本篇文章是对C++学习过程中,关于字符串这节部分的内容进行整理,本篇主要讲解以字符数组形式存储的字符串概念,及其相关函数。C++标准库提供了兼容C语言的字符串处理函数,其头文件为 string.h 或者使用 cstring。
用来存放字符型数据的数组成为字符数组,其元素是一个个的字符。
字符数组的定义形式为:
char 字符数组名[常量表达式],......; 例如: char s[20]; // 定义字符数组 char s[4] = {‘J‘, ‘a‘, ‘v‘, ‘a‘}; // 字符数组初始化
区分“a” 和 ‘a’
char c; char s[10] = "hello"; c = ‘a‘; // 正确 c = "a"; // 错误
C++语言总是在编译时为字符串常量自动在其后增加一个空字符,例如"Hello"的存储形式为:

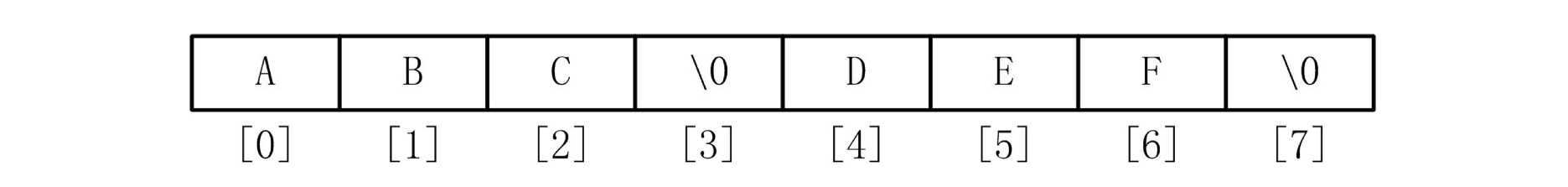
如果在字符串常量中插入空字符,则字符串常量的长度会比看到的字符数目少,例如"ABC\0DEF"的存储形式为:
(1)使用标准输入输出流,将整个字符串一次输入或输出
char str[80]; cin >> str; // 输入字符串 cout << str; // 输出字符串
(2)使用字符串输入输出函数
/* gets函数 */ char *gets(char *s); // 函数原型 char str[80]; gets(str); // 输入字符串
gets函数输入一个字符串到字符数组s中。s是字符数组或指向字符数组的指针,其长度应该足够大,以便能容纳输入的字符串。
/* puts函数 */ int puts(char *s); // 函数原型 char str[80] = "Programming"; puts(str); // 输出字符串
puts函数输出s字符串,遇到空字符结束,输出完后再输出一个换行(’\n’)。s是字符数组或指向字符数组的指针,返回值表示输出字符的个数。输出字符不包括空字符。
(1)字符串复制函数strcpy char str1[10], str2[] = "Computer"; strcpy(str1, str2); // 复制str2到str1 (2)字符串复制函数strncpy char str1[10], str2[] = "Computer"; strcpy(str1, str2, 4); // 复制str2的前4个字符到str1 (3)字符串连接函数strcat char str1[10] = "ABC", str2[] = "123"; strcat(str1, str2); // 在str1后面连接str2,str2未变化 (4)字符串连接函数strncat char str1[10] = "ABC", str2[] = "123"; strcat(str1, str2, 4); // 将str2前4个字符连接到str1后面 (5)字符串比较函数strcmp if (strcmp(str1, str2) == 0) // 比较字符串相等 ...... if (strcmp(str1, str2) >0) // str1大于str2,根据字典顺序比较,如aac > aab, a < aa ...... (6)计算字符串长度函数strlen n = strlen("Language"); // n = 8 char str[20] = "Visual Basic"; n = strlen(str); // n = 12 (7)字符串转换成数值函数 f = atof("123.456"); // f = 123.456 i = atoi("-456"); // i = -456
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/MK-XIAOYU/p/12796525.html