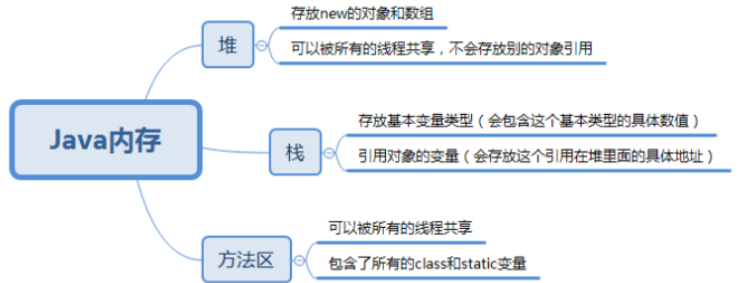
数组的定义:
数组的四个基本特点:
首先必须声明数组变量,才能在程序中使用数组。
声明语法格式:
dataType[] array; // 首选的方法
或
dataType array[]; // 效果相同,但不是首选方法
创建语法格式:
array = new dataType[arraySize];
解释:
数组的声明和创建可以一起完成:
dataType[] array = new dataType[arraySize];
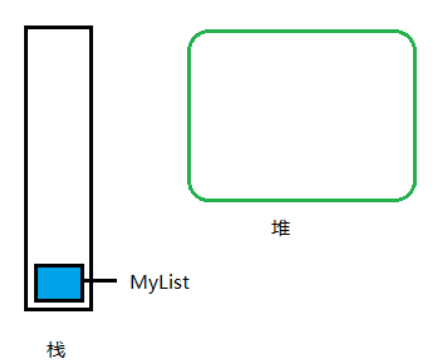
过程:
//1.声明一个数组
int[] myList = null;
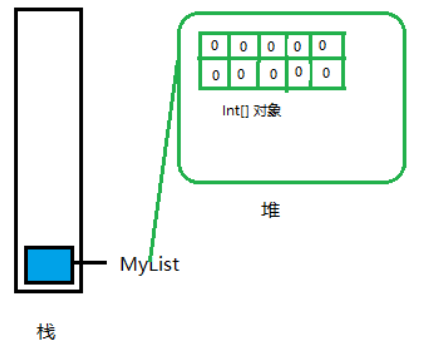
//2.创建一个数组
myList = new int[10];
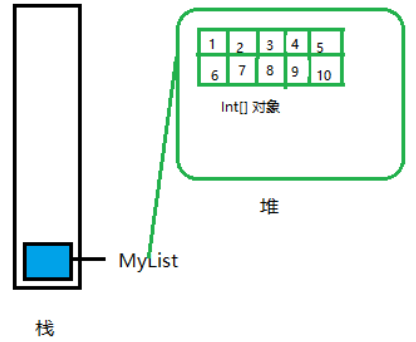
//3.像数组中存值
for(i = 0; i <= 10; i++){
myList[i] = i+1;
}
直接在定义数组的同时就为数组元素分配空间并赋值。
int[] a = {1,2,3};
数组定义、为数组元素分配空间、赋值的操作、分开进行。
int[] a = new int[2];
a[0]=1;
a[1]=2;
数组是引用类型,它的元素相当于类的实例变量,因此数组一经分配空间,其中的每个元素也被按照实 例变量同样的方式被隐式初始化。
? 即:new了之后会自动赋默认值
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[2];
boolean[] b = new boolean[2];
String[] s = new String[2];
System.out.println(a[0]+":"+a[1]); //0,0
System.out.println(b[0]+":"+b[1]); //false,false
System.out.println(s[0]+":"+s[1]); //null, null
}
下标的合法区间:[0, length-1],如果越界就会报错;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[2];
System.out.println(a[2]);
}
-->
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 2
at com.kuang.chapter3.Demo03.main(Demo03.java:6)
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException : 数组下标越界异常!
数组的元素类型和数组的大小都是确定的,
所以当处理数组元素时候,我们通常使用基本循环或者 For- Each循环。
创建、初始化和操纵数组:
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
// 打印所有数组元素
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
}
// 计算所有元素的总和
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
total += myList[i];
}
System.out.println("Total is " + total);
// 查找最大元素
double max = myList[0];
for (int i = 1; i < myList.length; i++) {
if (myList[i] > max) {
max = myList[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Max is " + max);
}
}
JDK 1.5 引进了一种新的循环类型,被称为 For-Each 循环或者加强型循环,它能在不使用下标的情况下 遍历数组。
语法格式如下:
for(type element: array){
System.out.println(element);
}
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
// 打印所有数组元素
for (double element: myList) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
数组可以作为参数传递给方法。
例如,下面的例子就是一个打印 int 数组中元素的方法 :
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
//做一个反转数组
public static int[] reverse(int[] list) {
int[] result = new int[list.length];
//第一种方法
for (int i = list.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[list.length - i] = list[i];
}
/*第二种方法
for (int i = 0, j = result.length - 1; i < list.length; i++, j--) {
result[j] = list[i];
} */
return result;
}
多维数组可以看成是数组的数组,比如二维数组就是一个特殊的一维数组,其每一个元素都是一个一维 数组。
语法格式:
type[][] typeName = new type[typeLength1][typeLength2];
type 可以为基本数据类型和复合数据类型,arraylenght1 和 arraylenght2 必须为正整数, arraylenght1 为行数,arraylenght2 为列数。
比如定义一个二维数组:
int a[][] = new int[2][5];
对二维数组中的每个元素,引用方式为 arrayName[index1] [index2]
例如: num[1][0];
a.length获取的二维数组第一维数组的长度(行数)
a[0].length才是获取第二维第一个数组长度(第一行的列数)。
数组的工具类java.util.Arrays
由于数组对象本身并没有什么方法可以供我们调用,但API中提供了一个工具类Arrays供我们使用
从而可以对数据对象进行一些基本的操作。
Arrays类中的方法都是static修饰的静态方法,在使用的时候可以直接使用类名进行调用,而"不用"使用对 象来调用(注意:是"不用" 而不是 "不能")
java.util.Arrays 类能方便地操作数组. 使用之前需要导包!
具有以下常用功能:
给数组赋值:通过 ?ll 方法。
对数组排序:通过 sort 方法,按升序。
比较数组:通过 equals 方法比较数组中元素值是否相等。
查找数组元素:通过 binarySearch 方法能对排序好的数组进行二分查找法操作。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2};
System.out.println(a); //[I@1b6d3586
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //[1, 2]
}
按数字升序进行排序:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,323,23,543,12,59};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
在数组中查找指定元素并返回其下标
注意:使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的数组,以获得指定的值。
必须在进行此调用之前先对数组进行排序(通 过sort方法等)。
如果没有对数组进行排序,则结果是不确定的。
如果数组包含多个带有指定值的元素,则无法保证找到的是哪一个。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,323,23,543,12,59};
Arrays.sort(a); //使用二分法查找,必须先对数组进行排序
System.out.println("该元素的索引:"+Arrays.binarySearch(a, 12));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,323,23,543,12,59};
Arrays.sort(a); //使用二分法查找,必须先对数组进行排序
Arrays.fill(a, 2, 4, 100); //将2到4索引的元素替换为100
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
int[] a = {3,5,1,9,7};
List<int[]> list = Arrays.asList(a);

冒泡排序(Bubble Sort),是一种计算机科学领域的较简单的排序算法。
它重复地走访过要排序的元素列,依次比较两个相邻的元素,如果他们的顺序(如从大到小、首字母从 A到Z)错误就把他们交换过来。
走访元素的工作是重复地进行直到没有相邻元素需要交换,也就是说该元素列已经 排序完成。
冒泡排序算法的原理:
class Bubble {
public int[] sort(int[] array) {
int temp = 0;
// 外层循环,它决定一共走几趟
//-1为了防止溢出
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
int flag = 0;
//通过标记位可以减少无谓的比较,如果已经有序了,就退出循环
//内层循环,它决定每趟走一次
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - i - 1; j++) {
//如果后一个大于前一个,则换位
if (array[j + 1] > array[j]) {
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
flag = 1;
}
}
//在最后一次进入外层循环时,还剩下一个元素,此时已经排好了顺序,不用再进行逐一比较
//也就是说只要其他全部排好了序,就不会进内层循环的if,此时flag=0 直接跳出外层循环
if (flag == 0) {
break;
}
}
return array;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bubble bubble = new Bubble();
int[] array = {2, 5, 1, 6, 4, 9, 8, 5, 3, 1, 2, 0};
int[] sort = bubble.sort(array);
for (int num : sort) {
System.out.print(num + "\t");
}
}
}
? 选择排序(Selection sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法。
? 它的工作原理是每一次从待排序的数据元素中 选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,存放在序列的起始位置,然后,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小 (大)元素,然后放到排序序列的末尾。
? 以此类推,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完。
? 选择排序是 不稳定 的排序方法。
class SelectSort{
public int[] sort(int arr[]) {
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
// 认为目前的数就是最小的, 记 录最小数的下标
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) {
// 修改最小值的下标
minIndex = j;
}
}
// 当退出for就找到这次的最小值,就需要交换位置了
if (i != minIndex) {
//交换当前值和找到的最小值的位置
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SelectSort selectSort = new SelectSort();
int[] array = {2, 5, 1, 6, 4, 9, 8, 5, 3, 1, 2, 0};
int[] sort = selectSort.sort(array);
for (int num : sort) {
System.out.print(num + "\t");
}
}
}
(了解)
https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6059914.html
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/feifan666/p/14404516.html