时长:55min
主要是注解装饰功能的一个完善。提供条件注解装配,即@Conditional注解使用。
其实,它是对是否进行bean装配的一个条件限制,如果条件返回true,刚允许装配。否则,不允许。
下面通过示例代码来,说明条件装配的应用。
首先,创建一个springboot项目。然后创建配置类:
package com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * @ClassName SpringConfiguration * @Description 统一的配置类 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/7/6 18:09 * @Version 1.0 */ @Configuration public class SpringConfiguration { /** * 在某个环境下不装载 * 或不满足某个条件不装载 * 或者已经装载过了,不要重复装载 * @return */ @Conditional(MyCondition.class) @Bean public DemoService demoService(){ return new DemoService(); } }
说明:
配置类中,通过@Bean进行bean装配。然而加上@Conditional注解,就能实现条件装配。
@Conditional注解,传参为Condition接口子类Class对象,可以传参多个子类对象,多个对象之间是且的关系。
package com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; /** * @ClassName MyCondition * @Description 实现条件子类 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/7/6 18:14 * @Version 1.0 */ public class MyCondition implements Condition { @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) { //TODO 这里可以写对应的判断逻辑 return false; } }
说明:
子类中实现match方法,进行条件判断,如果返回false,则不允许bean装配。
package com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.condition; /** * @ClassName DemoService * @Description service bean类 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/7/6 18:10 * @Version 1.0 */ public class DemoService { }
package com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.condition; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; /** * @ClassName ConditionMain * @Description 测试类 * @Author wf * @Date 2020/7/6 18:17 * @Version 1.0 */ public class ConditionMain { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); DemoService bean = context.getBean(DemoService.class); System.out.println(bean); } }
测试结果如下:
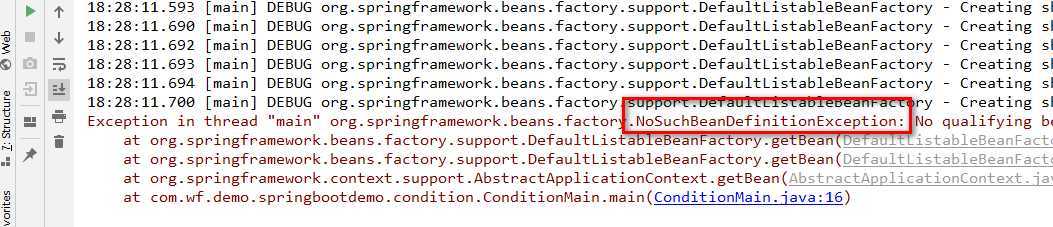
结果抛出异常,因为条件返回false,不允许装配。
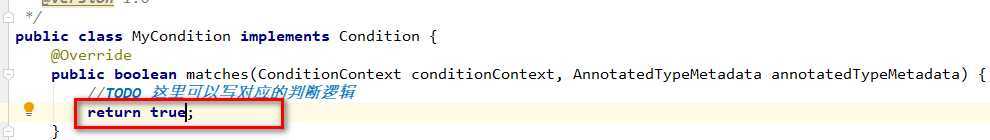
下面修改match方法,返回true,如下所示:
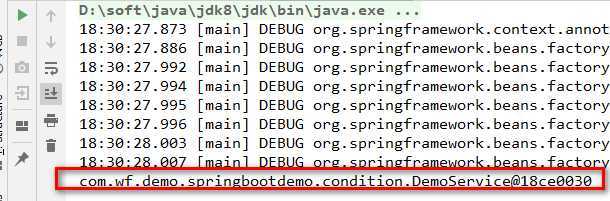
再次运行测试,成功装配,如下所示:
引入@Indexed注解。是用来提升性能的。当项目文件目录很多时,扫描@Component,@Service。。。这些注解时,
就会很耗时,而@Indexed注解,可以提升注解扫描的性能。
总结:
spring的注解驱动的发展,是为了bean装配更加简单。
下面通过springboot中整合redis来说明,注解驱动的简便性。
<!--整合redis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
版本由springboot-parent来管理。
在生产中会有专门的redis服务安装redis服务。而学习环境下,一般是在虚拟机上安装redis应用服务器。
package com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.web; import com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.dao.pojo.User; import com.wf.demo.springbootdemo.service.IUserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @ClassName HelloController * @Description 测试controller * @Author wf * @Date 2020/7/6 11:27 * @Version 1.0 */ @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate; //配置文件注入 // @Value("Mic") // private String name; @Autowired private IUserService userService; @GetMapping("hello") public String test(){ User user = new User(); user.setId(18); user.setName("MIc"); userService.insert(user); return "success"; } @GetMapping("/say") public String say(){ return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); } }
说明:
springboot已经为了我们使用redis封装了客户端工具类RedisTemplate。
只有使用它的api即可。
spring.redis.host=192.168.216.128
#redis.port=6379默认
只需要启动main,浏览器端访问controller接口即可。
说明:
我们可以看到,springboot整合redis是如此之简单。
这里RedisTemplate实例,能够直接引用,说明spring IOC容器中已经完成bean的装配。
但是,我们是没有做这部分工作的,而是由springboot进行了装配。
》xml配置
》@Configuration注解装配
》@Enable装配
现在,springboot提供了自动装配的功能。
自动装配的原理是什么?是如何实现的呢?
主要有两种:
ImportSelector:
Registator
所谓动态装载,即根据上下文,或某些条件去装载一些配置类。
下面通过代码示例,来说明springboot实现批量扫描配置类的原理。
所谓批量扫描,就是一次性扫描所有jar包中的配置类。示例代码中以分包的形式,来模拟不同jar包的扫描。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wfdespace/p/13256570.html