(1)增加样本量
(2)如果数据稀疏,使用L1正则,其他情况,用L2要好,可自己尝试。
(3)通过特征选择,剔除一些不重要的特征,从而降低模型复杂度。
(4)如果还过拟合,那就看看是否使用了过度复杂的特征构造工程,比如,某两个特征相乘/除/加等方式构造的特征,不要这样做了,保持原特征
(5)检查业务逻辑,判断特征有效性,是否在用结果预测结果等。
(6)逻辑回归特有的防止过拟合方法:进行离散化处理,所有特征都离散化。
正则化:
2.用logiftic回归来进行实践操作,数据不限。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
def logistic():
#加载数据集
names = [‘Sample code number‘,‘ Clump Thickness‘,‘Uniformity of Cell Size‘,‘Uniformity of Cell Shape‘,
‘Marginal Adhesion‘,‘Single Epithelial Cell Size‘,‘Bare Nuclei‘,‘Bland Chromatin‘,
‘Normal Nucleoli‘,‘Mitoses‘,‘Class‘]
data = pd.read_csv(‘breast-cancer-wisconsin_4.csv‘,names=names)
#数据集预处理,缺失值删除
data = data.replace(to_replace=‘?‘,value=np.nan)
data = data.dropna()
#进行数据的分割
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(data.loc[:,‘Sample code number‘:‘Mitoses‘],
data.loc[:,‘Class‘],test_size=0.25)
#特征值的标准化
std = StandardScaler()
x_train = std.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std.transform(x_test)
#使用逻辑回归进行预测
lr = LogisticRegression(C=1.0)
lr.fit(x_train,y_train)
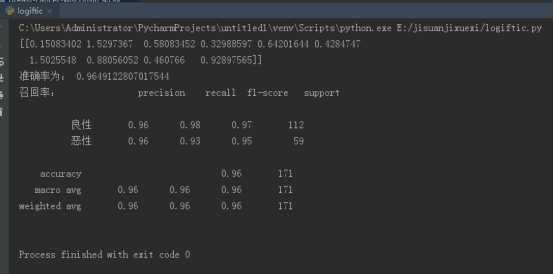
print(lr.coef_)
y_predict = lr.predict(x_test)
print("准确率为:",lr.score(x_test,y_test))
print("召回率:",classification_report(y_test,y_predict,labels=[2,4],target_names=["良性","恶性"]))
# print(x_train)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
logistic()
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/pangminhua/p/12784672.html