进程是资源(CPU、内存等)分配的基本单位,它是程序执行时的一个实例。程序运行时系统就会创建一个进程,并为它分配资源,然后把该进程放入进程就绪队列,进程调度器选中它的时候就会为它分配CPU时间,程序开始真正运行。
线程是一条执行路径,是程序执行时的最小单位,它是进程的一个执行流,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,一个进程可以由很多个线程组成,线程间共享进程的所有资源,每个线程有自己的堆栈和局部变量。线程由CPU独立调度执行,在多CPU环境下就允许多个线程同时运行。同样多线程也可以实现并发操作,每个请求分配一个线程来处理。
并行:指在同一时刻,有多条指令在多个处理器上同时执行。
并发:指在同一时刻只能有一条指令执行,但多个进程指令被快速的轮换执行,使得在宏观上具有多个进程同时执行的效果,但在微观上并不是同时执行的,只是把时间分成若干段,使多个进程快速交替的执行。
并行在多处理器系统中存在,而并发可以在单处理器和多处理器系统中都存在;并行要求程序能够同时执行多个操作,而并发只是要求程序假装同时执行多个操作(每个小时间片执行一个操作,多个操作快速切换执行)
/**
* 实现runnable接口创建线程
*/
public class CreateThread implements Runnable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new CreateThread(), "thread-1");
thread.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("用Runnable方式创建线程");
}
}
/**
* 继承Thread类实现多线程
*/
public class CreateThread2 extends Thread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateThread2 createThread2 = new CreateThread2();
createThread2.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("继承Thread创建线程");
}
}
方法一:最终调用target.run方法
Thread类中run方法如下
private Runnable target;
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
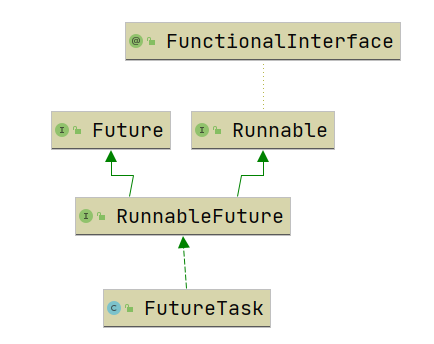
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
如果同时使用两种方法创建多线程,会发生什么?
/**
* 同时使用两种方法创建多线程
* 输出结果:Thread Thread中的run方法会覆盖target中的run方法
*/
public class CreateThread3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Runnable");
}
}){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread");
}
}.start();
}
}
问:创建线程的方法
通常我们分为两类,Oracle官方文档也是如此描述
准确的说,创建线程只有一种方式,那就是构造Thread类,而实现线程的执行单元有两种方式
典型错误观点
/**
* 使用线程池创建线程
*/
public class ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executorService.submit(new Task(){});
}
}
}
class Task implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
/**
* 使用定时器创建线程
*/
public class TimmerTask {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}, 1000, 1000);
}
}
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread");
}
}.start();
new Thread(()-> System.out.println("lambda表达式")).start();
重复调用start方法,抛出异常的原因:会进行线程状态检查判断是否为0,JAVA线程状态初始的时候是0表示还没有启动,则调用start0方法
正确的停止线程的方法,应该是使用interrupt来通知,而不是强制停止线程,而线程是否中断取决于线程本身。
/**
* 目的: 普通线程下停止线程
* 功能: 10000倍数的值
*/
public class StopThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 0;
//Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted判断当前线程是否被中断,如果中断返回true,没有中断返回false
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() && num <= Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2){
if(num % 10000 == 0){
System.out.println(num + "是10000的倍数");
}
num++;
}
System.out.println("任务运行结束");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new StopThread());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
//通知线程进行中断将线程的状态修改为true
thread.interrupt();
}
}
/**
* 目的: 带有阻塞的终端线程写法,当线程被中断的时候会抛出java.lang.InterruptedException: sleep interrupted的异常,因此这里就不必提添加判读是否被中断的方法!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()
*/
public class StopThread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 0;
try {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() && num <= 300){
if(num % 100 == 0){
System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数");
}
num++;
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new StopThread2());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
//通知线程
thread.interrupt();
}
}
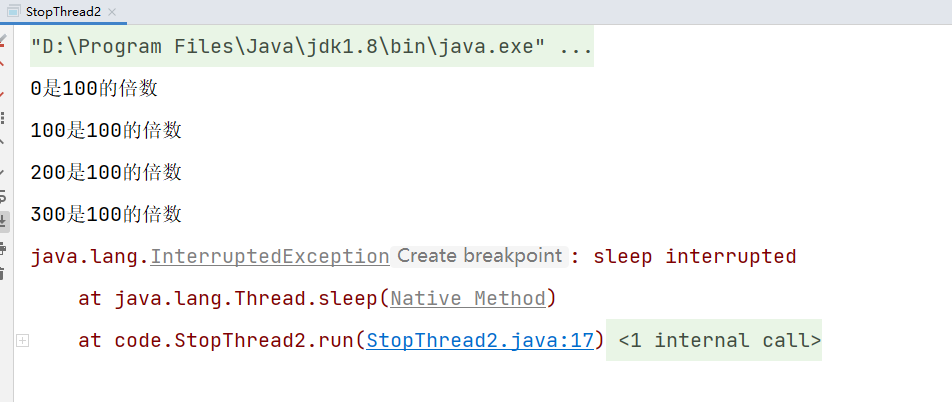
/**
* 目的: 在遍历中存在带有阻塞的中断线程写法
* sleep和wait等方法不需要每次迭代都检查是否已中断
*/
public class StopThread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 0;
try {
while (num <= 10000){
if(num % 100 == 0){
System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数");
}
num++;
Thread.sleep(10);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new StopThread2());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
//通知线程
thread.interrupt();
}
}
用stop来停止线程,会导致线程运行一半突然停止,没办法完成一个基本单位的操作,会造成脏数据/**
* 描述:领枪的时候突然叫上一个连队(一个基本单位)去前线战斗(对应stop方法,突然把线程中断)会导致这一基本单位没有全部领取到枪就去前线了。
*/
public class StopThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//模拟指挥军队:一共有5个连队,每个连队10人,以连队为单位,发放武器弹药,叫到号的士兵前去领取
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("连队" + i + "开始领取武器");
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(j);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("连队"+i+"已经领取完毕");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new StopThread());
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
thread.stop();
}
}
/**
* 陷入阻塞时,volatile是无法停止线程的
* 此例中,生产者的生产速度很快,消费者消费速度慢,所以阻塞队列满了以后,生产者会阻塞,等待消费者进一步消费
*/
public class WrongWayVolatileCantStop {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue storage = new ArrayBlockingQueue(10);
Producer producer = new Producer(storage);
Thread producerThread = new Thread(producer);
producerThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(storage);
while (consumer.needMoreNums()) {
System.out.println(consumer.storage.take()+"被消费了");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
System.out.println("消费者不需要更多数据了。");
//一旦消费不需要更多数据了,我们应该让生产者也停下来,但是实际情况
producer.canceled=true;
System.out.println(producer.canceled);
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable {
public volatile boolean canceled = false;
BlockingQueue storage;
public Producer(BlockingQueue storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 0;
try {
while (num <= 100000 && !canceled) {
if (num % 100 == 0) {
storage.put(num);
System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数,被放到仓库中了。");
}
num++;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("生产者结束运行");
}
}
}
class Consumer {
BlockingQueue storage;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
public boolean needMoreNums() {
if (Math.random() > 0.95) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
sleep函数在while内,并且在while内try/catch来捕获异常会发生的问题:
sleep函数中,当它一旦响应中断会把线程内interrupt标记位清除,因此线程中断失效了。
/**
* 描述: 如果while里面放try/catch,会导致中断失效
*/
public class CantInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = () -> {
int num = 0;
while (num <= 10000 && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
if (num % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数");
}
num++;
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
解决上述问题的方法:
public class RightWayStopThreadInProd implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("go");
try {
throwInMethod();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
//保存日志、停止程序
System.out.println("保存日志");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void throwInMethod() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new RightWayStopThreadInProd());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
public class RightWayStopThreadInProd2 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("Interrupted,程序运行结束");
break;
}
reInterrupt();
}
}
private void reInterrupt() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//在异常处理中将线程中断,从而将线程中断的结果标为true
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new RightWayStopThreadInProd2());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
响应中断的列表方法:
static boolean interrupted方法会清除当前线程的中断状态,它中断的目标是执行它的线程boolean isInterrupted不会清除当前线程的中断状态Thread.interrupted的目标对象不管是什么,都会返回当前主线程的中断状态public class RightWayInterrupted {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread threadOne = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (; ; ) {
}
}
});
// 启动线程
threadOne.start();
//设置中断标志
threadOne.interrupt();
//获取中断标志
System.out.println("isInterrupted: " + threadOne.isInterrupted());
//获取中断标志并重置
System.out.println("isInterrupted: " + threadOne.interrupted());
//获取中断标志并重直
System.out.println("isInterrupted: " + Thread.interrupted());
//获取中断标志
System.out.println("isInterrupted: " + threadOne.isInterrupted());
threadOne.join();
System.out.println("Main thread is over.");
}
}
返回结果为: true false false true
解释:
结果一:第一次使用threadOne.isInterrupted()方法的时候线程被中断返回true;
结果二:threadOne.interrupted()方法的时候当前线程状态是执行该方法的线程也就是这里的main线程,而main线程没有被中断因此返回false
结果三:Thread.interrupted()返回的永远是主线程的状态
结果四:threadOne.isInterrupted()该方法不会清除threadOne线程的状态因此返回true
已创建但是还没有启动的线程,还没有执行start方法。
一旦调用了start方法就会进人runnable状态,该状态其实是两种一个是可运行的状态,一个是正在运行状态。
当一个线程运行被synchronize修饰的代码块时,并且该线程没有拿到锁的时候就是Blocked。
waiting是等待,只能通过方法唤醒
Timed Waiting是计时等待,当时间到达后自动唤醒
Terminated表示线程已终止
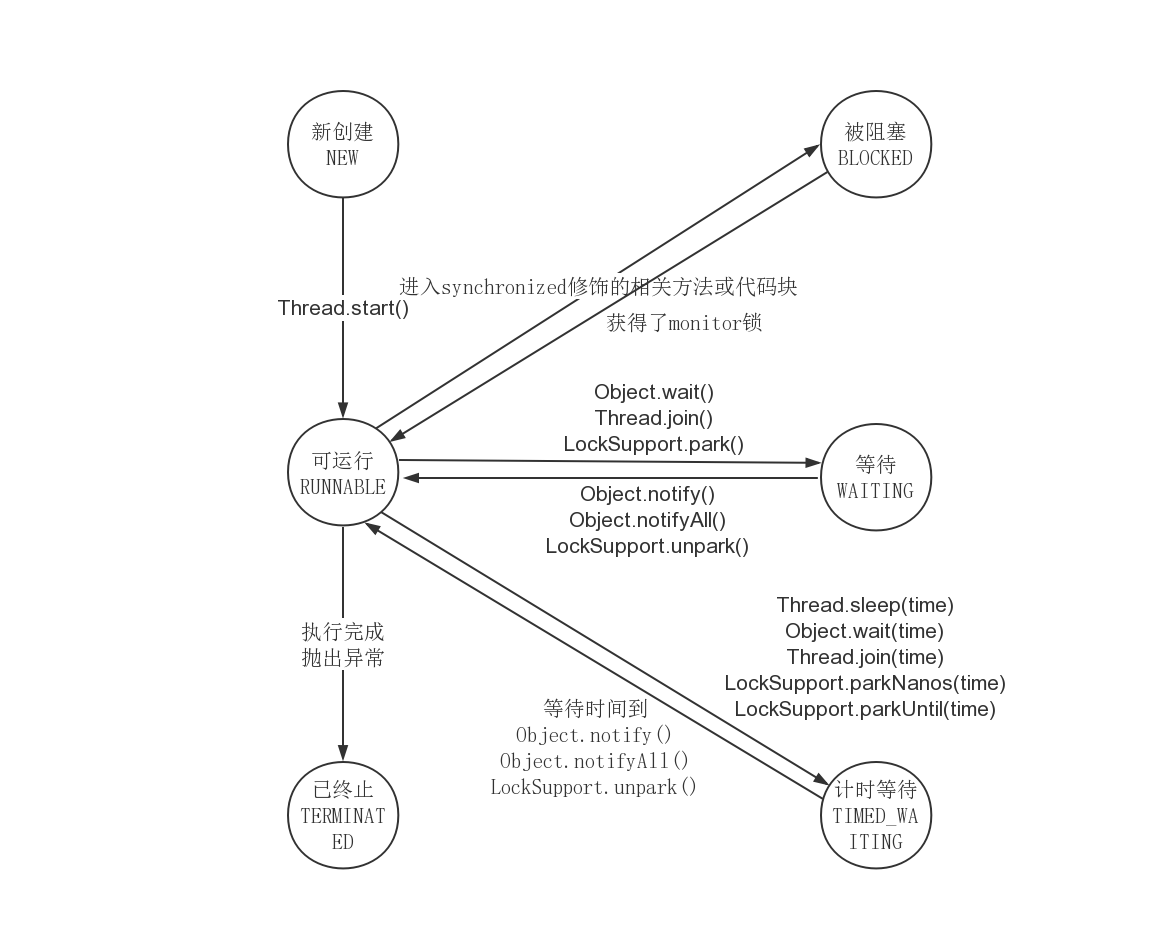
什么是阻塞状态:一般而言,把Blocked、Waiting、Timed_waiting称之为阻塞状态。
/**
* 描述:展示线程的NEW、RUNNABLE、Terminated状态。即使是正在运行,也是Runnable状态,而不是Running。
*/
public class NewRunnableTerminated implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new NewRunnableTerminated());
//打印出NEW的状态
System.out.println(thread.getState());
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//打印出RUNNABLE的状态,即使是正在运行,也是RUNNABLE,而不是RUNNING
System.out.println(thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//打印出TERMINATED状态
System.out.println(thread.getState());
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
/**
* 描述: 展示Blocked, Waiting, TimedWaiting
*/
public class BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting implements Runnable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting runnable = new BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable);
thread1.start();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable);
thread2.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//打印出Timed_Waiting状态,因为正在执行Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread1.getState());
//打印出BLOCKED状态,因为thread2想拿得到sync()的锁却拿不到
System.out.println(thread2.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//打印出WAITING状态,因为执行了wait()
System.out.println(thread1.getState());
}
@Override
public void run() {
syn();
}
private synchronized void syn() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/cafebaba/p/14485500.html