B站一个up主总结的回溯算法的模板
void backtracking(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
处理节点;
backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
实际上回溯算法就是树形结构,然后遍历整个树,重点就是需要回溯,这是一个组合问题的树形结构
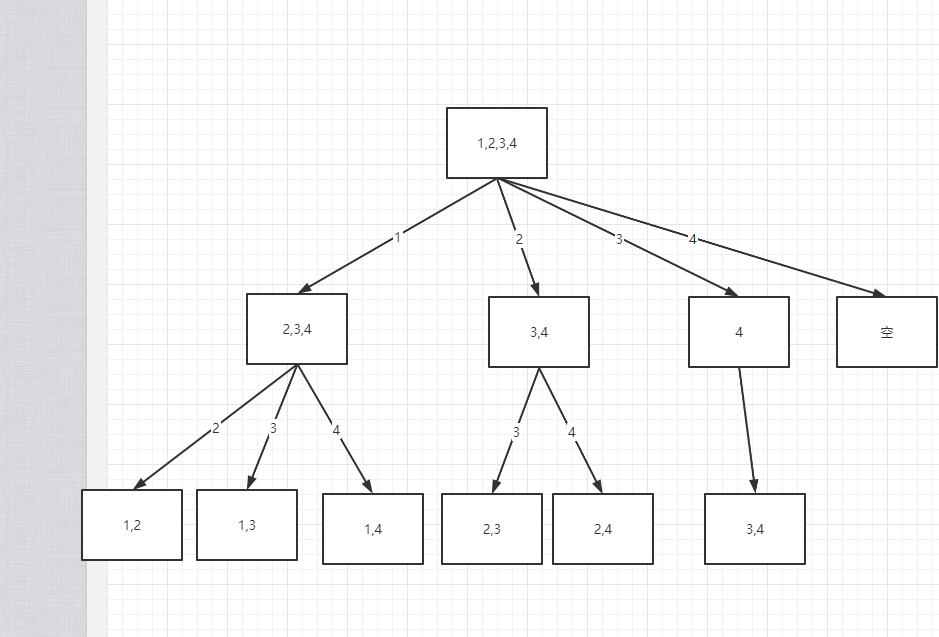
回溯算法可以解决很多问题 比如 组合问题 排列问题 切割问题 子集问题等
题目描述:
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
示例:
输入: n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
在组合问题中,关键参数就是就是数据集n,组合大小数k,搜索起点 begin,用来记录路径的path,结果集res
思路就是从begin开始遍历,一直遍历到n,将遍历的元素添加到路径path中,如果深度等于k时,就将path添加到结果集,
具体代码:
public class combinationProblem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
combinationProblem combinationProblem = new combinationProblem();
System.out.println(combinationProblem.combine(5, 2));
}
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (k <= 0 || n < k) {
return res;
}
// 从 1 开始是题目的设定
Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>();
dfs(n, k, 1, path, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int n, int k, int begin, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// 递归终止条件是:path 的长度等于 k,实际上就是叶子节点,我们需要在这里收集结果
if (path.size() == k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 遍历可能的搜索起点
for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++) {
// 向路径变量里添加一个数
path.addLast(i);
System.out.println(path);
// 下一轮搜索,设置的搜索起点要加 1,因为组合数理不允许出现重复的元素
dfs(n, k, i + 1, path, res);
// 重点理解这里:深度优先遍历有回头的过程,因此递归之前做了什么,递归之后需要做相同操作的逆向操作
//path.pop(); //pop和removelist一样
//这里就是回溯的过程,弹出最后一个元素
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
来查看一下每一步的path 和最后的 res
path:
[1]
[1, 2]
[1, 3]
[1, 4]
[1, 5]
[2]
[2, 3]
[2, 4]
[2, 5]
[3]
[3, 4]
[3, 5]
[4]
[4, 5]
[5]
res:
[[1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [1, 5], [2, 3], [2, 4], [2, 5], [3, 4], [3, 5], [4, 5]]
可以更好的理解回溯算法的整个过程
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/spx88/p/14479456.html