Throwable是Java中所有错误和异常的超类。它的下一级是Error和Exception
Error是指程序运行时系统的内部错误和资源耗尽错误。程序不会抛出该类对象。如果出现了Error,代表程序运行时JVM出现了重大问题,比如常见的OutOfMemoryError(OOM),这时应当告知用户并尽量让程序安全结束。
Exception是指程序可以自身处理的异常。Exception又分为检查异常(CheckedException)和运行异常(RuntimeException):
在Java中,异常处理机制主要是:抛出异常和捕获异常。
遇到异常不进行具体的处理,而是通过throw、throws继续抛给调用者。这两者有一定的区别:
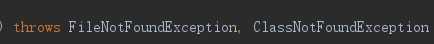
抛出异常后都是让调用者去接收并进行相关处理
通过try-catch语句在catch中捕获相关异常,并进行处理。try来捕获其中代码的异常,catch负责处理具体的异常。
try {
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("test.txt")));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("FileNotFoundException文件未找到异常。");
}
一旦try中捕获的异常进行catch块中,程序将不再执行try后面的语句,同时也不会再进入其他catch块中,所以在多个catch块中应该将更加底层的catch放在前面,当与finally同时使用时,catch块中执行结束会进入finally中
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
System.out.println("try1");
int i = 1/0;
System.out.println("try2");
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("ArithmeticException");
}catch (RuntimeException e){
System.out.println("RuntimeException");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception");
}finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
执行结果:
try1
ArithmeticException
finally
在实际开发中,通常在项目中封装一个自定义异常类BaseException来继承RuntimeException,业务异常可以继承BaseException。
public class BaseException extends RuntimeException {
public BaseException() {
super();
}
public BaseException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public BaseException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public BaseException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/homeSicker/p/12956629.html