
String getName() 返回此线程的名称。
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1 ; i<100 ; i++){ //String getName() 返回此线程的名称。 System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt1 = new MyThread(); MyThread mt2 = new MyThread(); mt1.start(); mt2.start(); }
在未设置线程名字情况下,线程的默认名字:
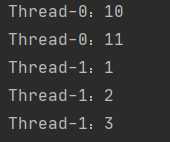
void setName(String name) 将此线程的名称更改为等于参数 name 。
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1 ; i<100 ; i++){ //String getName() 返回此线程的名称。 System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt1 = new MyThread(); MyThread mt2 = new MyThread(); //void setName(String name) 将此线程的名称更改为等于参数 name 。 mt1.setName("This is Thread_1"); mt2.setName("This is Thread_2"); mt1.start(); mt2.start(); }
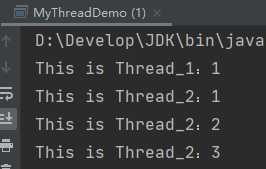
通过构造方法来设置线程名称,需要注意的是,要在线程类中定义构造方法。
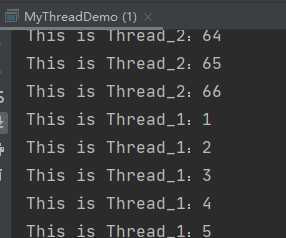
public class MyThread extends Thread { //定义无参构造方法 public MyThread() {} //定义带参构造方法 public MyThread(String name){ super(name); } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1 ; i<100 ; i++){ //String getName() 返回此线程的名称。 System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt1 = new MyThread("This is Thread_1"); MyThread mt2 = new MyThread("This is Thread_2"); mt1.start(); mt2.start(); }
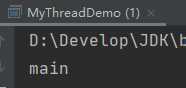
static Thread currentThread() 返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用。
public class MyThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //static Thread currentThread() 返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用。 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/pxy-1999/p/12788029.html