String shippingNo = "666";
return shippingNo;
}
}
//商品
public class GiftInfo {
private String name;
public GiftInfo(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
QualifyService qualifyService = new QualifyService();
PaymentService paymentService = new PaymentService();
ShippingService shippingService = new ShippingService();
GiftInfo giftInfo = new GiftInfo("《Spring 5核心原理》");
if(qualifyService.isAvailable(giftInfo)){
if(paymentService.pay(giftInfo)){
String shippingNo = shippingService.delivery(giftInfo);
System.out.println("物流系统下单成功,物流单号是:" + shippingNo);
}
}
}
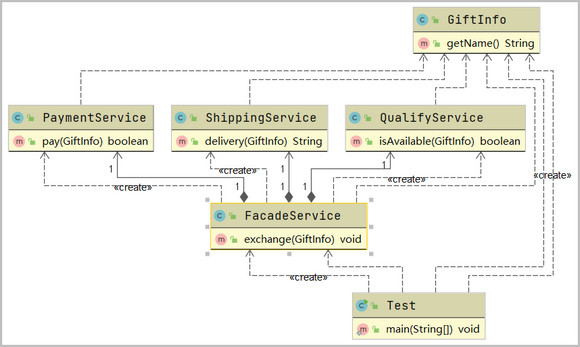
门面模式改进
//门面服务(调用支付,校验,物流等多个服务)
public class FacadeService {
private QualifyService qualifyService = new QualifyService();
private PaymentService paymentService = new PaymentService();
private ShippingService shippingService = new ShippingService();
public void exchange(GiftInfo giftInfo){
if(qualifyService.isAvailable(giftInfo)){
if(paymentService.pay(giftInfo)){
String shippingNo = shippingService.delivery(giftInfo);
System.out.println("物流系统下单成功,物流单号是:" + shippingNo);
}
}
}
}
//再次测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
FacadeService facadeService = new FacadeService();
GiftInfo giftInfo = new GiftInfo("《Spring 5核心原理》");
facadeService.exchange(giftInfo);
}
1、实际上,工作中一直都在用门面模式,例如常用的 Controller,逻辑代码 [ DistributedService ] 等....
2、各种 Utils 工具包 都是门面模式。
1、Spring JDBC 模块下的 JdbcUtils 类,封装了 JDBC 的相关操作。
2、Mybatis 中 Configuration 类中有很多 new 开头的方法
3、在 Tomcat 中也有体现,例如 RequestFacade 类
1)门面模式与代理模式
1、门面模式就是一种代理模式,只不过它是特殊的静态代理模式。
2、门面模式 重点在于封装
3、静态代理 重点在于增强
4、不做增强的静态代理就是门面模式
2)门面模式与委派模式
1、委派模式也是一种静态代理模式
2、门面模式与代理模式都属于《结构型模式》
3、委派模式属于《行为型模式》,并且不属于《 GOF 23 》
3)门面模式与单例模式
1、门面模式一般都做成单例,例如各种 Utils 工具包
2、门面模式也是一种组合模式
1)优点
1、简单调用过程,无需深入了解子系统,以防给子系统带来风险
2、减少系统依赖,松散耦合
3、更好的划分访问层次,提高了安全性
4、遵循迪米特法则,即最少知道原则
2)缺点
1、当增加子系统和扩展子系统行为时,可能容易带来未知风险
2、不符合开闭原则
3、某些情况下可能违背单一职责原则 [ 整合的内容过多 ]
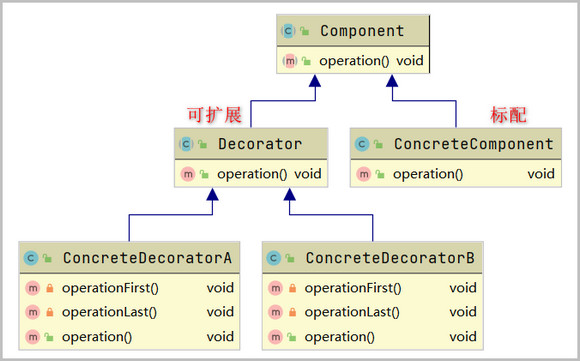
1、装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)也叫包装模式(Wrapper Pattern),是指在不改变原有对象的基础之上,将功能附加到对象上,提供了比继承更有弹性的替代方案(扩展原有对象的功能)
2、属于《结构型模式》
使用场景
1、用于扩展一个类的功能或给一个类添加附加职责
2、动态的给一个对象添加功能,这些功能可以再动态的撤销
//抽象功能
public abstract class Component {
public abstract void operation();
}
//标配
public class ConcreteComponent extends Component {
public void operation() {
System.out.println("处理业务逻辑");
}
}
//装饰器扩展入口
public abstract class Decorator extends Component {
// 持有组件对象
protected Component component;
/**
* 构造方法,传入组件对象
* @param component 组件对象
*/
public Decorator(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
public void operation() {
//转发请求给组件对象,可以在转发前后执行一些附加动作
component.operation();
}
}
//扩展A
public class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator {
public ConcreteDecoratorA(Component component) {
super(component);
}
private void operationFirst(){ } //在调用父类的operation方法之前需要执行的操作
private void operationLast(){ } //在调用父类的operation方法之后需要执行的操作
public void operation() {
//调用父类的方法,可以在调用前后执行一些附加动作
operationFirst(); //添加的功能
super.operation(); //这里可以选择性的调用父类的方法,如果不调用则相当于完全改写了方法,实现了新的功能
operationLast(); //添加的功能
}
}
//扩展B
public class ConcreteDecoratorB extends Decorator {
public ConcreteDecoratorB(Component component) {
super(component);
}
private void operationFirst(){ } //在调用父类的operation方法之前需要执行的操作
private void operationLast(){ } //在调用父类的operation方法之后需要执行的操作
public void operation() {
//调用父类的方法,可以在调用前后执行一些附加动作
operationFirst(); //添加的功能
super.operation(); //这里可以选择性的调用父类的方法,如果不调用则相当于完全改写了方法,实现了新的功能
operationLast(); //添加的功能
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args){
Component c1 = new ConcreteComponent (); //首先创建需要被装饰的原始对象(即要被装饰的对象)
Decorator decoratorA = new ConcreteDecoratorA(c1); //给对象透明的增加功能A并调用
decoratorA .operation();
Decorator decoratorB = new ConcreteDecoratorB(c1); //给对象透明的增加功能B并调用
decoratorB .operation();
Decorator decoratorBandA = new ConcreteDecoratorB(decoratorA);//装饰器也可以装饰具体的装饰对象,此时相当于给对象在增加A的功能基础上在添加功能B
decoratorBandA.operation();
}
摊煎饼,加鸡蛋?加肠?各加多少个?
//煎饼
public class Battercake {
protected String getMsg(){ return "煎饼";}
public int getPrice(){ return 5;}
}
//加鸡蛋
public class BattercakeWithEgg extends Battercake {
protected String getMsg(){ return super.getMsg() + "+1个鸡蛋";}
public int getPrice(){ return super.getPrice() + 1;}
}
//加鸡蛋加香肠
public class BattercakeWithEggAndSauage extends BattercakeWithEgg {
protected String getMsg(){ return super.getMsg() + "+1根香肠";}
public int getPrice(){ return super.getPrice() + 2;}
}
//....加俩鸡蛋或加俩香肠,继承无法有效的实现每种情况
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Battercake battercake = new Battercake();
System.out.println(battercake.getMsg() + ",总价:" + battercake.getPrice());
BattercakeWithEgg battercakeWithEgg = new BattercakeWithEgg();
System.out.println(battercakeWithEgg.getMsg() + ",总价:" + battercakeWithEgg.getPrice());
BattercakeWithEggAndSauage battercakeWithEggAndSauage = new BattercakeWithEggAndSauage();
System.out.println(battercakeWithEggAndSauage.getMsg() + ",总价:" + battercakeWithEggAndSauage.getPrice());
}
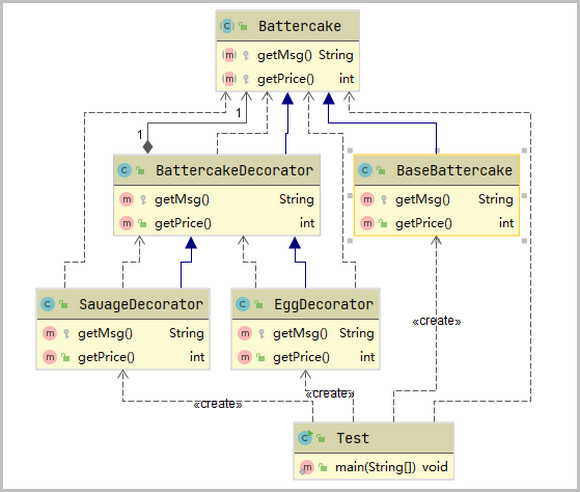
装饰器改进方案
//煎饼抽象功能
public abstract class Battercake {
protected abstract String getMsg();
protected abstract int getPrice();
}
//标配,什么都不加
public class BaseBattercake extends Battercake{
protected String getMsg(){ return "煎饼";}
public int getPrice(){ return 5;}
}
//装饰器功能入口
public class BattercakeDecorator extends Battercake{
private Battercake battercake;
public BattercakeDecorator(Battercake battercake) {
this.battercake = battercake;
}
protected String getMsg(){ return this.battercake.getMsg();}
public int getPrice(){ return this.battercake.getPrice();}
}
//扩展功能,加1个鸡蛋
public class EggDecorator extends BattercakeDecorator{
public EggDecorator(Battercake battercake) {
super(battercake);
}
protected String getMsg(){ return super.getMsg() + "1个鸡蛋";}
public int getPrice(){ return super.getPrice() + 1;}
}
//扩展功能,加一根香肠
public class SauageDecorator extends BattercakeDecorator{
public SauageDecorator(Battercake battercake) {
super(battercake);
}
protected String getMsg(){ return super.getMsg() + "1根香肠";}
public int getPrice(){ return super.getPrice() + 2;}
}
//调用测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Battercake battercake;
battercake = new BaseBattercake();
battercake = new EggDecorator(battercake);
battercake = new SauageDecorator(battercake);
battercake = new EggDecorator(battercake);
//加了两个鸡蛋一根香肠
System.out.println(battercake.getMsg() + ",总价" + battercake.getPrice());
}
1、在 JDK 中体现最明显的类就是 IO 相关的类
2、在 Spring 中的 TransactionAwareCacheDecorator 类,这个类主要处理缓存
3、Mybatis 中的一段处理缓存的设计 org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache.decorators 包下的类
1)装饰器模式与代理模式
1、装饰器模式就是一种特殊的代理模式
2、装饰器模式强调自身的功能扩展,透明的扩展 [用户自己说了算],可动态定制的扩展
3、代理模式强调代理过程的控制
1)优点
1、装饰器是继承的有力补充,比继承灵活,不改变原有对象的情况下动态的给一个对象扩展功能,即插即用
2、通过使用不同装饰类以及这些装饰类的排列组合,可实现不同效果
3、装饰器完全遵守开闭原则
2)缺点
1、会出现更多的代码,更多的类,增加程序复杂性
2、动态装饰时,多层装饰时会更复杂
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/JustDoIt-1221/p/14596236.html