| query()方法参数 | 对应SQL部分 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| table | from table_name | 表名 |
| colums | select colum1,colum2 | 要查询的列名 |
| selection | where column = value | 约束条件 |
| selectionArgs | - | 为where中的占位符提供具体的值 |
| groupBy | group by column | 需要分组的列 |
| having | having column = value | 对分组后的结果进一步约束 |
| orderBy | order by column1,column2 | 排序方式 |
<LinearLayout>
..........省略代码...........
<Button
android:id="@+id/query_data"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Query data"
/>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.javapackage com.example.databasetest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private MyDatabaseHelper dbHelper;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
dbHelper = new MyDatabaseHelper(this,"BookStore.db",null,2);
...............省略代码..........................
Button queryButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.query_data);
queryButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
//查询Book表中的所有数据
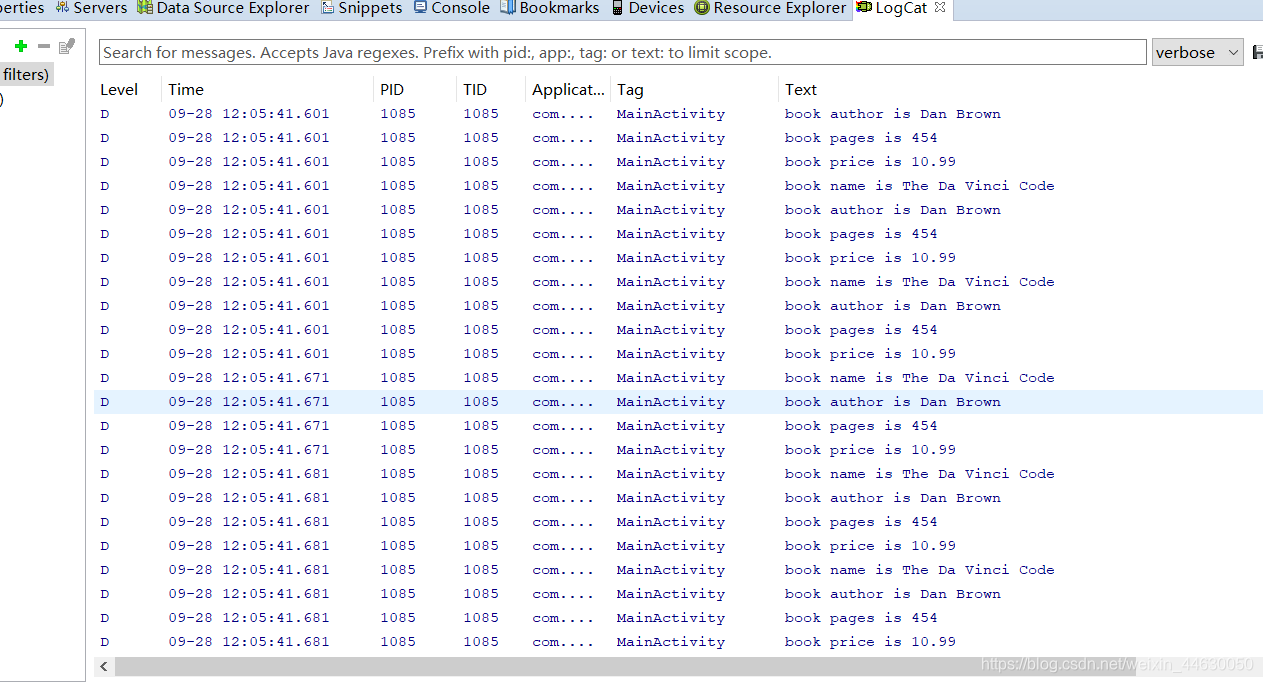
Cursor cursor = db.query("Book",null,null,null,null,null,null);
if(cursor.moveToFirst()) {
do {
//遍历Cursor对象,取出数据并打印
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
String author = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("author"));
int pages = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("pages"));
double price = cursor.getDouble(cursor.getColumnIndex("price"));
Log.d("MainActivity","book name is "+name);
Log.d("MainActivity","book author is "+ author);
Log.d("MainActivity","book pages is " + pages);
Log.d("MainActivity","book price is " + price);
}while(cursor.moveToNext());
}
cursor.close();
}
});
}
}
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
db.execSQL("insert into Book(name,author,pages,prices) values(?,?,?,?)",new String[] {"xiaoming","Dan Brown","454","16.69");
//类似预编译的方法
<LinearLayout>
..........省略代码...........
<Button
android:id="@+id/replace_data"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Replace data"
/>
</LinearLayout>
Button replaceData = (Button)findViewById(R.id.replace_data);
replaceData.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
db.beginTransaction();//开启事务
try {
db.delete("Book", null, null);
if(true) {
//在这里手动抛出一个异常,让事务失败
throw new NullPointerException();
}
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name","Game of Thrones");
values.put("author", "George Martin");
values.put("pages", 720);
values.put("price", 20.85);
db.insert("Book",null, values);
db.setTransactionSuccessful();//事务已经执行成功
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
db.endTransaction();//结束事务
}
}
});
Android连载36-查询数据、使用原生SQL以及事务的使用
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ruigege0000/p/13747649.html