Handler使用例1
这个例子是最简单的介绍handler使用的,是将handler绑定到它所建立的线程中.
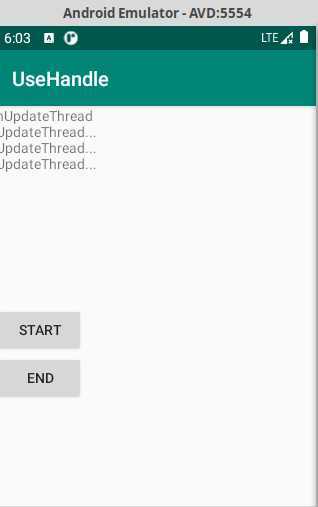
本次实验完成的功能是:单击Start按钮,程序会开始启动线程,并且线程程序完成后延时1s会继续启动该线程,每次线程的run函数中完成对界面输出nUpdateThread...文字,不停的运行下去,当单击End按钮时,该线程就会停止,如果继续单击Start,则文字又开始输出了。
MainActivity
package com.example.usehandle;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView text_view = null;
private Button start = null;
private Button end = null;
//使用handler时首先要创建一个handler
Handler handler = new Handler();
Runnable update_thread = new Runnable()
{
public void run()
{
//线程每次执行时输出"UpdateThread..."文字,且自动换行
//textview的append功能,不会覆盖前面的内容
text_view.append("\nUpdateThread...");
//延时1s后又将线程加入到线程队列中
handler.postDelayed(update_thread, 1000);
}
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
text_view = findViewById(R.id.text_view);
end = findViewById(R.id.end);
start = findViewById(R.id.start);
start.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
handler.post(update_thread);
}
});
end.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
handler.removeCallbacks(update_thread);
}
});
}
}
activity_main
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="200dip"
android:text="nUpdateThread"
tools:context=".MainActivity" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/start"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="start" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/end"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="end" />
</LinearLayout>
Handler使用例2
这个例子比刚才那个例子稍微复杂些。因为这个例子中用到了handler的消息队列机制,即通过handler中一个线程向消息队列中用sendMessage方法发送消息,发送的消息当然可以用来传递参数。在handler中用handleMessage来处理消息,处理方法是获得消息队列中的消息参数,用这些参数来完成另外一些功能。
本实验实现的是当开始按钮按下时,会启动一个线程,并绑定到handler中,该线程发送带有参数的message到handler的消息队列中,消息队列的另一端获取该消息,并且用该消息的参数来更新进度条。
MainActivity
package com.example.usehandle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import com.example.usehandle.R;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ProgressBar progress_bar = null;
private Button start = null;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
progress_bar = findViewById(R.id.progress_bar);
start = findViewById(R.id.start);
start.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
//让进度条显示出来
progress_bar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
//将线程加入到handler的线程队列中
update_progress_bar.post(update_thread);
}
});
}
//创建一个handler,内部完成处理消息方法
Handler update_progress_bar = new Handler()
{
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
//显示进度条
progress_bar.setProgress(msg.arg1);
//重新把进程加入到进程队列中
update_progress_bar.post(update_thread);
}
};//不加这个分号则不能自动添加代码
Runnable update_thread = new Runnable()
{
int i = 0;
public void run() {
i += 10;
//首先获得一个消息结构
Message msg = update_progress_bar.obtainMessage();
//给消息结构的arg1参数赋值
msg.arg1 = i;
//延时1s,java中的try+catch用来排错处理
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//把消息发送到消息队列中
update_progress_bar.sendMessage(msg);
if(i == 100)
//把线程从线程队列中移除
update_progress_bar.removeCallbacks(update_thread);
}
};
}
activity_main
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/start"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="start"
/>
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progress_bar"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="100dip"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:visibility="gone"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wcyMiracle/p/13386890.html