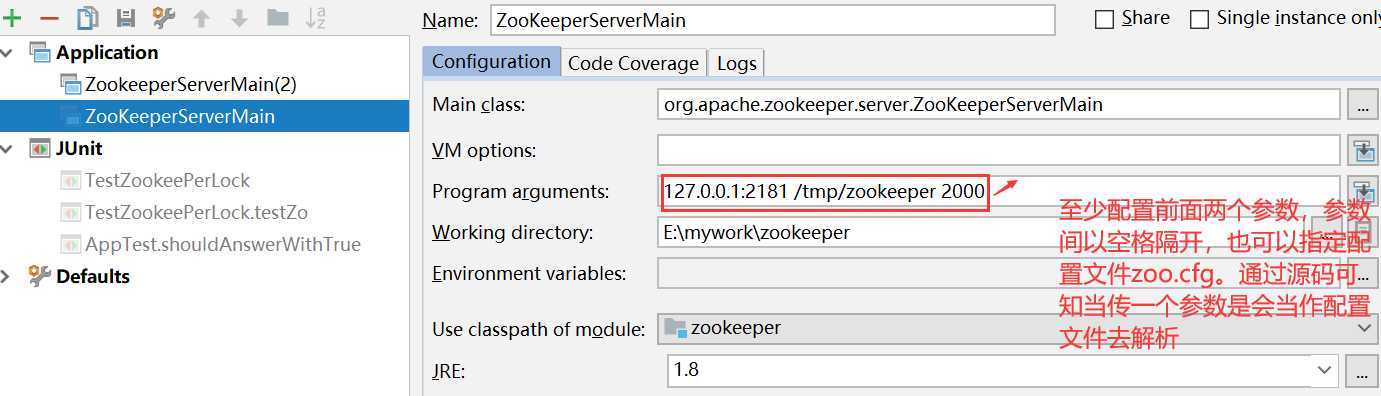
基本思路是:通过每个连接创建 临时节点(避免宕机后节点不释放)后规定节点最小的拥有获取锁的权利,那么其他的就拿不到了,但是每个节点都对前一个节点建立delete的watch机制。那么每次前一个节点释放锁(delete)触发watch 后一个节点就能获取锁 本地启动zkServer:
package xyz.luofu.www;
import org.apache.zookeeper.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class TestZookeePerLock {
private String seqNodeNamePar = "/Order"; //这个节点先建好 create /Order
private ThreadLocal<String> currentNodeNameThr = new ThreadLocal<>();
private ThreadLocal<ZooKeeper> zk = new ThreadLocal<>();
public boolean tryLock() {
try {
String seqNodeName = "/sq";
zk.set(new ZooKeeper("localhost:2181", 3000, new Watcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
}
}));
//Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,这就表明之后对这个节点的任何操作都不受权限控制
currentNodeNameThr.set(zk.get().create(seqNodeNamePar + seqNodeName, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL));
List<String> children = zk.get().getChildren(seqNodeNamePar, false);
Collections.sort(children);
String currentNodeNameStr = currentNodeNameThr.get().substring(currentNodeNameThr.get().lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
int index = children.indexOf(currentNodeNameStr);
String preNodeName = "";
if(index != 0){
preNodeName = children.get(index - 1);
}
String first = children.get(0);
if (currentNodeNameStr.equals(first)) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁成功");
return true;
} else {
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
zk.get().exists(seqNodeNamePar + "/" + preNodeName, new Watcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
if (Event.EventType.NodeDeleted == event.getType()) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"重新获得锁成功");
}
}
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"等待锁");
countDownLatch.await();
return true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
public void unlock(){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);//避免还没建立监听这个节点就已delete。那么后面建立的delete watch 就触发不了了。
zk.get().delete(currentNodeNameThr.get(),-1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeeperException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"释放锁成功");
}
class TestZoo implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
new Order().create();
tryLock();
boolean flag = new Store().descStore();
unlock();
if(flag){
new Pay().doPay();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"支付成功");
}
}
}
@Test
public void testZo() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(new TestZoo(),"线程一").start();
new Thread(new TestZoo(),"线程二").start();
int count = Thread.activeCount();
while(count > 2){
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println("主线程结束");
}
}
public class Order {
public void create(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"创建订单");
}
}
public class Pay {
public void doPay(){
}
}
public class Store {
public int count =1;
public boolean descStore(){
if(count > 0){
count--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"减库存成功 count:"+count);
return true;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"减库存失败");
return false;
}
}
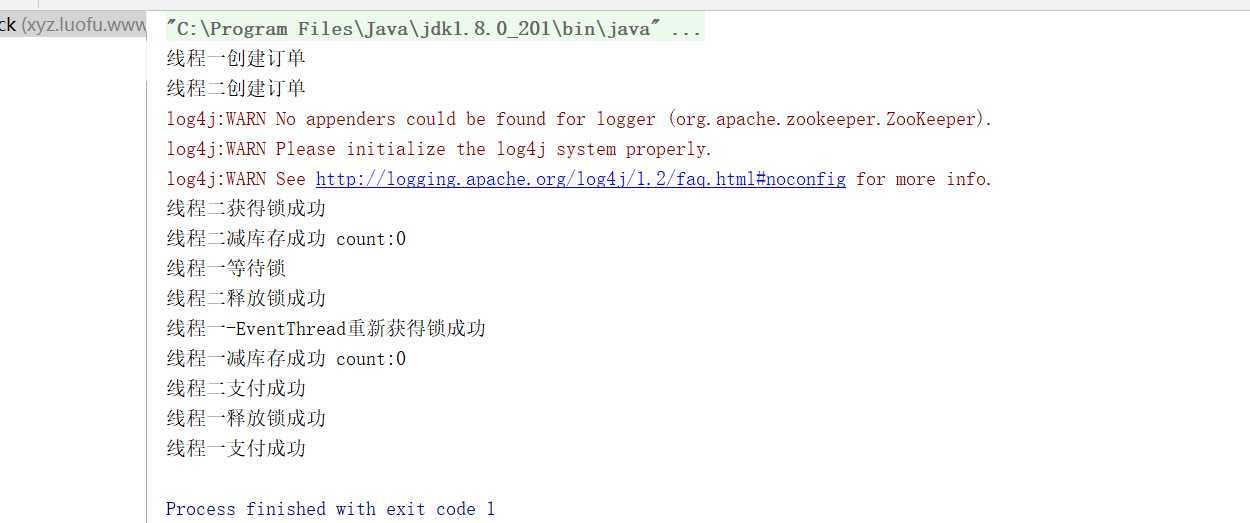
运行截图:
对于分布式配置中心,也是结合watch机制,加cache。每次新增zk.create并且加入cache其他操作类似。初始化时加载配置节点/config下的所有节点进入cache,并且设置对数据操作的watch相应的操作缓存。然后其他服务只需从cache中读取数据。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/leifonlyone/p/12851534.html