pycharm编辑器搭建python3.*
第三方库
鸢尾花数据集是一个经典的机器学习数据集,非常适合用来入门。
鸢尾花数据集链接:下载鸢尾花数据集
鸢尾花数据集包含四个特征和一个标签。这四个特征确定了单株鸢尾花的下列植物学特征:
该表确定了鸢尾花品种,品种必须是下列任意一种:
数据集中三类鸢尾花各含有50个样本,共150各样本
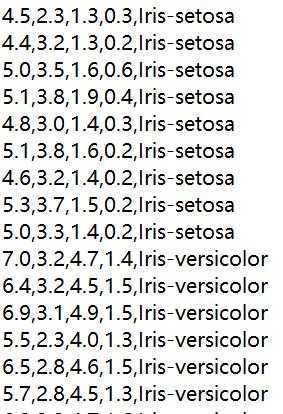
下面显示了数据集中的样本:
机器学习中,为了保证测试结果的准确性,一般会从数据集中抽取一部分数据专门留作测试,其余数据用于训练。所以我将数据集按7:3(训练集:测试集)的比例进行划分。
def dealIrisData(IrisDatapath):
"""
:param IrisDatapath:传入数据集路径
:return: 返回 训练特征集,测试特征集,训练标签集,测试标签集
"""
# 读取数据集
iris = pd.read_csv(IrisDatapath, header=None)
# 数据集转化成数组
iris = np.array(iris)
# 提取特征集
X = iris[:, 0:4]
# 提取标签集
Y = iris[:, 4]
# One-Hot编码
encoder = LabelEncoder()
Y = encoder.fit_transform(Y)
Y = np_utils.to_categorical(Y)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.3)
return x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test
??One-Hot编码,又称为一位有效编码,主要是采用N位状态寄存器来对N个状态进行编码,每个状态都由他独立的寄存器位,并且在任意时候只有一位有效。
??One-Hot编码是分类变量作为二进制向量的表示。这首先要求将分类值映射到整数值。然后,每个整数值被表示为二进制向量,除了整数的索引之外,它都是零值,它被标记为1。
??One-Hot编码是将类别变量转换为机器学习算法易于利用的一种形式的过程。
??比如:["山鸢尾","杂色鸢尾","维吉尼亚鸢尾"]---->[[1,0,0][0,1,0][0,0,1]]
??由于结构简单并没有建立隐藏层。
建立模型代码
def getIrisModel(saveModelPath,step):
"""
:param saveModelPath: 模型保存路径
:param step: 训练步数
:return: None
"""
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = dealIrisData("iris.data")
# 输入层
with tf.variable_scope("data"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,4])
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[None,3])
# placeholder()函数是在神经网络构建graph的时候在模型中的占位,此时并没有把要输入的数据传入模型,
# 它只会分配必要的内存。等建立session,在会话中,运行模型的时候通过feed_dict()函数向占位符喂入数据。
# 无隐藏层
# 输出层
with tf.variable_scope("fc_model"):
weight = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4,3],mean=0.0,stddev=1.0)) # 创建一个形状为[4,3],均值为0,方差为1的正态分布随机值变量
bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[3])) # 创建 张量为0,形状为3变量
y_predict = tf.matmul(x,weight)+bias # 矩阵相乘
# Variable()创建一个变量
# 误差
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict))
# 优化器
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# 准确率
with tf.variable_scope("acc"):
equal_list = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_true,1),tf.arg_max(y_predict,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32))
# 开始训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(step):
_train = sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train})
_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train})
print("训练%d步,准确率为%.2f" % (i + 1, _acc))
print("测试集的准确率为%.2f" %sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test}))
saver.save(sess, saveModelPath)
def predictIris(modelPath,data):
"""
:param modelPath: 载入模型路径
:param data: 预测数据
:return: None
"""
with tf.Session() as sess:
#
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model/iris_model.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess,"model/iris_model")
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name(‘data/x_pred‘).outputs[0]
y = tf.get_collection("pred_network")[0]
predict = np.argmax(sess.run(y,feed_dict={x:data}))
if predict == 0:
print("山鸢尾 Iris-Setosa")
elif predict == 1:
print("杂色鸢尾 Iris-versicolor")
else:
print("维吉尼亚鸢尾 Iris-virginica")
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.utils import np_utils
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1" # 不启动GPU
def dealIrisData(IrisDatapath):
"""
:param IrisDatapath:传入数据集路径
:return: 返回 训练特征集,测试特征集,训练标签集,测试标签集
"""
# 读取数据集
iris = pd.read_csv(IrisDatapath, header=None)
# 数据集转化成数组
iris = np.array(iris)
# 提取特征集
X = iris[:, 0:4]
# 提取标签集
Y = iris[:, 4]
# One-Hot编码
encoder = LabelEncoder()
Y = encoder.fit_transform(Y)
Y = np_utils.to_categorical(Y)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.3)
return x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test
def getIrisModel(saveModelPath,step):
"""
:param saveModelPath: 模型保存路径
:param step: 训练步数
:return: None
"""
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = dealIrisData("iris.data")
# 输入层
with tf.variable_scope("data"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,4],name=‘x_pred‘)
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[None,3])
# placeholder()函数是在神经网络构建graph的时候在模型中的占位,此时并没有把要输入的数据传入模型,
# 它只会分配必要的内存。等建立session,在会话中,运行模型的时候通过feed_dict()函数向占位符喂入数据。
# 无隐藏层
# 输出层
with tf.variable_scope("fc_model"):
weight = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4,3],mean=0.0,stddev=1.0)) # 创建一个形状为[4,3],均值为0,方差为1的正态分布随机值变量
bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[3])) # 创建 张量为0,形状为3变量
y_predict = tf.matmul(x,weight)+bias # 矩阵相乘
tf.add_to_collection(‘pred_network‘, y_predict) # 用于加载模型获取要预测的网络结构
# Variable()创建一个变量
# 误差
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict))
# 优化器
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# 准确率
with tf.variable_scope("acc"):
equal_list = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_true,1),tf.arg_max(y_predict,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32))
# 开始训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(step):
_train = sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train})
_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train})
print("训练%d步,准确率为%.2f" % (i + 1, _acc))
print("测试集的准确率为%.2f" %sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test}))
saver.save(sess, saveModelPath)
def predictIris(modelPath,data):
"""
:param modelPath: 载入模型路径
:param data: 预测数据
:return: None
"""
with tf.Session() as sess:
#
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model/iris_model.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess,"model/iris_model")
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name(‘data/x_pred‘).outputs[0]
y = tf.get_collection("pred_network")[0]
predict = np.argmax(sess.run(y,feed_dict={x:data}))
if predict == 0:
print("山鸢尾 Iris-Setosa")
elif predict == 1:
print("杂色鸢尾 Iris-versicolor")
else:
print("维吉尼亚鸢尾 Iris-virginica")
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
model_path = "model/iris_model"
# 模型训练
# model = getIrisModel(model_path,1000)
# 模型预测
# predictData = [[5.0,3.4,1.5,0.2]] # 填入数据集
# predictIris(model_path,predictData)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/lyhLive/p/13332178.html