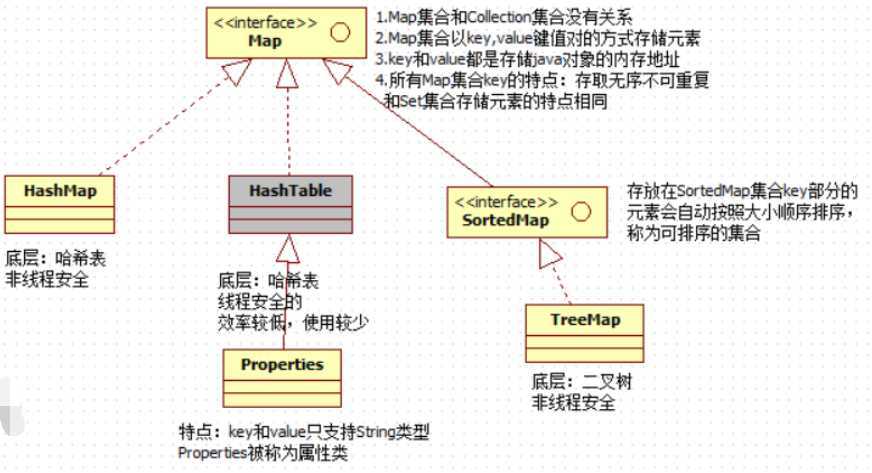
鉴于HashSet、TreeSet和Map集合中的HashMap、TreeMap关联,所以放在一起
主要内容:
1.TreeSet、TreeMap、比较器
2.HashSet、HashMap、哈希表
V put(K key, V value) 向集合中添加键值对
V get(Object key) 通过key 获取value
void clear() 清空Map集合
boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断Map中是否包含某个key
boolean containsValue(Object value) 判断Map中是否包含某个value
boolean isEmpty() 判断Map集合中元素个数是否为0
Set
Collection
V remove(Object key) 通过key删除键值对
int size() 获取Map集合这键值对的个数
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 将Map集合转换成Set集合
以及Map.Entry静态内部类中的实例方法:
K getKey() 获取key
V getValue() 获取value
Map集合通过entrySet()方法转换成成的这个Set集合,Set集合中元素的类型是Map.Entry(静态内部类)
例如:
HashMap<Integer,String> map1 = new HashMap<>;
key value
1 zhangsan
2 lisi
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> s = map1.entrySet();
则s集合对象如下:
1=zhangsan
2=lisi
public class MapTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Map对象
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"zhagnsan");
map.put(2,"lisi");
//通过key获取value
String value = map.get(2);
System.out.println(value);
//判断集合是否包含某个key
System.out.println(map.containsKey(1)); //true
//判断集合是否包含某个value
System.out.println(map.containsValue("lisi")); //true
//获取Map集合所有的key(所有的键是一个set集合)
Set<Integer> set = map.keySet();
for(Integer integer : set){
System.out.println(integer); // 1\n 2
}
//获取Map集合所有的value(所有的值是一个Collection集合)
Collection<String> collection = map.values();
for(String str : collection){
System.out.println(str);
}
//遍历Map的第一种方式 : KeySet + get方法来遍历键值对
for(Integer integer : set){
System.out.println(integer + "=" + map.get(integer));
}
//遍历Map的第二种方式 : Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
//推荐第二种方式,第二种方式的效率高
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> set1 = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> it2 = set1.iterator();
while(it2.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Integer, String> node = it2.next();
Integer key = node.getKey();
String value1 = node.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value1);
}
//foreach
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> node : set1){
Integer key = node.getKey();
String value1 = node.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value1);
}
}
}
可以通过以下程序类比:
public class StaticInClassTest {
//声明一个静态内部类
private static class InnerClass{
public static void m1(){
System.out.println("静态内部类的静态方法");
}
public void m2(){
System.out.println("静态内部类的实例方法");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StaticInClassTest.InnerClass mi = new StaticInClassTest.InnerClass();
mi.m2();
//Set集合中存储的StaticInClassTest.InnerClass类型
Set<StaticInClassTest.InnerClass> s = new HashSet<>();
}
}
部分源码:
// 在java.util.TreeMap中
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) { //比较器分支
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); //直接调用比较器的compare方法
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else { //Comparable接口分支
if (key == null)
//先强制类型转换之后,在调用compareTo方法
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
public class TreeMapTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Comparable接口的方式:
//如果没有实现接口Comparable,会报类型转换异常:java.lang.ClassCastException
TreeSet<Person> people = new TreeSet<>();
Person p1 = new Person("zs",20);
Person p2 = new Person("ls",12);
Person p3 = new Person("zd",20);
people.add(p1);
people.add(p2);
people.add(p3);
for(Person p : people){
System.out.println(p);
}
//===================================================
//Comparator接口,编写一个类的方式实现Comparator接口
//有参数构造方法:TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) 传递比较器
TreeSet<Person> people1 = new TreeSet<>(new PerSonComparator());
people1.add(p1);
people1.add(p2);
people1.add(p3);
for(Person p : people1){
System.out.println(p);
}
//=================================================
//Comparator接口,使用匿名内部类的语法实现Comparator接口
TreeSet<Person> people2 = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
});
}
}
//Comparable接口是java.lang下的
class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
String name;
int age;
public Person(){
}
public Person(String name, int age){
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
//compareTo方法的返回值
//返回值相同,value会覆盖,返回值>0,会在右子树上找
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
if(this.age == o.age){
return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
}else {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
‘}‘;
}
}
//编写类实现java.util.Comparator接口。
class PerSonComparator implements Comparator<Person>{
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if(o1.age == o2.age){
return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);
}else {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
}
}
HashMap集合底层是哈希表/散列表的数据结构
哈希表是一个数组和单向链表的结合体
-hashMap集合的默认初始化容量是16,默认加载因子是0.75(数组使用75%时就开始扩容)扩容为二倍
(重点)HashMap集合初始化容量必须是2的倍数,这是因为达到散列均匀,为了提高HashMap集合的存取效率所必需的
public class HashMap{
//HashMap底层实际上是一个数组
Node<K,V>[] table;
//静态内部类HashMap.Node
static class Node<K,V>{
final int hash; //哈希值
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; //next对象
}
}
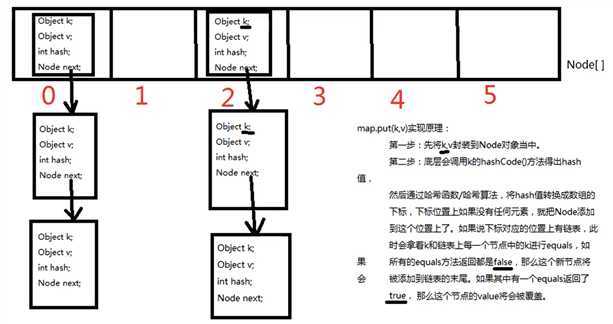
如果hashCode()方法返回值为某个固定值,会导致哈希表变成一个单向链表
如果hashCode()方法返回值均不相同,会导致哈希表变成一个一维数组
这些情况都称之为: 散列分布不均匀
要想实现散列分布均匀,需要重写hashCode()方法有一定的技巧
public class HashMapTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
}
}
class Usr {
private String name;
public Usr(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Usr)) return false;
Usr usr = (Usr) o;
return getName().equals(usr.getName());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getName());
}
}
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties pro = new Properties();
//需要掌握两个方法
pro.setProperty("a","ddddf");
pro.setProperty("b","dfbgdfd");
//通过key获取value
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("a"));
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("b"));
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zy200128/p/13027412.html