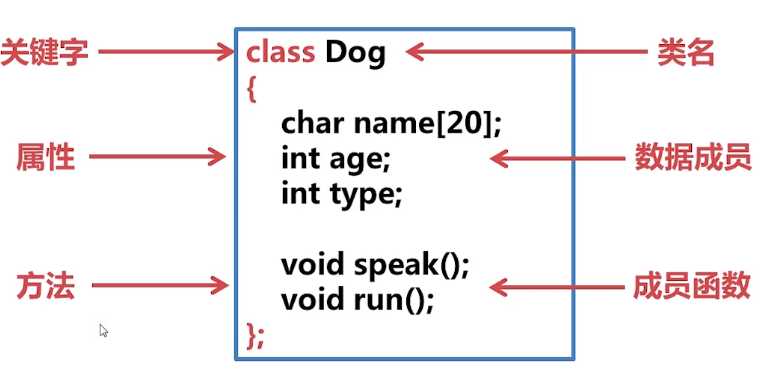
一、类和对象
1、类的定义

class Coordinate{ public: int x; int y; void printX() { cout << x << endl; } void printY() { cout << y << endl; } }; int main(void) { Coordinate coor; coor.x = 10; coor.y = 20; coor.printX(); coor.printY(); Coordinate *p = new Coordinate(); if(NULL == p) { return 0; } p->x = 100; p->y = 200; p->printX(); p->printY(); delete p; p = NULL; system("pause"); return 0; }
2、类的访问限定符
public:公共的
protected:受保护的
private:私有的
二、字符串类型(string类型)
1、初始化string对象的方法
string s1; >> s1为空串 string s2("ABC"); >> 用字符串字面值初始化s2 string s3(s2); >> 将s3初始化为s2的一个副本 string s4(n,‘c‘); >> 将s4初始化为字符‘c‘的n个副本
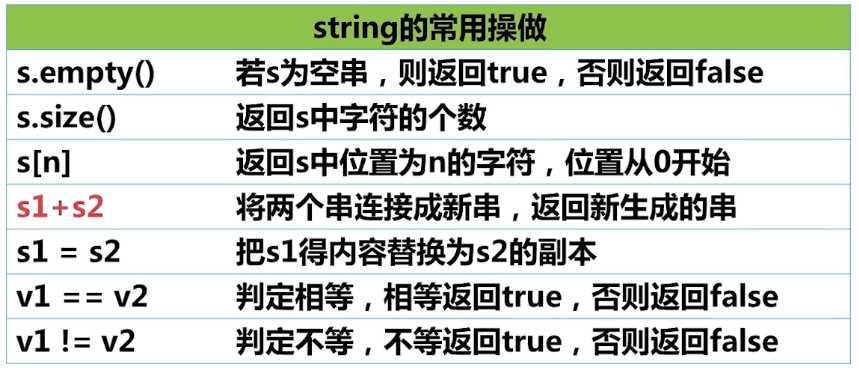
2、string 类型的常用操作
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>


#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { string name; cout << "please input your name:"; getline(cin, name); if (name.empty()) { cout << "input is null..." << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } if (name == "imooc") { cout << "you are a administrator" << endl; } cout << "hello " + name << endl; cout << "your name length: " << name.size() << endl; cout << "your name first letter is: " << name[0] << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
三、封装
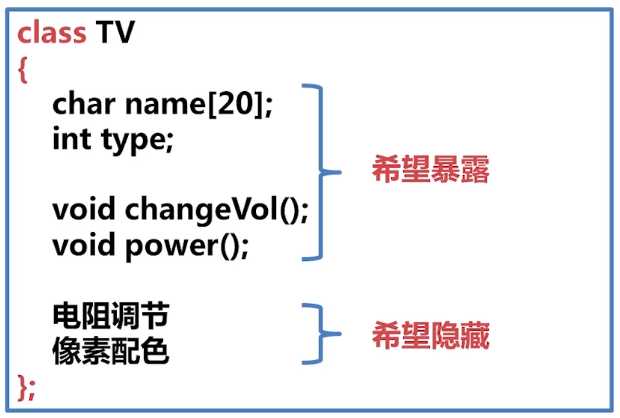
1、什么是封装
通过限制对属性和操作的访问权限,可以将属性“隐藏”在对象内部,对外提供一定的接口,在对象之外只能提供接口对对象的属性进行操作。
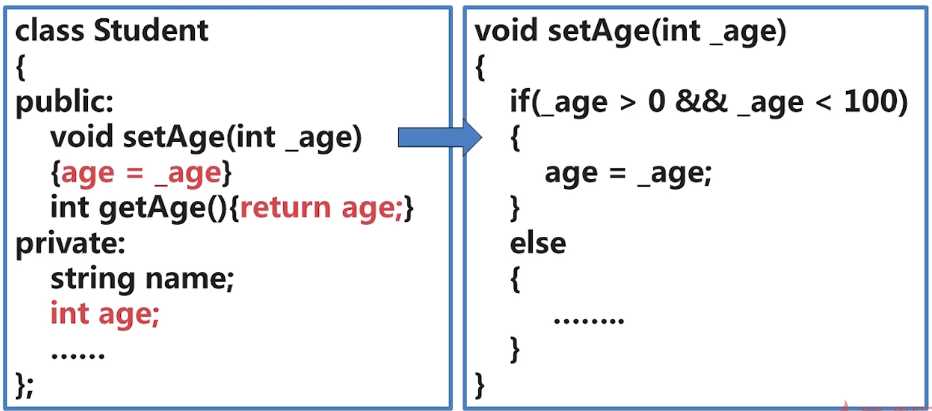
2、封装的好处
封装性增加了对象的独立性,对象内部的私有成员可以受到保护,其它对象不能直接修改,从而保证了数据的可靠性。一个定义完好的类可以作为独立的模块使用。
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>


#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string> using namespace std; class Student{ private: string m_strName; string m_strGender; int m_iScore; public: void setName(string _name) { m_strName = _name; } string getName() { return m_strName; } void setGender(string _gender) { m_strGender = _gender; } string getGender() { return m_strGender; } int getScore() { return m_iScore; } void initScore() { m_iScore = 0; } void study(int _score) { m_iScore += _score; } }; int main() { Student stu; stu.initScore(); stu.setName("小红"); stu.setGender("女"); stu.study(5); stu.study(2); cout << stu.getName() << " " << stu.getGender() << " " << stu.getScore() << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
四、类外定义
1、类内定义与内联函数

2、类外定义
是指成员函数的函数体写在类的外面
(1)同文件类外定义 —— 成员函数虽然定义在类的外面,但是与类在同一个文件中

(2)分文件类外定义 —— 成员函数定义在类的外面,并且与类不在同一个文件中

>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>


#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string> using namespace std; class Teacher{ private: string m_strName; string m_strGender; int m_iAge; public: void setName(string _name); string getName(); void setGender(string _gender); string getGender(); void setAge(int _age); int getAge(); void teach(); }; void Teacher::setName(string _name) { m_strName = _name; } string Teacher::getName() { return m_strName; } void Teacher::setGender(string _gender) { m_strGender = _gender; } string Teacher::getGender() { return m_strGender; } void Teacher::setAge(int _age) { m_iAge = _age; } int Teacher::getAge() { return m_iAge; } void Teacher::teach() { cout << "现在上课.." << endl; } int main() { Teacher t; t.setName("庄子"); t.setGender("男"); t.setAge(50); cout << t.getName() << " " << t.getGender() << " " << t.getAge() << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }

#include <string> using namespace std; class Teacher{ private: string m_strName; string m_strGender; int m_iAge; public: void setName(string _name); string getName(); void setGender(string _gender); string getGender(); void setAge(int _age); int getAge(); void teach(); };

#include "Teacher.h" #include <stdlib.h> #include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; void Teacher::setName(string _name) { m_strName = _name; } string Teacher::getName() { return m_strName; } void Teacher::setGender(string _gender) { m_strGender = _gender; } string Teacher::getGender() { return m_strGender; } void Teacher::setAge(int _age) { m_iAge = _age; } int Teacher::getAge() { return m_iAge; } void Teacher::teach() { cout << "正在上课.." << endl; } int main() { Teacher t; t.setName("庄子"); t.setGender("男"); t.setAge(50); cout << t.getName() << " " << t.getGender() << " " << t.getAge() << endl; t.teach(); system("pause"); return 0; }
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
五、构造函数
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dabj-yb/p/13945104.html