1、设计四个类,分别是:(知识点:抽象类及抽象方法)
(1)Shape表示图形类,有面积属性area、周长属性per,颜色属性color,有两个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为颜色赋值的),还有3个抽象方法,分别是:getArea计算面积、getPer计算周长、showAll输出所有信息,还有一个求颜色的方法getColor。
(2)2个子类:
1)Rectangle表示矩形类,增加两个属性,Width表示长度、height表示宽度,重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,另外又增加一个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为高度、宽度、颜色赋值的)。
2)Circle表示圆类,增加1个属性,radius表示半径,重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,另外又增加两个构造方法(为半径、颜色赋值的)。
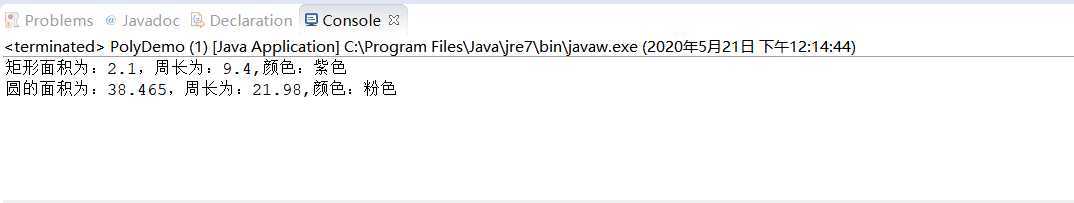
(3)一个测试类PolyDemo,在main方法中,声明创建每个子类的对象,并调用2个子类的showAll方法。
package practice10.Shape;
public abstract class Shape {
protected double area;
protected double per;
protected String color;
public Shape() {
}
public Shape(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public abstract void getArea();
public abstract void getPer();
public abstract void showAll();
}
package practice10.Shape;
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
double width;
double height;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double width, double height, String color) {
super();
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.color = color;
}
public void getArea() {
area = width * height;
}
public void getPer() {
per = (width + height) * 2;
}
public void showAll() {
System.out.println("矩形面积为:" + area + ",周长为:" + per+",颜色:"+color);
}
}
package practice10.Shape;
public class Circle extends Shape {
double radius;
double pai = 3.14;
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(double radius, String color) {
this.color = color;
this.radius = radius;
}
public void getArea() {
area = radius * radius * pai;
}
public void getPer() {
per = 2 * radius * pai;
}
public void showAll() {
System.out.println("圆的面积为:" + area + ",周长为:" + per+",颜色:"+color);
}
}
package practice10.Shape;
public class PolyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(4.2,0.5,"紫色");
rectangle.getArea();
rectangle.getPer();
rectangle.showAll();
Circle circle = new Circle(3.5,"粉色");
circle.getArea();
circle.getPer();
circle.showAll();
}
}
2、Cola公司的雇员分为以下若干类:(知识点:多态)
(1) ColaEmployee :这是所有员工总的父类,属性:员工的姓名,员工的生日月份。
(2) SalariedEmployee : ColaEmployee 的子类,拿固定工资的员工。
(3) HourlyEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,按小时拿工资的员工,每月工作超出160 小时的部分按照1.5 倍工资发放。
(4) SalesEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,销售人员,工资由月销售额和提成率决定。
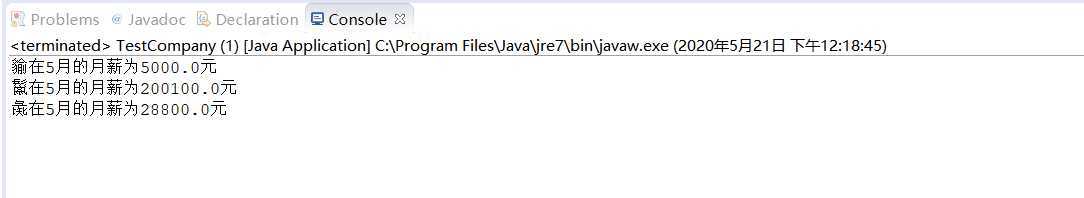
(5) 定义一个类Company,在该类中写一个方法,调用该方法可以打印出某月某个员工的工资数额,写一个测试类TestCompany,在main方法,把若干各种类型的员工放在一个ColaEmployee 数组里,并单元出数组中每个员工当月的工资。
package practice10.Cola;
public class ColaEmployee {
String name;
int month;
public ColaEmployee() {
}
public ColaEmployee(String name, int month) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.month = month;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
return 0;
}
}
package practice10.Cola;
public class SalarriedEmloyee extends ColaEmployee {
double salary;
public SalarriedEmloyee() {
super();
}
public SalarriedEmloyee(String name, int month,int salary) {
super(name,month);
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
if (super.month == month) {
return salary + 100;
}else {
return salary;
}
}
}
package practice10.Cola;
public class HourlyEmployee extends ColaEmployee {
private int hourlysalary;
private int hourlytime;
public HourlyEmployee() {
super();
}
public HourlyEmployee(String name, int month,int hourlytime,int hourlysalary) {
super(name, month);
this.hourlytime = hourlytime;
this.hourlysalary = hourlysalary;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
if (super.month == month) {
if (hourlytime > 160) {
return hourlysalary * 160 + hourlysalary * (hourlytime - 160) * 1.5 + 100;
} else {
return hourlysalary * hourlytime + 100;
}
} else {
if (hourlytime > 160) {
return hourlysalary * 160 + hourlysalary * (hourlytime - 160) * 1.5;
} else {
return hourlysalary * hourlytime;
}
}
}
}
package practice10.Cola;
public class SalesEmployee extends ColaEmployee {
private int monthSales;
private double royaltyRate;
public SalesEmployee(String name, int month, int monthSales, double royaltyRate) {
super(name, month);
this.monthSales = monthSales;
this.royaltyRate = royaltyRate;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
if (super.month == month) {
return monthSales * royaltyRate + 100;
} else {
return monthSales * royaltyRate;
}
}
}
package practice10.Cola;
public class Company {
public void getSalary(ColaEmployee c,int month) {
System.out.println(c.name + "在" + month + "月的月薪为" + c.getSalary(month)+"元");
}
}
package practice10.Cola;
public class TestCompany {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ColaEmployee[] all = {
new SalarriedEmloyee("貐", 9, 5000),
new HourlyEmployee("鬣", 8, 4500, 30),
new SalesEmployee("彘", 2, 36000, 0.8)
};
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
new Company().getSalary(all[i],5);
}
}
}
3、利用接口实现动态的创建对象:(知识点:接口 )
(1)创建4个类
1苹果
2香蕉
3葡萄
4园丁
(2)在三种水果的构造方法中打印一句话.
以苹果类为例
class apple
{
public apple()
{
System.out.println(“创建了一个苹果类的对象”);
}
}
(3)类图如下:
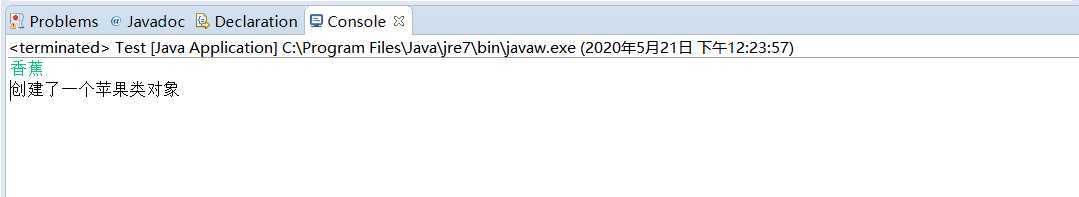
(4)要求从控制台输入一个字符串,根据字符串的值来判断创建三种水果中哪个类的对象。
运行结果如图:
package practice10.Fruit;
public interface Fruit {
}
package practice10.Fruit;
public class Apple implements Fruit {
public Apple() {
System.out.println("创建了一个苹果类对象");
}
}
package practice10.Fruit;
public class Banana implements Fruit {
public Banana() {
System.out.println("创建了一个苹果类对象");
}
}
package practice10.Fruit;
public class Grape {
public Grape() {
System.out.println("创建了一个葡萄类对象");
}
}
package practice10.Fruit;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Gardener {
public void creater() {
String s = "";
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
s = input.nextLine();
if (s.equals("苹果")) {
new Apple();
} else if (s.equals("香蕉")) {
new Banana();
} else if (s.equals("葡萄")) {
new Grape();
} else {
System.out.println("请输入正确的对象");
}
}
}
package practice10.Fruit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new Gardener().creater();
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wu-di-821-821/p/12929931.html