
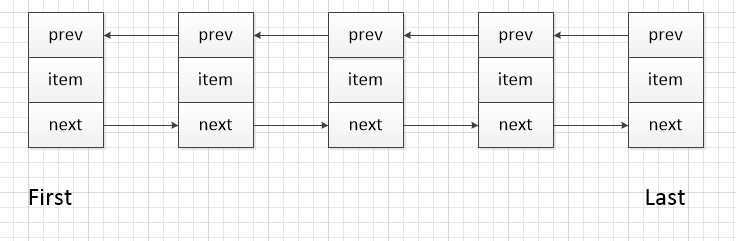
//关于Node构造函数 private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
//transient 保证以下几个属性不被序列化 /** * The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>. * 该字段表示list结构上被修改的次数。结构上的修改指的是那些改变了list的长度 * 大小或者使得遍历过程中产生不正确的结果的其它方式。 * */ protected transient int modCount = 0; transient int size = 0; /** * Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */ transient Node<E> first; /** * Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */ transient Node<E> last;
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } /** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
LinkedList的删除中,会根据传递进来的参数进行null判断,因为在LinkedList的元素移除中,null和非null的处理不一样,对于nul使用==去判断是否匹配,对于非null使用.equals(Object o)去判断,至于==和equals的区别,读者自行百度。
E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } private void checkElementIndex(int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size; } Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dsxie/p/12945384.html