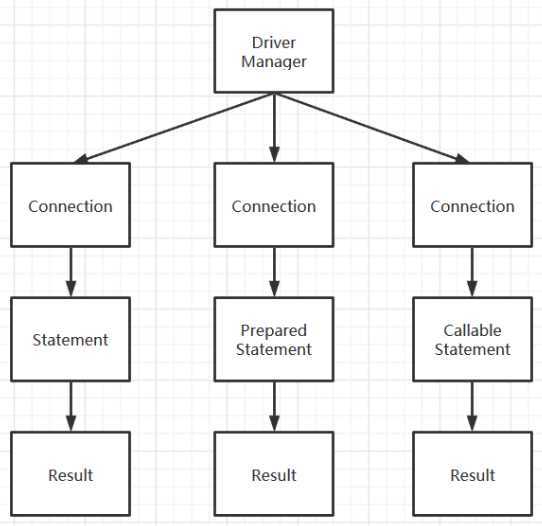
createStatement() 方法创建该对象。该对象用于发送 SQL 语句到数据库,并且返回执行结果。SELECT user, password FROM user_table WHERE user=‘a‘ OR 1 = ‘ AND password = ‘ OR ‘1‘ = ‘1‘) ,从而利用系统的 SQL 引擎完成恶意行为的做法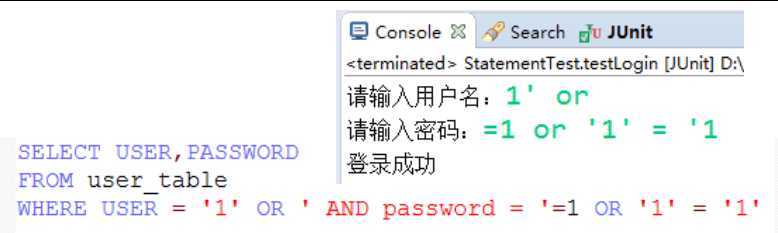
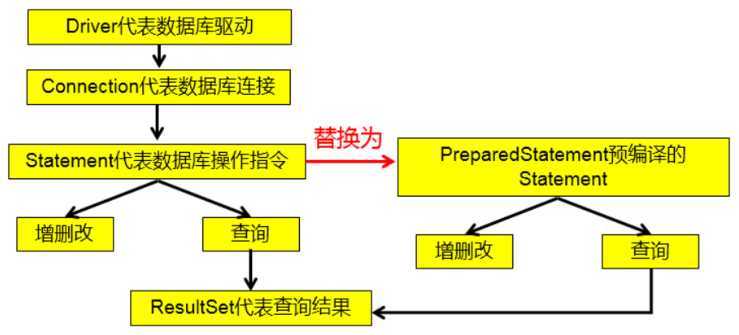
preparedStatement(String sql) 获取 PreparedStatement 对象setXxx() 来设置这些参数
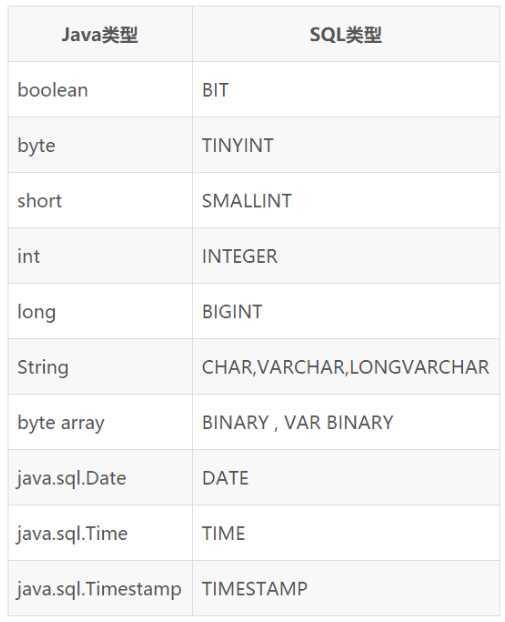
PreparedStatement 的 executeQuery(),查询结果是一个 ResultSet 对象next() 移动到下一行。调用 next() 检测下一行是否有效。若有效,该方法返回 true,且指针下移。相当于 Iterator 对象的 hasNext() 和 next() 的结合体getXxx(int index) 或 getXxx(int columnName) 获取每一列的值
getInt(1),getString("name")boolean next()int nextInt()String getString()Java.sql.Date getDate()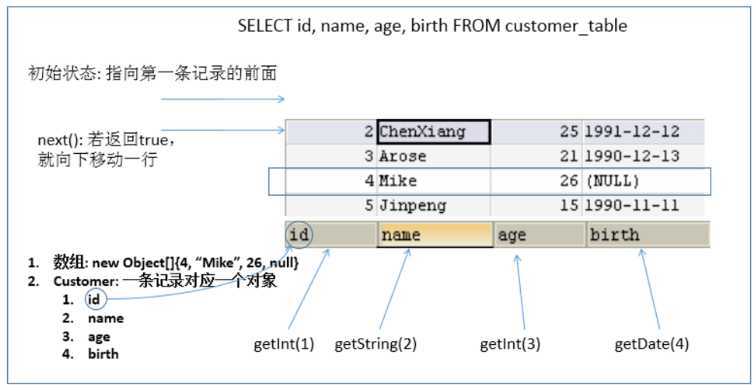
getColumnName(int column):获取指定列的名称getColumnLabel(int column):获取指定列的别名getColumnCount():返回当前 ResultSet 对象中的列数getColumnTypeName(int column):检索指定列的数据库特定的类型名称getColumnDisplaySize(int column):指示指定列的最大标准宽度,以字符为单位isNullable(int column):指示指定列中的值是否可以为 nullisAutoIncrement(int column):指示是否自动为指定列进行编号,这样这些列仍然是只读的Q1:得到结果集后, 如何知道该结果集中有哪些列 ? 列名是什么?
需要使用一个描述 ResultSet 的对象, 即 ResultSetMetaData。
Q2:关于ResultSetMetaData:
getMetaData() 即可getColumnCount()getColumnLabel()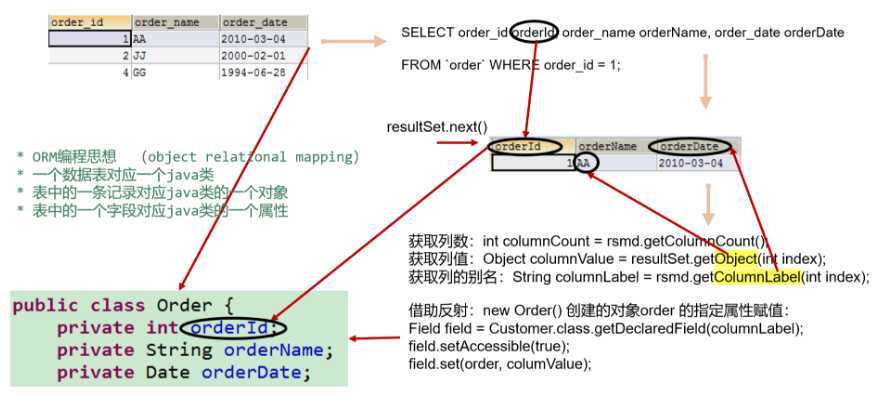
说明:使用 PreparedStatement 实现的查询操作可以替换 Statement 实现的查询操作,解决 Statement 拼串和 SQL 注入问题。
ORM(Object Relational Mapping) 思想:1. 表 ~ 类;2. 记录 ~ 对象;3. 字段 ~ 属性
getConnection() 和 close() 操作由于经常使用,故封装成工具类静态方法,方便直接调用。
public class JDBCUtils {
private static Properties prop = null;
static {
prop = new Properties();
try {
// 1. 读取配置文件
prop.load(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
// 2. 加载驱动
Class.forName(prop.getProperty("driverClass"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
// 3. 获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(prop.getProperty("url")
, prop.getProperty("user"), prop.getProperty("password"));
return connection;
}
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stat, ResultSet rs) {
if(rs != null)
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
if(stat != null)
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(conn != null)
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 通用的增删改操作
* @param sql 要执行的SQL语句
* @param args SQL中的参数
* @return SQL影响到的数据库中的记录条数
*/
public int update(String sql, Object... args) {
// 1. 获取连接
Connection conn = null;
// 2. 获取PreparedStatement的实例 (或:预编译SQL语句)
PreparedStatement stat = null;
int line = 0;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
int count = args.length;
// 3. 填充占位符
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
stat.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
// 4. 执行SQL语句
// excute() 执行的若是查询则return true,增删改return false)
// stat.execute(); // 如果只是单纯执行SQL,不需要返回值则使用这个方法
// 返回值int类型:表示此条SQL语句影响的记录条数
line = stat.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 5. 关闭资源
JDBCUtils.close(conn, stat, null);
}
return line;
}
针对 table 的字段名和 class 的属性名不一致:
getColumnLable() 替代 getColumnName() 来获取列的别名注:如果未指定 SQL AS,则从 getColumnLabel() 返回的值将和 getColumnName() 返回的值相同。
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(query("SELECT order_id orderId, order_name orderName"
+ ", order_date orderDate FROM `order` WHERE order_id = ?", 4));
}
// 针对Order表的通用查询方法
public static Order query(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Order order = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++)
stat.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
rs = stat.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if(rs.next()) {
order = new Order();
for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// 获取第 i 列的列值
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i+1);
// 获取第 i 列的列名(万万不可啊~)
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 获取第 i 列的别名(如果没起别名,返回列名)
String columnLable = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1);
Field field = Order.class.getDeclaredField(columnLable);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(order, columnValue);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(conn, stat, rs);
}
return order;
}
通用的表查询方法:
// 使用PreparedStatement实现不同表的通用查询多条记录操作
public static<T> List<T> queryRecords(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<T> list = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++)
stat.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
rs = stat.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
list = new ArrayList<>();
T instance = null;
while (rs.next()) {
instance = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// 获取第i列的列值
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i+1);
// 获取第i列的别名
String columnLable = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1);
// 反射方式赋值
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLable);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, columnValue);
}
list.add(instance);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(conn, stat, rs);
}
return null;
}
// 使用PreparedStatement实现不同表的通用查询单条记录操作
public static <T> T queryRecord(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
T instance = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++)
stat.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
rs = stat.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
instance = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// 获取第i列的列值
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i+1);
// 获取第i列的别名
String columnLable = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1);
// 反射方法赋值
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLable);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, columnValue);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(conn, stat, rs);
}
return instance;
}
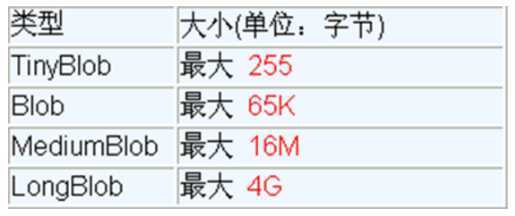
PacketTooBigException: Packet for query is too large,需在 MySQL 的安装目录下,找到 my.ini 文件加上如下的配置参数: max_allowed_packet=16M。同时注意:修改了 my.ini 文件之后,需要重新启动 MySQL 服务@Test
public void testInsert() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
FileInputStream is = null;
String sql = "insert into customers(name, email, birth, photo) values(?, ?, ?, ?)";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
stat.setObject(1, "燃烧女子的画像");
stat.setObject(2, "shaonv@gmail.com");
stat.setObject(3, "2020-10-10");
// com.mysql.jdbc.PacketTooBigException: Packet for query is too large
// change this value on the server by setting the ‘max_allowed_packet‘ variable
is = new FileInputStream(new File("p28.png"));
stat.setBlob(4, is);
stat.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(is != null)
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
JDBCUtils.close(conn, stat, null);
}
}
@Test
public void testQuery() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
InputStream is = null;
String sql = "select id, name, email, birth, photo from customers where id = ?";
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
stat.setObject(1, 25);
rs = stat.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()) {
Customer cust = new Customer();
cust.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
cust.setName(rs.getString("name"));
cust.setEmail(rs.getString("email"));
cust.setBirth(rs.getDate("birth"));
Blob photo = rs.getBlob("photo");
is = photo.getBinaryStream();
os = new FileOutputStream(new File("伞哥牛逼.jpeg"));
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buf)) != -1)
os.write(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println(cust);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(is != null)
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
if(os != null)
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
JDBCUtils.close(conn, stat, null);
}
}
当需要成批插入或者更新记录时,可以采用Java的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。通常情况下比单独提交处理更有效率。
JDBC 的批量处理语句包括下面 3 个方法:
addBatch(String) 添加需要批量处理的 SQL 语句或是参数executeBatch() 执行批量处理语句clearBatch() 清空缓存的数据通常我们会遇到 2 种批量执行 SQL 语句的情况:
执行如下演示代码前要做 2 处修改:
?rewriteBatchedStatements=true 在配置文件的url 后,让 MySQL 开启批处理的支持。此时的批量操作,主要指的是批量插入,使用预编译语句实现更高效的插入:
@Test
public void batchInsert() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 设置不允许自动提交数据
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "insert into goods(name) values(?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= 20000; i++) {
ps.setObject(1, "name_" + i);
// 1. "攒" SQL
ps.addBatch();
if (i % 500 == 0) {
// 2. 执行 batch
ps.executeBatch();
// 3. 清空 batch
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
// 提交数据
conn.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start)); // 2130, 662
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujiaqi1101/p/13356092.html