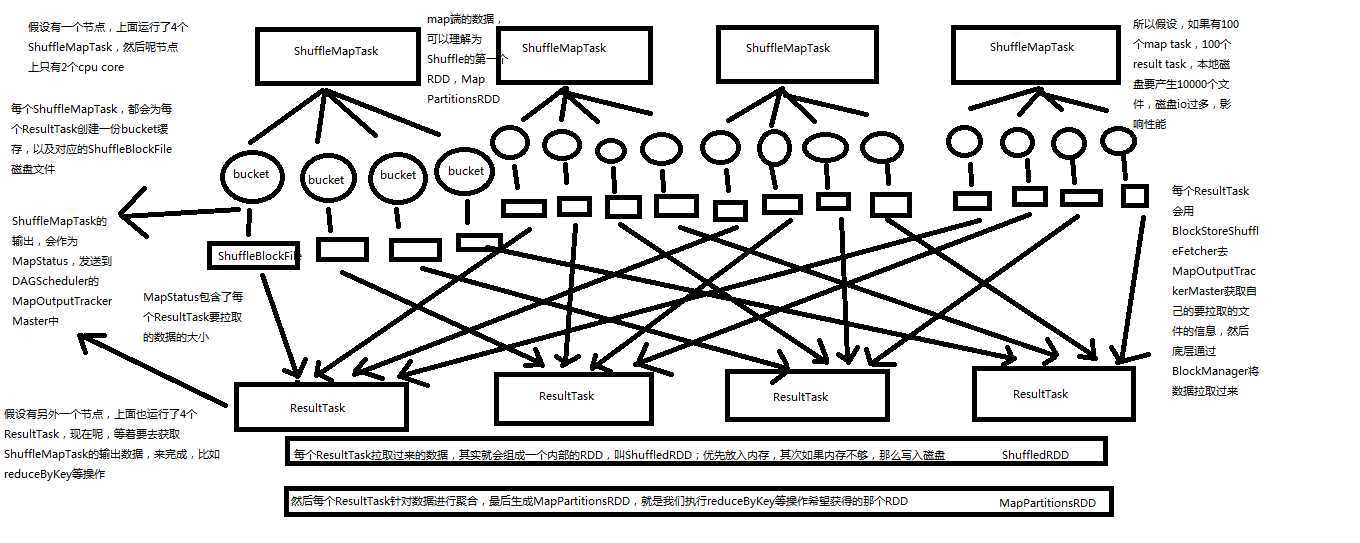
shuffle原理图如下
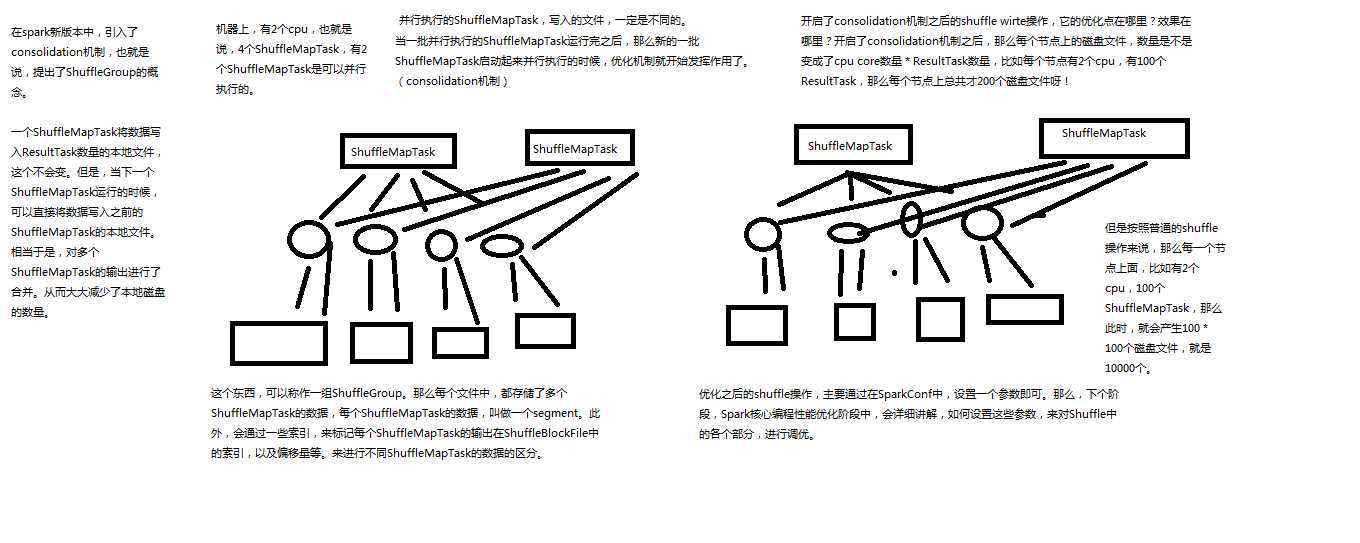
优化后也就是加入consolidation机制后的原理图如下,主要解决产生的文件太多
在executor中执行任务时,主要是task的实现类来执行任务,其中shuffleMapTask,将针对rdd执行算子后的结果写入磁盘
// 有mapstatus返回值, override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = { // Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable. // 对要处理的rdd相关数据,做一些反序列化的,这个rdd是怎么拿到的,多个task运行在executor里面,并行运行或者并发运行 // 可能不在一个地方,但是一个stage的task,要处理的rdd都是一样的,通过broadcast variable拿到 val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])]( ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) metrics = Some(context.taskMetrics) var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null try { // 获取shuffleManager val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context) // 调用rdd的iterator方法,并且传入当前task要处理哪个partition,核心逻辑就在rdd的iterator // 方法中在这里实现了针对某个partition执行算子和函数,针对rdd的partition进行处理,有返回数据通过shuffleWriter经过 // HashPartition写入自己的分区,mapstatus封装了shufflemaptask计算后的数据,存储在那里,就是blockmanager信息 // blockmanager就是spark底层内存、数据、磁盘管理组件 writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]]) return writer.stop(success = true).get } catch { case e: Exception => try { if (writer != null) { writer.stop(success = false) } } catch { case e: Exception => log.debug("Could not stop writer", e) } throw e } }
shuffle写的入口再HashShuffleWriter里面
/** Write a bunch of records to this task‘s output * 将每个shuffleMapTask计算出来的新的RDD的partition数据,写入磁盘 * */ override def write(records: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, V]]): Unit = { // 首先判断,是否需要在map端本地进行聚合,这里的话,如果是reduceBykey这种操作,它的dep.aggregator.isDefined就是true // 包括dep.mapSideCombine也是true // 那么就就进行map端的本地聚合 val iter = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) { if (dep.mapSideCombine) { // 执行本地聚合,如(hello,1)(hello,1)就成了(hello,2) dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(records, context) } else { records } // } else { require(!dep.mapSideCombine, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!") records } // 如果要本地聚合,那么先本地聚合,然后遍历数据,对每个数据掉用partitioner // ,默认是hashPartitioner,生成bucketId,也就是决定每一份数据要写入那个bucket。 // 调用shuffleBlockManager.forMapTask()方法,来生成bucketid对应的writer,然后调用Writer将数据写入bucket for (elem <- iter) { val bucketId = dep.partitioner.getPartition(elem._1) shuffle.writers(bucketId).write(elem) } }
FileShuffleBlockManager
def forMapTask(shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int, numBuckets: Int, serializer: Serializer, writeMetrics: ShuffleWriteMetrics) = { new ShuffleWriterGroup { shuffleStates.putIfAbsent(shuffleId, new ShuffleState(numBuckets)) private val shuffleState = shuffleStates(shuffleId) private var fileGroup: ShuffleFileGroup = null // 对应之前的shuffle有两种shuffle方式,就是是否开启consolidateShuffleFiles,如 // 果开启了就不会为每个bucket获取独立文件,为这个bucket获取一个shuffleGroup的writer val writers: Array[BlockObjectWriter] = if (consolidateShuffleFiles) { fileGroup = getUnusedFileGroup() Array.tabulate[BlockObjectWriter](numBuckets) { bucketId => // 首先根据shuffleId,mapId,bucketId,生成一个唯一的ShuffleBlockId,然后调用bucketId, // 来调用ShuffleGroupD的Apply函数,为bucket获取一个shuffleGroup, val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, bucketId) // 然后调用BlockManager的getDiskWriter方法,针对ShuffleFileGroup获取一个Writer,这样的话我们就清除了, // 如果开启了consolidation机制,实际上对于每一个bucket,都会获取一个针对shuffleFileGroup的writer, // 而不是一个独立的shuffleBlockFile的writer,实现了多个shuffleMapTask的输出合并 blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, fileGroup(bucketId), serializer, bufferSize, writeMetrics) } } else { // 普通shuffle操作,就是先生存一个shuffleBlockId,然后调用BlockManager // 的DiskBlockManager,获取一个代表了要写入本地文件的blockFile Array.tabulate[BlockObjectWriter](numBuckets) { bucketId => val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, bucketId) val blockFile = blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile(blockId) // Because of previous failures, the shuffle file may already exist on this machine. // If so, remove it. if (blockFile.exists) { if (blockFile.delete()) { logInfo(s"Removed existing shuffle file $blockFile") } else { logWarning(s"Failed to remove existing shuffle file $blockFile") } } // 然后针对这个blockFile采用blockManager调用getDiskWriter生成一个writer,所以普通的shuffle针对每一个shuffleMapTask // 输出的一个bucket都会再本地生成一个blockFile blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, blockFile, serializer, bufferSize, writeMetrics) } }
shuffle的读的入口,shuffleRdd的compute方法
override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[(K, C)] = { /** * ResultTask或者ShuffleMapTask,在执行shuffleRDD时,肯定会调用shuffleRdd的compute方法 * 来计算当前这个RDD的partition的数据,Task原理剖析的时候,已经结合TaskRunner,深度剖析过相关源码 * 这里会调用shuffleFileManager的getReader方法,获取一个HashShuffleReader然后调用它的read方法 * 拉取该ResultTask/ShuffleMapTask,需要聚合的数据 */ val dep = dependencies.head.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]] SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(dep.shuffleHandle, split.index, split.index + 1, context) .read() .asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]] }
HashShuffleReader中的read方法
/** Read the combined key-values for this reduce task */
override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = {
val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer)
val iter = BlockStoreShuffleFetcher.fetch(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, context, ser)
val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(iter, context))
} else {
new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(iter, context))
}
} else {
require(!dep.mapSideCombine, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
// Convert the Product2s to pairs since this is what downstream RDDs currently expect
iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]].map(pair => (pair._1, pair._2))
}
// Sort the output if there is a sort ordering defined.
dep.keyOrdering match {
case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) =>
// Create an ExternalSorter to sort the data. Note that if spark.shuffle.spill is disabled,
// the ExternalSorter won‘t spill to disk.
val sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](ordering = Some(keyOrd), serializer = Some(ser))
sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter)
context.taskMetrics.incMemoryBytesSpilled(sorter.memoryBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics.incDiskBytesSpilled(sorter.diskBytesSpilled)
sorter.iterator
case None =>
aggregatedIter
}
}
/** Read the combined key-values for this reduce task */ override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = { val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer) val iter = BlockStoreShuffleFetcher.fetch(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, context, ser) val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) { if (dep.mapSideCombine) { new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(iter, context)) } else { new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(iter, context)) } } else { require(!dep.mapSideCombine, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!") // Convert the Product2s to pairs since this is what downstream RDDs currently expect iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]].map(pair => (pair._1, pair._2)) } // Sort the output if there is a sort ordering defined. dep.keyOrdering match { case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) => // Create an ExternalSorter to sort the data. Note that if spark.shuffle.spill is disabled, // the ExternalSorter won‘t spill to disk. val sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](ordering = Some(keyOrd), serializer = Some(ser)) sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter) context.taskMetrics.incMemoryBytesSpilled(sorter.memoryBytesSpilled) context.taskMetrics.incDiskBytesSpilled(sorter.diskBytesSpilled) sorter.iterator case None => aggregatedIter } }
def fetch[T]( shuffleId: Int, reduceId: Int, context: TaskContext, serializer: Serializer) : Iterator[T] = { logDebug("Fetching outputs for shuffle %d, reduce %d".format(shuffleId, reduceId)) val blockManager = SparkEnv.get.blockManager val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis // 复制一份全局的MapOutputTrackerMaster的引用,然后调用其方法getServerStatuses,通过shuffleId, // reduceId,shuffleId可以代表当前这个stage的上一个stage,shuffle write发生在上一个stage,shuffle read // 发生在当前stage,首先通过shuffleId可以限制到上一个stage的所有ShuffleMapTask的输出MapStatus,接着通过reduceId // 也就是bucketId,来限制每个mapstatus中获取当前这个ResultTask需要获取的每个shuffleMapTask的输出信息 // getServerStatuses一定是要走网络通信的,因为要联系Driver上电DAGScheduler的MapOutputTrackerMaster val statuses = SparkEnv.get.mapOutputTracker.getServerStatuses(shuffleId, reduceId) logDebug("Fetching map output location for shuffle %d, reduce %d took %d ms".format( shuffleId, reduceId, System.currentTimeMillis - startTime)) // 对拉取到的数据进行一些格式上的转换 val splitsByAddress = new HashMap[BlockManagerId, ArrayBuffer[(Int, Long)]] for (((address, size), index) <- statuses.zipWithIndex) { splitsByAddress.getOrElseUpdate(address, ArrayBuffer()) += ((index, size)) } val blocksByAddress: Seq[(BlockManagerId, Seq[(BlockId, Long)])] = splitsByAddress.toSeq.map { case (address, splits) => (address, splits.map(s => (ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, s._1, reduceId), s._2))) } def unpackBlock(blockPair: (BlockId, Try[Iterator[Any]])) : Iterator[T] = { val blockId = blockPair._1 val blockOption = blockPair._2 blockOption match { case Success(block) => { block.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]] } case Failure(e) => { blockId match { case ShuffleBlockId(shufId, mapId, _) => val address = statuses(mapId.toInt)._1 throw new FetchFailedException(address, shufId.toInt, mapId.toInt, reduceId, e) case _ => throw new SparkException( "Failed to get block " + blockId + ", which is not a shuffle block", e) } } } } // ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator 构造以后,在其内部就直接根据拉取到的地理位置信息, // 通过BlockManager,去远程的ShuffleMapTask所在节点的blockMananger拉取数据 val blockFetcherItr = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator( context, SparkEnv.get.blockManager.shuffleClient, blockManager, blocksByAddress, serializer, SparkEnv.get.conf.getLong("spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight", 48) * 1024 * 1024) val itr = blockFetcherItr.flatMap(unpackBlock) // 将拉取到的数据进行封装 val completionIter = CompletionIterator[T, Iterator[T]](itr, { context.taskMetrics.updateShuffleReadMetrics() }) new InterruptibleIterator[T](context, completionIter) { val readMetrics = context.taskMetrics.createShuffleReadMetricsForDependency() override def next(): T = { readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1) delegate.next() } } }
ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator
// 切分本地和远程的block,切分完后就随机排序,发现还有数据就去远程拉取数据, // maxBytesInFlight定义拉取最多多少数据就必须要进行自定义的reduce计算 private[this] def initialize(): Unit = { // Add a task completion callback (called in both success case and failure case) to cleanup. context.addTaskCompletionListener(_ => cleanup()) // Split local and remote blocks. val remoteRequests = splitLocalRemoteBlocks() // Add the remote requests into our queue in a random order fetchRequests ++= Utils.randomize(remoteRequests) // Send out initial requests for blocks, up to our maxBytesInFlight while (fetchRequests.nonEmpty && (bytesInFlight == 0 || bytesInFlight + fetchRequests.front.size <= maxBytesInFlight)) { // 发送请求去获取远程数据 sendRequest(fetchRequests.dequeue()) } val numFetches = remoteRequests.size - fetchRequests.size logInfo("Started " + numFetches + " remote fetches in" + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime)) // Get Local Blocks,获取本地数据 fetchLocalBlocks() logDebug("Got local blocks in " + Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTime)) }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaofeiyang/p/12913305.html