当SpringApplicationRunListeners初始化完毕后,接下来就是执行环境配置的初始化了,该初始化分为以下几个步骤。
CommandLineProperty即命令行参数,当启动时通过类似指定配置例如--server.port=8888的方式作为参数传递进来时,Spring对它是这么解析的:
# 这里的args就是--server.port=9090
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
# 实例化DefaultApplicationArguments对象
public DefaultApplicationArguments(String... args) {
Assert.notNull(args, "Args must not be null");
this.source = new Source(args);
this.args = args;
}
# 初始化Source
private static class Source extends SimpleCommandLinePropertySource {
Source(String[] args) {
super(args);
}
}
# 通过父类构造获取解析器解析该命令行参数
public class SimpleCommandLinePropertySource extends CommandLinePropertySource<CommandLineArgs> {
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String... args) {
super((new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser()).parse(args));
}
}
# 核心解析命令行参数方法
class SimpleCommandLineArgsParser {
SimpleCommandLineArgsParser() {}
public CommandLineArgs parse(String... args) {
CommandLineArgs commandLineArgs = new CommandLineArgs();
String[] var3 = args;
int var4 = args.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String arg = var3[var5];
if (arg.startsWith("--")) {
String optionText = arg.substring(2);
String optionValue = null;
int indexOfEqualsSign = optionText.indexOf(61);
String optionName;
if (indexOfEqualsSign > -1) {
optionName = optionText.substring(0, indexOfEqualsSign);
optionValue = optionText.substring(indexOfEqualsSign + 1);
} else {
optionName = optionText;
}
if (optionName.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid argument syntax: " + arg);
}
commandLineArgs.addOptionArg(optionName, optionValue);
} else {
commandLineArgs.addNonOptionArg(arg);
}
}
return commandLineArgs;
}
}
最终初始化完毕后得到这么一个对象,以下图示显示该对象以及初始化后的信息:
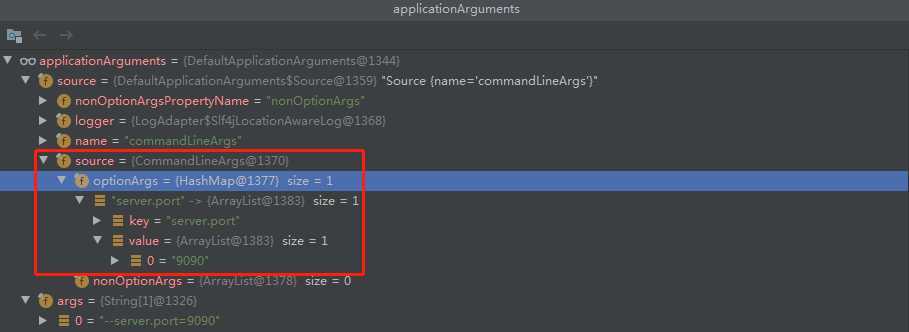
这个对象,将会在下面进行环境初始化时作为一个重要的参数。
调用prepareEnvironment方法查看源码:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
getOrCreateEnvironment获取默认环境
这里的getOrCreateEnvironment()由于在之前的SpringApplication初始化时已设置为SERVLET,所以该方法返回一个StandardServletEnvironment环境对象,以下是StandardServletEnvironment环境对象的类图:
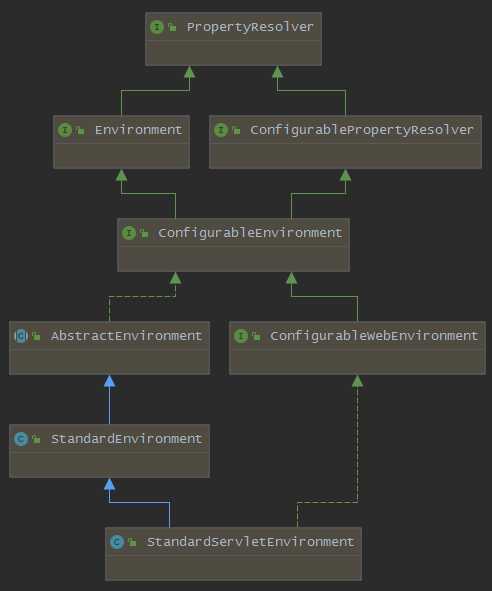
以下是对于该类图继承关系的说明:
configureEnvironment配置环境
基于web的环境对象获取到之后,会将该环境对象和命令行参数对象作为参数传入开始执行配置:
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
首先获取共享实例ApplicationConversionService,该实例用于提供应用程序的转换器和格式化程序,对于该实例的获取采用的是懒汉式的模式:
public static ConversionService getSharedInstance() {
ApplicationConversionService sharedInstance = ApplicationConversionService.sharedInstance;
if (sharedInstance == null) {
synchronized (ApplicationConversionService.class) {
sharedInstance = ApplicationConversionService.sharedInstance;
if (sharedInstance == null) {
sharedInstance = new ApplicationConversionService();
ApplicationConversionService.sharedInstance = sharedInstance;
}
}
}
return sharedInstance;
}
若该实例一开始就不存在,就会对它进行初始化,初始化工作主要是添加大量的格式转换器等,例如:
public static void configure(FormatterRegistry registry) {
DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(registry);
DefaultFormattingConversionService.addDefaultFormatters(registry);
addApplicationFormatters(registry);
addApplicationConverters(registry);
}
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeToCalendarConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}
......
将该格式转换器设置到StandardServletEnvironment中,后续其它初始化时通过环境对象拿出来。
其次,调用configurePropertySources方法配置属性源:
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(
new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
这里仅仅是将命令行参数添加到StandardServletEnvironment环境对象的propertySourceList集合中,若存在命令行参数的话,加入到propertySourceList也是为了后续的初始化,另外后面还会在该集合对象中加入其他的属性源配置。
最后就开始配置最常见见到的Profiles环境标识了:
configureProfiles(environment, args);
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
当启动应用时没有指定activeProfiles时,这里使用默认的profiles即default。
attachEnvironment连接环境
待续。。。
SpringBoot启动分析3:prepareEnvironment准备环境
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Json1208/p/13352752.html