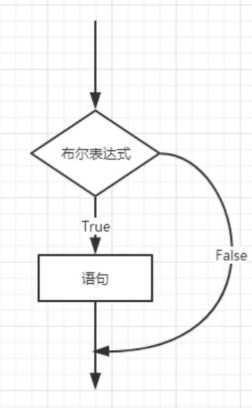
if(布尔值表达式){ //如果布尔表达式结果为true,将执行的语句 }
package com.steven.demo; import java.util.Scanner; public class IfDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String strScanner = scanner.nextLine(); if (strScanner.contains("Hello")){ System.out.println(strScanner); } System.out.println("End");
scanner.close(); } }
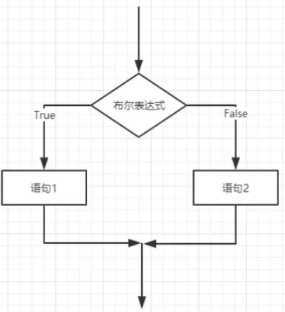
if(布尔表达式){
//如果布尔表达式的值为true
}else{
//如果布尔表达式的值为false
}
package com.steven.demo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double score = scanner.nextDouble();
if (score >= 60){
System.out.println("成绩及格");
}else{
System.out.println("成绩不及格");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
if(布尔表达式 1){ //如果布尔表达式 1的值为true执行代码 }else if(布尔表达式 2){ //如果布尔表达式 2的值为true执行代码 }else if(布尔表达式 3){ //如果布尔表达式 3的值为true执行代码 }else { //如果以上布尔表达式都不为true执行代码 }
public class Test { public static void main(String args[]){ int x = 30; if( x == 10 ){ System.out.print("Value of X is 10"); }else if( x == 20 ){ System.out.print("Value of X is 20"); }else if( x == 30 ){ System.out.print("Value of X is 30"); }else{ System.out.print("这是 else 语句"); } } }
4、嵌套的if结构
if(布尔表达式 1){ ////如果布尔表达式 1的值为true执行代码 if(布尔表达式 2){ ////如果布尔表达式 2的值为true执行代码 } }
public class Test { public static void main(String args[]){ int x = 30; int y = 10; if( x == 30 ){ if( y == 10 ){ System.out.print("X = 30 and Y = 10"); } } } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/stevenx/p/12952862.html