package com.qf.demo03;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test1Map {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* Map,操作是键值对,成对的对象。
* key和value必须是一一对应的。
* key不能重复
*/
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
/*
* 1.put(key,value)-->value
*
* 将制定的参数键值对,存入map集合中。
* 存储的key不允许重复,如果重复,会覆盖原来的value值。
* 返回值是被替换的value。如果key不重复,就返回null
*/
String s1 = map.put("A", "aaa");
String s2 = map.put("B", "bbb");
String s3 = map.put("C", "ccc");
String s4 = map.put("D", "ddd");
System.out.println(map);//{A=aaa, B=bbb, C=ccc, D=ddd}
System.out.println(s1+","+s2+","+s3+","+s4);//null,null,null,null
String s5 = map.put("D", "XXX");
System.out.println(map);//{A=aaa, B=bbb, C=ccc, D=XXX}
System.out.println(s5);//ddd
//2.clear(),清空map集合,就是删除所有的键值对
// map.clear();
// System.out.println(map);
//3.containsKey(key)-->boolean,是否包含指定的key
System.out.println(map.containsKey("D"));
//4.containsValue(value)-->boolean,是否包含指定的value
System.out.println(map.containsValue("ddd"));
/*
* 5.get(key)-->value
* 根据key,获取它所对应的value值。
* 如果key不存在,返回null
*/
System.out.println(map.get("D"));//XXX
System.out.println(map.get("DD"));//null
if(map.containsKey("DD")){
System.out.println(map.get("DD"));
}else{
System.out.println("map中查无此数据。。");
}
/*
* 6.remove(key)->value
* 从map中,根据指定的key,移出该键值对。返回值是被删除的value
* 如果map中没有这个key,返回值就是null。
*/
String s6 = map.remove("DD");
System.out.println(map); //{A=aaa, B=bbb, C=ccc}
System.out.println(s6); //XXX
System.out.println(map.size());//4,获取map集合中,键值对的数量
}
}
package com.qf.demo03;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Test3HashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建Map集合,key:整数,value:人对象
//key一定是去重的。
HashMap<Integer, Person> map1 = new HashMap<Integer, Person>();
map1.put(1, new Person("张三", 20));
map1.put(2, new Person("李四", 25));
map1.put(3, new Person("王五", 28));
System.out.println(map1);
map1.put(1, new Person("赵六", 40));
System.out.println(map1);
HashMap<Person, String> map2 = new HashMap<>();
/*
* hashMap的key,如何去重?同hashSet去重原理相同。
* 底层自动调用hashCode和equals()
*
* hashCode:
* 相同的对象,哈希值必须相同
* 不同的对象,哈希值尽量不同
*
* equals:
* 相同的对象:必须true
* 不同的对象:必须false
*/
map2.put(new Person("王二狗", 30), "矮矬穷");
map2.put(new Person("李小花", 28), "美美哒");
map2.put(new Person("王二狗", 30), "高富帅");
System.out.println(map2.size());
System.out.println(map2);
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("aaa");
}
}
package com.qf.demo03;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Test3HashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建Map集合,key:整数,value:人对象
//key一定是去重的。
HashMap<Integer, Person> map1 = new HashMap<Integer, Person>();
map1.put(1, new Person("张三", 20));
map1.put(2, new Person("李四", 25));
map1.put(3, new Person("王五", 28));
System.out.println(map1);
map1.put(1, new Person("赵六", 40));
System.out.println(map1);
HashMap<Person, String> map2 = new HashMap<>();
/*
* hashMap的key,如何去重?同hashSet去重原理相同。
* 底层自动调用hashCode和equals()
*
* hashCode:
* 相同的对象,哈希值必须相同
* 不同的对象,哈希值尽量不同
*
* equals:
* 相同的对象:必须true
* 不同的对象:必须false
*/
map2.put(new Person("王二狗", 30), "矮矬穷");
map2.put(new Person("李小花", 28), "美美哒");
map2.put(new Person("王二狗", 30), "高富帅");
System.out.println(map2.size());
System.out.println(map2);
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("aaa");
}
}
package com.qf.demo03;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test4TreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map1 = new TreeMap<>();
map1.put(1, "面朝大海,春暖花开");
map1.put(3, "你说的都对");
map1.put(2, "Jerry爱大米");
System.out.println(map1);
map1.put(3, "床前明月光");
System.out.println(map1);
Map<String, String> map2 = new TreeMap<>();
map2.put("C", "地上鞋三双");
map2.put("B", "举头望明月");
map2.put("A", "疑是地上霜");
System.out.println(map2);
}
}
package com.qf.demo03;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Student{
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + "]";
}
}
public class Test6TreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//题目:将Student对象,存入到Map中,作为key,value:【优秀,良好,中等,及格,不及格】
/*
* new TreeSet()-->Comparable
* new TreeSet(Comparator)-->Comparator
*
* new TreeMap()-->Comparable
* new TreeMap(Comparator)-->Comparator
*/
TreeMap<Student, String> map =new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//1.成绩:从高到低
if(o1.getScore()>o2.getScore()){
return -1;
}else if(o1.getScore()<o2.getScore()){
return 1;
}else{
//2.年龄:从小到大
if(o1.getAge() < o2.getAge()){
return -1;
}else if(o1.getAge() > o2.getAge()){
return 1;
}else{
//3.姓名
return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
}
}
}
});
map.put(new Student("王二狗", 18, 88), "良好");
map.put(new Student("李小花", 17, 98), "优秀");
map.put(new Student("Rose", 17, 88), "良好");
map.put(new Student("李铁柱", 18, 88), "良好");
// Set<Student> keySet = map.keySet();
// Iterator<Student> it2 = keySet.iterator();
Iterator<Student> it = map.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Student student = it.next();
System.out.println(student+"\t"+map.get(student));
}
}
}

package com.qf.demo01;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test1Entry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("A", "aaa");
map.put("B", "bbb");
map.put("C", "ccc");
map.put("D", "ddd");
/*
* map中存储了4个键值对:
*
* 4个键值对——>4个Entry对象
*
* map:
* key-->value
* key-->value
* key-->value
* ...
*
* Set:
* entry:key,value
* entry:key,value
* entry:key,value
* ....
*
* 获取map中的每一个元素:迭代map集合?
* 1.map中的所有的key,存储到一个Set中
* A:keySet()--->Set集合
* B:iterator()-->迭代获取每一个key
* C:根据key获取map中对应的value
*
* 2.map中的键值对组合entry,存储到一个Set中
* A:entrySet()--->Set集合
* B:iterator()-->迭代获取每一个entry
* C:根据entry对象,获取里面的key和value
*
*
*
* 注意点:
* iterator()--->Collection接口
* List,Set。。。ArrayList,linkedList,HashSet,TreeSet....
*
* map是没有迭代器
*/
//step1:获取map集合对应set:entry
Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//step2:操作set集合,获取迭代器对象
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> it = entrySet.iterator();
//step3:循环遍历迭代
while(it.hasNext()){
//调用next(),获取Set集合中对象:entry
Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();
//step4:操作entry,获取key和value
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"\t"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("--------------");
/*
* for(数据类型 变量名:数组/集合){
* }
*/
for(Entry<String,String> entry:map.entrySet()){//集合Set<Entry>
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"\t"+entry.getValue());
}
for(String key:map.keySet()){//集合Set<Key>
System.out.println(key+"\t"+map.get(key));
}
}
}

package com.qf.demo01;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class Test2LinkedHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* LinkedHashMap集合
* 记录了存储的顺序。
*/
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("ddd", "ddd");
map.put("aaa", "aaa");
map.put("ccc", "ccc");
map.put("bbb", "bbb");
System.out.println(map);
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map2 = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map2.put("D", "ddd");
map2.put("A", "aaa");
map2.put("C", "ccc");
map2.put("B", "bbb");
System.out.println(map2);
}
}
package com.qf.demo02;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Test3HashTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* HashMap,支持null
*
* HashTable,不支持null,抛出异常:NullPointerException
*/
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("A", "aaa");
map.put("B", "bbb");
map.put("C", null);//null对象
map.put("D", null);
System.out.println(map);
map.put(null, "haha");
System.out.println(map);
map.put(null, "hehe");
System.out.println(map);
Hashtable<String, String> table = new Hashtable<>();
table.put("AA", "aaa");
table.put("BB", "bbb");
// table.put("CC", null);
table.put(null, "ddd");
System.out.println(table);
}
}

package com.qf.demo03;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test4Properties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* Map
* HashTable
* Properties
* 看系统的配置信息:演示效果
*
*
* Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
* System.out.println();
*/
//1.通过System类,获取系统的一些属性信息,在Properties集合中
Properties properties = System.getProperties();
// System.out.println(properties);
//2.显示到屏幕上
properties.list(System.out);//System.out-->PrintStrem(打印流),属于IO范畴的,现在超纲
}
}
package com.qf.demo03;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test5Properties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//默认泛型:String类型
Properties properties = new Properties();
//向集合中存储一些属性信息
System.out.println(properties);
// properties.put("name", "zhangsan");
properties.setProperty("username", "zhangsan");//用户名这个属性
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");
System.out.println(properties);
/*
* 支持持久化存储:
* 瞬时存储:内存中,存储的数据,都叫瞬时数据。当程序结束的时候,对象,变量,常量。。。从内存中销毁,释放内存。
* 持久存储:程序关闭,电脑关机等,数据还在。数据库,本地文件。
*/
//将Properties中的属性信息持久化存储——>存储到文件。
//从此行开始,代码超纲:听思路,代码看懂注释
//step1.创建一个文件对象File类的对象,表示C盘Ruby目录下的message.properties文件
File file = new File("C:\\Ruby\\message.properties");
//step2:创建文件输出流,用于将数据写入到file文件中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
//step3:将properties里面的属性信息,存储到file文件里
properties.store(fos, "mymessage");
System.out.println("信息保存完毕。。。");
}
}
package com.qf.demo03;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test6Properties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.step1:创建文件对象,表示存储了数据的本地文件:C盘Ruby文件夹,message.properties
File file = new File("C:\\Ruby\\message.properties");
//2.创建集合Properties,用于存储从文件中读来的数据
Properties properties2 = new Properties();
System.out.println(properties2);//{}
//3.从文件上创建输入流,用于读取文件中的数据
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//4.将file中的数据,到properties集合中
properties2.load(fis);
System.out.println(properties2);
}
}

package com.qf.demo04;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Point1{
private int x;
private int y;
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
class Point2{
private double x;
private double y;
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
class Point3{
private String x;
private String y;
public String getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(String x) {
this.x = x;
}
public String getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(String y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
//1.泛型作用在类上,当创建该类对象的时候,决定这个泛型
class Point<T>{//type
private T x;//声明一个属性,属性名x,属性类型T
private T y;//晟敏一个属性,属性名y,属性类型T
//get和set方法。。
public void setX(T x){//2.用于普通的方法
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(T y){
this.y = y;
}
public T getX(){
return x;
}
public T getY(){
return y;
}
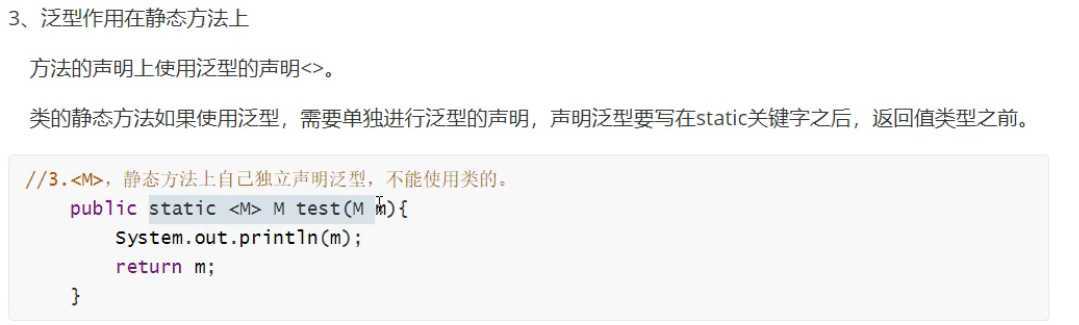
//3.<M>,静态方法上自己独立声明泛型,不能使用类的。
public static <M> M test(M m){
System.out.println(m);
return m;
}
}
public class Test7Generics {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//描述一个点:x轴,y轴
// Point1 p1 = new Point1();
// p1.setX(1);//int
// p1.setY(2);//int
// System.out.println(p1.getX()+"\t"+p1.getY());
//
// Point2 p2 = new Point2();
// p2.setX(1.34);//double
// p2.setY(4.21);//double
// System.out.println(p2.getX()+"\t"+p2.getY());
//
// Point3 p3 = new Point3();
// p3.setX("北纬108");//String
// p3.setY("东经89");//String
// System.out.println(p3.getX()+"\t"+p3.getY());
/*
* 作用在类上的泛型,给对象用的,凡是对象的属性和方法,都可以直接使用这个泛型。
* 该泛型,随着对象的创建而确定。
*/
Point<Integer> p1 = new Point<>();//x,y两个属性
p1.setX(1);//int-->Integer
p1.setY(2);
System.out.println(p1.getX()+"\t"+p1.getY());
Point<Double> p2 = new Point<>();
p2.setX(3.14);
p2.setY(4.56);
System.out.println(p2.getX()+"\t"+p2.getY());
Point<String> p3 = new Point<>();
p3.setX("北纬108");
p3.setY("东经89");
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
//泛型的擦除:定义类有泛型,但是创建对象的时候没有指明泛型。该类型就是Object类型了
List list3 = new ArrayList<>();
// list3.add(Object);
Point p4 = new Point();//泛型被擦除,没有具体的类型了,——>Object类型
String s1 = Point.test("abc");//M-->String
Integer i1 = Point.test(100);//M-->Integer
}
}
package com.qf.demo04;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Person{
}
class Student extends Person{
}
public class Test8Generics {
/*
* 该方法,打印一个list集合
* ?代表了该方法的参数为List里存储任意类型的数据
* List<Person>
* List<Student>
* List<String>
* List<Object>
*/
public static void printList(List<?> list){
}
//该方法只能接受List<Object>
public static void test(List<Object> list){
}
/*
* ? extends Person:限定了上限
* 接受集合的泛型是Person。或者是Person的子类类型。
* List<Person>
* List<Student>
*/
public static void test2(List<? extends Person> list){
}
/*
* ? super Student:限定了下限
* 接收集合的泛型是Student,以及Student的父类类型
* List<Student>
* List<Person>
* List<Object>
*/
public static void test3(List<? super Student> list){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> l1 = new ArrayList<>();
l1.add(new Person());
l1.add(new Student());//Student-->Person
List<Student> l2 = new ArrayList<>();
l2.add(new Student());
List<String> l3 = new ArrayList<>();
l3.add("haha");
l3.add("hehe");
List<Object> l4 = new ArrayList<>();
l4.add(new Object());//Object
l4.add(new Person());//Person-->Object
l4.add(new Student());//Student-->Object
l4.add("abc");//String-->Object
printList(l1);
printList(l2);
// test2(l2);
test3(l1);
test3(l2);
test3(l4);
/*
* 注意点:
* Student继承Person类
* List<Student> 不是List<Person>的子类
*/
}
}
package com.qf.demo05;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
public class Test9Collections {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> l1 = new ArrayList<String>();
l1.add("abc");
l1.add("ccc");//add方法每次只能添加一个元素。
/*
* 1、Collections.addAll(容器,要添加的元素)
* 向容器中同时添加多个元素对象
*/
Collections.addAll(l1, "hello","world","haha","hehe");
System.out.println(l1);
ArrayList<String> l2 = new ArrayList<>();//线程不安全
/*
* synchronizedList(集合)-->集合
* synchronizedSet()
* synchronizedMap()...
* 参数是线程不安全的集合,返回值线程安全的集合。
*/
List<String> newL2 = Collections.synchronizedList(l2);
/*
* List集合:有序,存储顺序。有下标
* 排序:将list集合中的元素进行排序。
* 类比数组排序
*
* int[] arr = {1,7,4,6,2,5}
* 排序:冒泡,选择,Arrays.sort()
*/
List<Integer> l3 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(l3, 1,7,4,6,2,5);
System.out.println(l3);
//list->sort,排序,排序规则
Collections.sort(l3);
System.out.println(l3);
List<Person> l4 = new ArrayList<>();
l4.add(new Person("王二狗", 18));
l4.add(new Person("李小花", 17));
l4.add(new Person("李铁柱", 19));
System.out.println(l4);
Collections.sort(l4);//使用的是默认的比较器:Comparable
Collections.sort(l4, new Comparator<Person>() {//使用的自定义的比较器:Comparator
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return 0;
}
});
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yzg-14/p/13398528.html