一.主题式网络爬虫设计方案
1.爬虫名称:爬取2020搜狗热搜电影
2.爬取内容:影片的排名及其评分
3.网络爬虫设计方案的大致内容:
网页内容的选取 对所选取网页进行html解析 ,单击鼠标右键查看网页源代码,找到关键内容的索引标签,对标签进行分析理解,提取关键字眼。
导入第三方库,再将所爬取到的内容进行数据清洗.分析,绘制图形方程,以及可视化处理
4.技术难点:在进行标签寻找时,父子标签无法正常提取 以及在读取csv文件时,文档的编码格式存在问题,以及在后置图形绘制的时候图象标题无法
正常显示中文。
二.主题页面的html分析
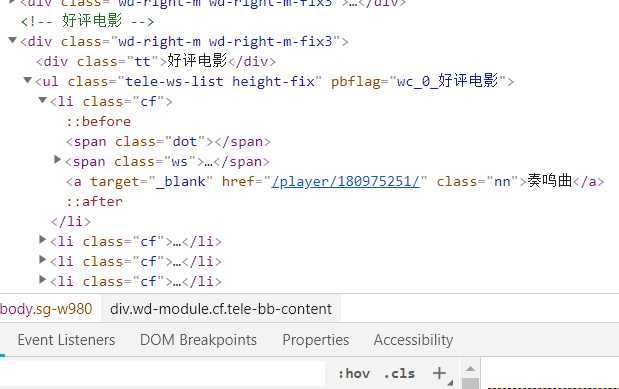
1.主题页面的结构与特征分析:找到所需要的爬取数据都在div class="tt"标签下,在寻找到各个评分标签span class="ws" span class="nn"名称标签。
三,网络爬虫的程序设计代码:
1.数据的爬取及采集
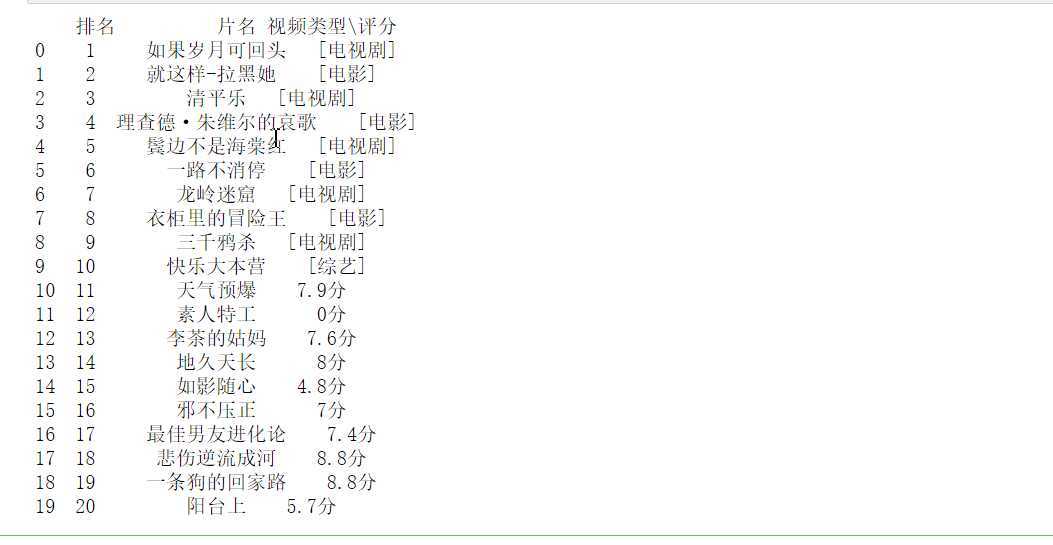
def get_html(url): headers = {‘user-agent‘: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/70.0.3538.102 Safari/537.36 Edge/18.18362‘}#伪装爬虫 resp = requests.get(url, headers = headers) return resp.text url = ‘http://kan.sogou.com/‘ html = get_html(url) soup = BeautifulSoup(html, ‘html.parser‘) #排名 b=soup.find_all(‘div‘,class_=‘tt‘) #片名 v=soup.find_all(‘a‘,class_=‘nn‘) #视频类型 rating_score = soup.find_all(‘span‘, class_=‘jishu‘) curry = [] num =20 for i in range(num): curry.append([i+1,v[i].string, rating_score[i].string]) df = pd.DataFrame(curry,columns = [‘排名‘, ‘片名‘, ‘视频类型\评分‘]) print(df) #将文件保存,使数据可修改 df.to_csv(‘2020搜狗热搜电影数据‘)
2,数据的清洗及处理分析
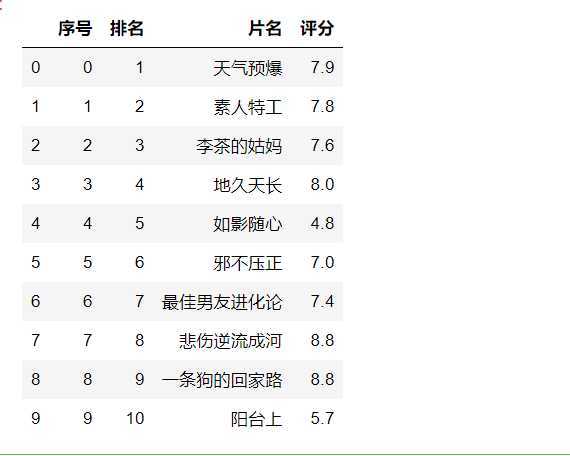
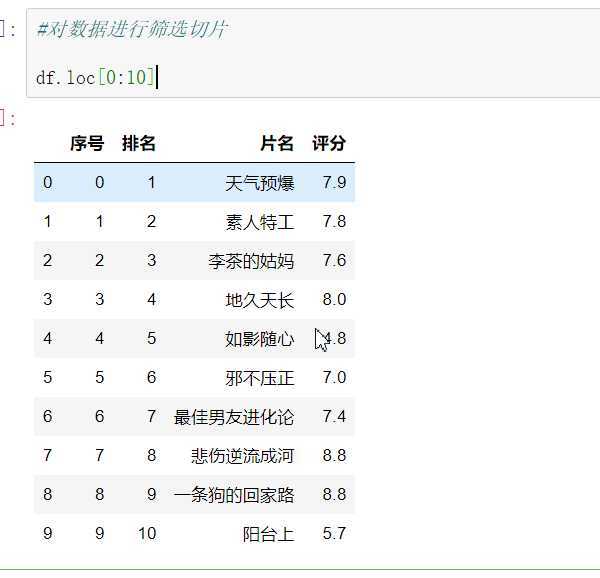
#读取文件 显示前10行 df = pd.DataFrame(pd.read_csv(‘D:\\jupyy\\2020sougo.csv‘)) df.head(10)
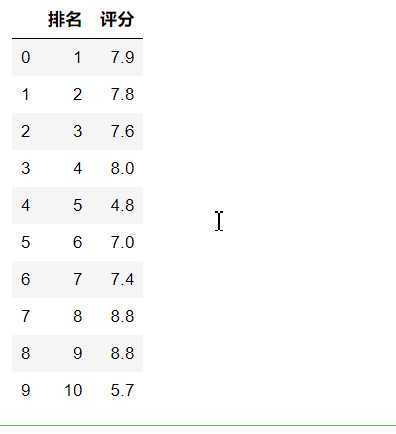
#删除无效行和列 df.drop(‘片名‘, axis=1, inplace = True) df.drop(‘序号‘, axis=1, inplace = True) df.head(10)
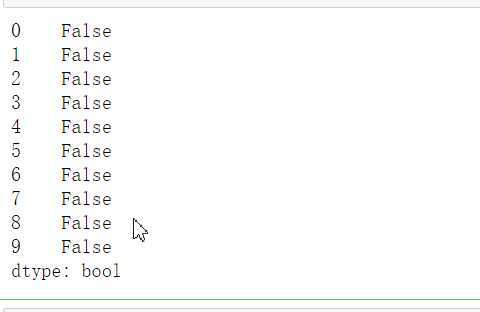
#检查是否有重复值 df.duplicated()
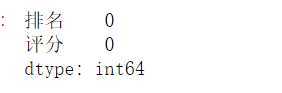
#对空值进行处理 df.isnull().sum() #返回0,则表示没有空值
#缺失值处理 df[df.isnull().values==True] #返回无缺失值

#用describe()命令显示描述性统计指标 df.describe()
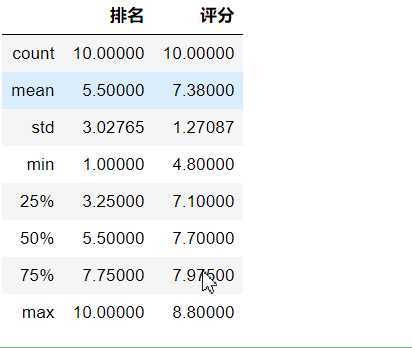
#用describe()命令显示描述性统计指标 df.describe()

#求最小值 df.min()

#求最大值 df.max()
#数据分析 X = df.drop("排名",axis=1) predict_model = LinearRegression() predict_model.fit(X,df[‘评分‘]) print("回归系数为:",predict_model.coef_)
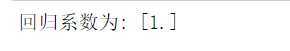
3,数据分析可视化
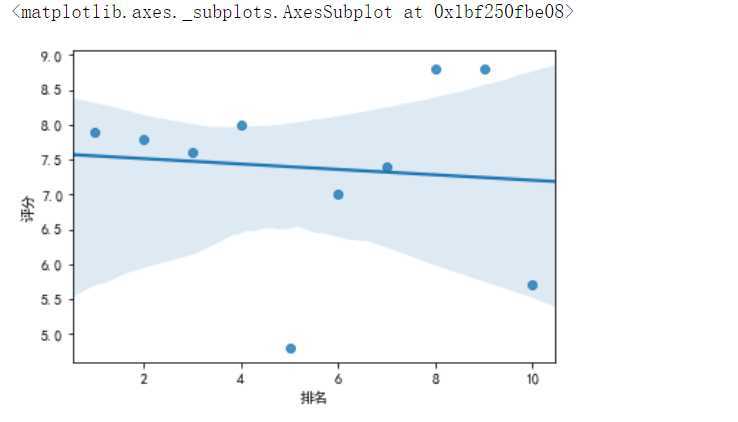
#绘制排名与评分的回归图 from pylab import * plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘]=[‘SimHei‘]#显示中文 sns.regplot(df.排名,df.评分)
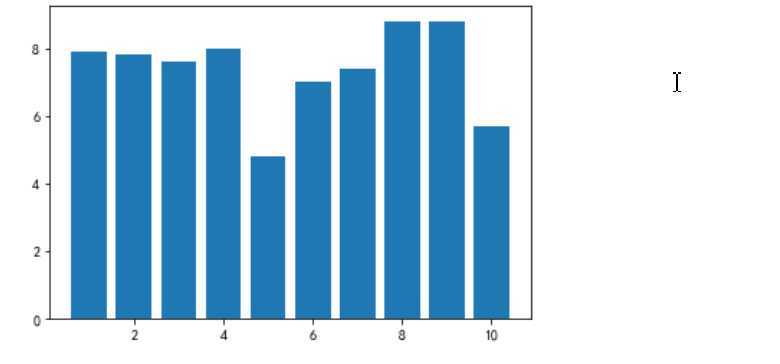
# 绘制垂直柱状图 plt.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘]=False #用来正常显示负号 plt.bar(df.排名, df.评分, label="排名与评分柱状图") plt.show()
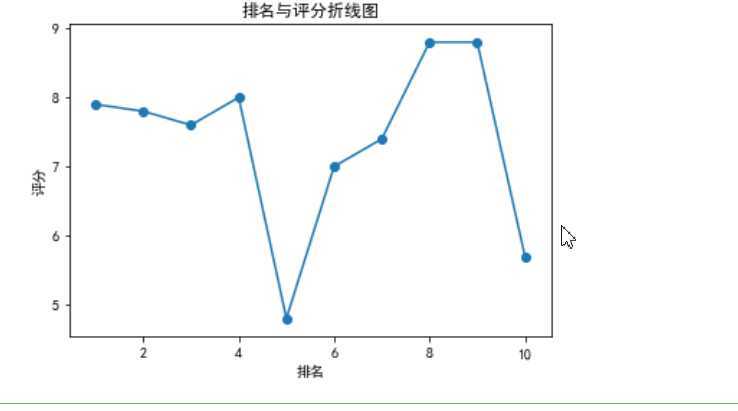
def fill(): x = df[‘排名‘] y = df[‘评分‘] plt.xlabel(‘排名‘) plt.ylabel(‘评分‘) plt.plot(x,y) plt.scatter(x,y) plt.title("排名与评分折线图") plt.show() fill()
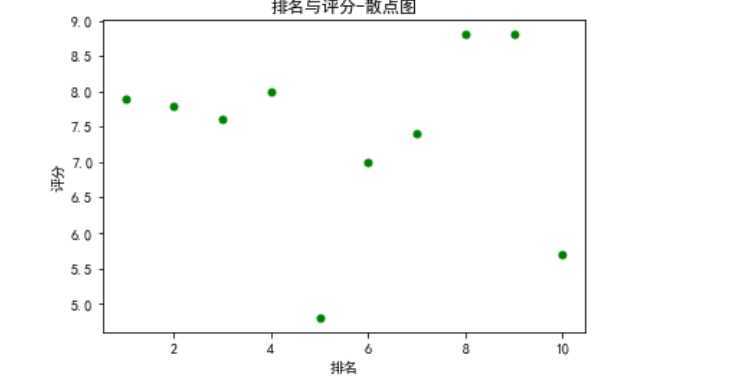
def fill0(): plt.scatter(df.排名, df.评分, color=‘green‘, s=25, marker="o") plt.xlabel("排名") plt.ylabel("评分") plt.title("排名与评分-散点图") plt.show() fill0()
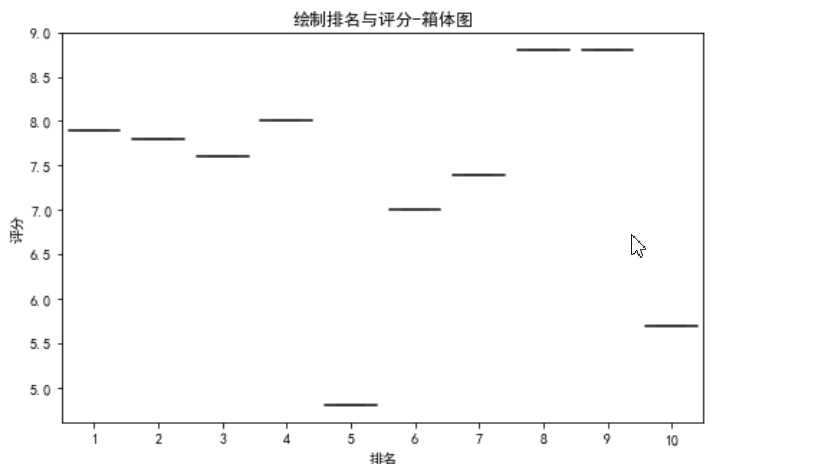
#绘制排名与评分-箱体图(盒图) def fill2(): plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5)) plt.title(‘绘制排名与评分-箱体图‘) sns.boxplot(x=‘排名‘,y=‘评分‘, data=df) fill2()
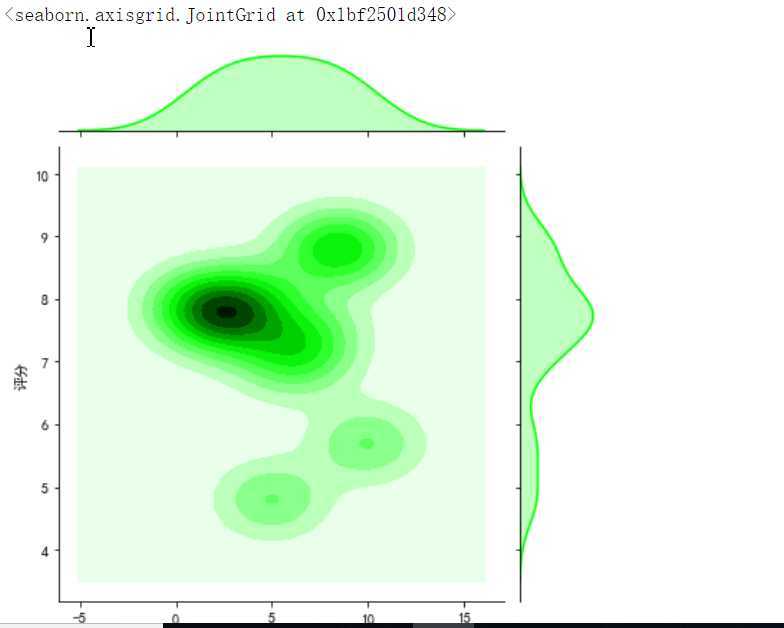
#绘制部分分布图 sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df, kind=‘kde‘, color=‘lime‘) sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df) sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df, kind=‘reg‘) sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df, kind=‘hex‘)
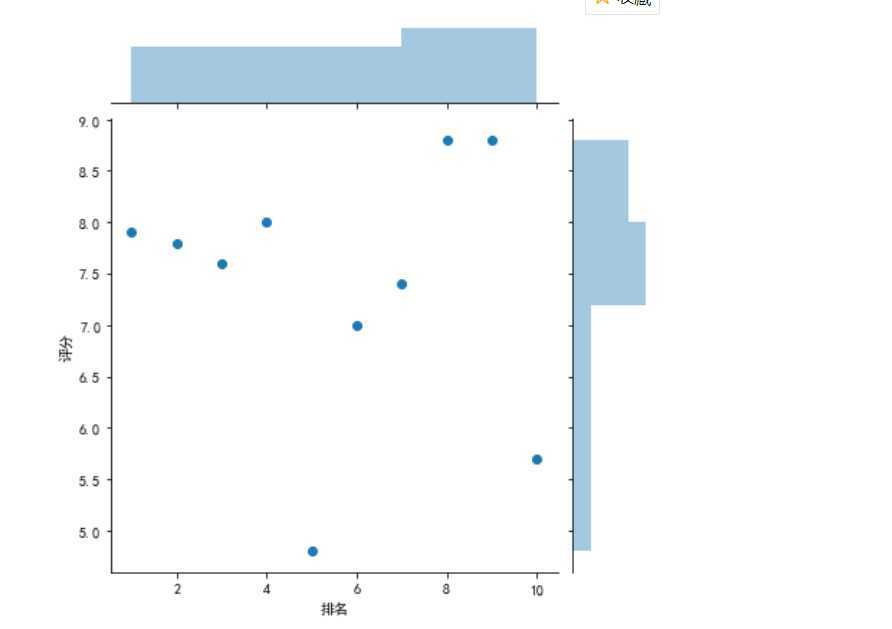
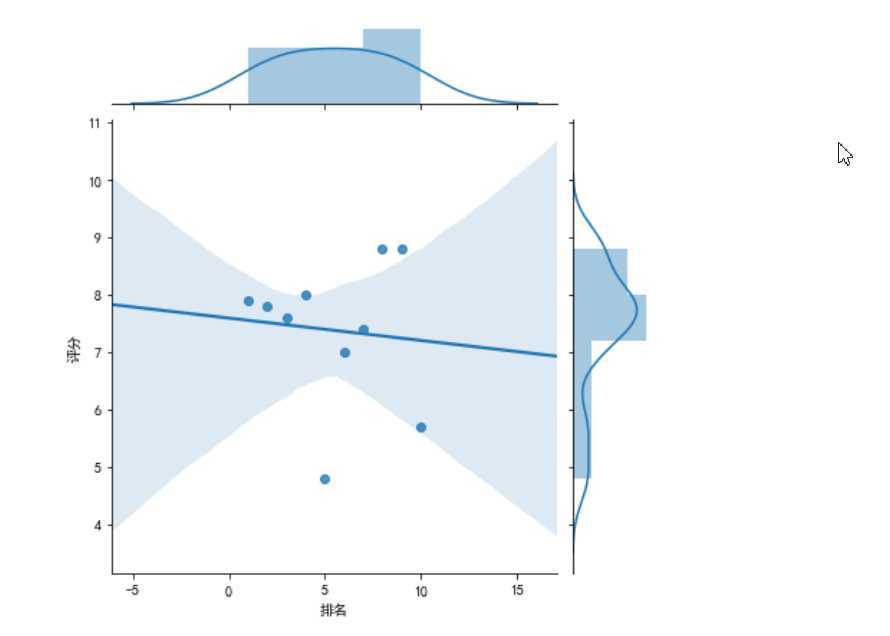

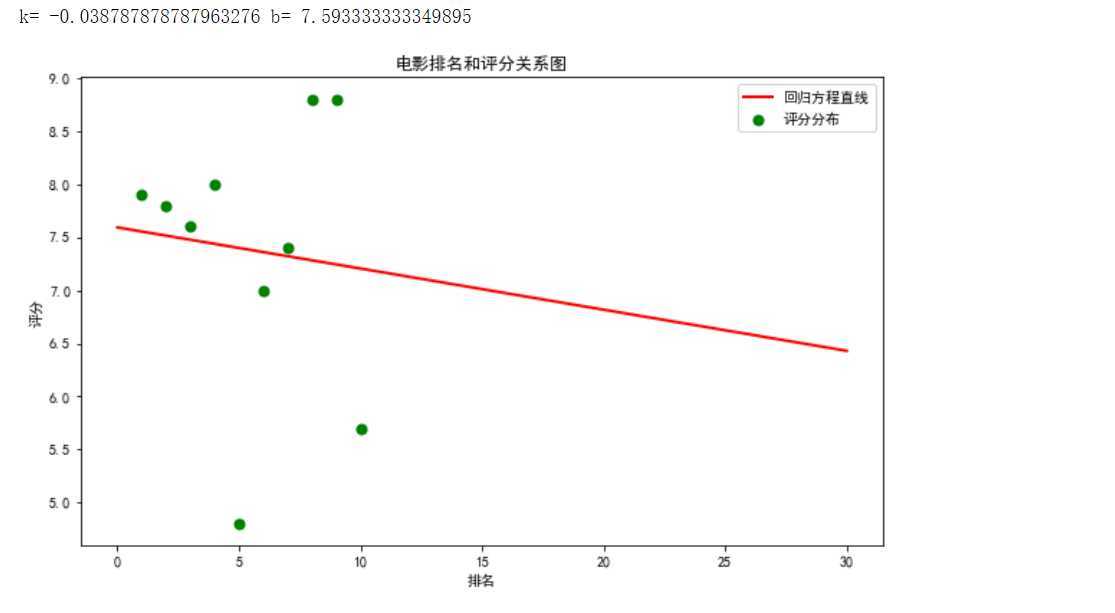
4.根据数据之间的关系绘制散点图,并进行方程的构建拟合出关系曲线图。
#绘制一元一次回归方程 def mainly(): colnames = ["序号", "排名", "片名", "评分"] df = pd.read_csv(‘D:\\jupyy\\2020sougo.csv‘,skiprows=1,names=colnames) X = df.排名 Y = df.评分 def King(p, x): k, b = p return k * x + b def own_King(p, x, y): return King(p,x)-y p0 = [0,0] Para = leastsq(own_King, p0, args = (X, Y)) k, b = Para[0] print("k=",k,"b=",b) plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) plt.scatter(X,Y,color="green",label=u"评分分布",linewidth=2) x=np.linspace(0,30,20) y=k*x+b plt.plot(x,y,color="red",label=u"回归方程直线",linewidth=2) plt.title("电影排名和评分关系图") plt.xlabel(‘排名‘) plt.ylabel(‘评分‘) plt.legend() plt.show() mainly()
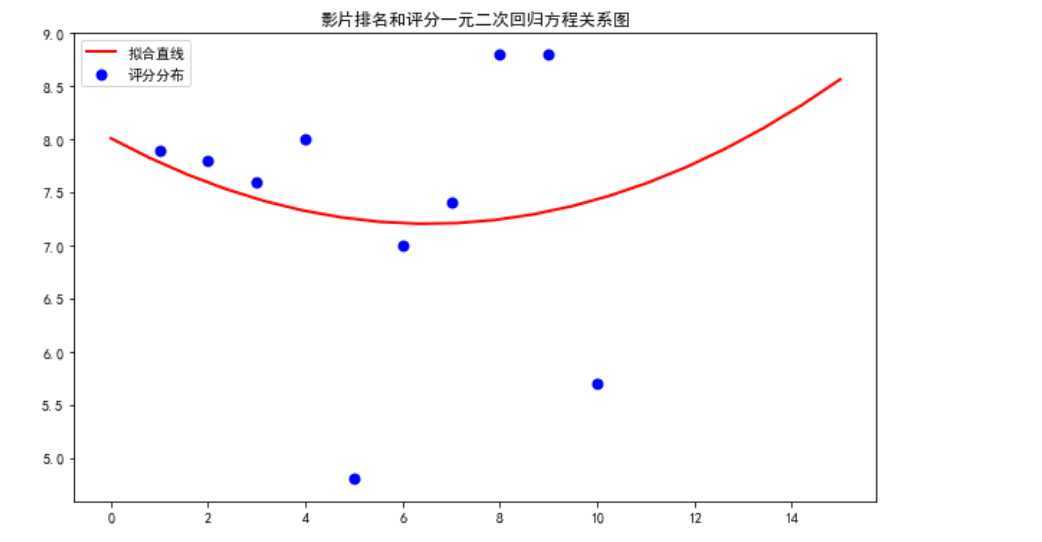
#绘制一元二次回归方程 def man(): colnames = ["序号", "排名", "片名", "评分"] df = pd.read_csv(‘D:\\jupyy\\2020sougo.csv‘,skiprows=1,names=colnames) X = df.排名 Y = df.评分 def aim(p,x): a,b,c=p return a*x*x+b*x+c def error_aim(p,x,y): return aim(p,x)-y p0=[0,0,0] Para=leastsq(error_aim,p0,args=(X,Y)) a,b,c=Para[0] plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) plt.scatter(X,Y,color="b",label=u"评分分布",linewidth=2) x=np.linspace(0,15,20) y=a*x*x+b*x+c plt.plot(x,y,color="r",label=u"拟合直线",linewidth=2) plt.title("影片排名和评分一元二次回归方程关系图") plt.legend() plt.show() man()
5.对数据进行持久化处理,便于查看已经清理好的数据。
#数据持久化 def create_file(file_path,msg): #定义一个创建文件夹,将爬取的资源用excel格式打开 Resou =r‘D:\juppy\2020sogo.xlsx‘ df = pd.DataFrame(msg,columns=[‘排名‘,‘片名‘,‘评分‘]) df.to_excel(Resou) print(‘创建完成‘)
6.将以上各代码汇总,附上完整的程序代码:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import pandas as pd from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression import seaborn as sns import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib from scipy.optimize import leastsq def get_html(url): headers = {‘user-agent‘: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/70.0.3538.102 Safari/537.36 Edge/18.18362‘}#伪装爬虫 resp = requests.get(url, headers = headers) return resp.text url = ‘http://kan.sogou.com/‘ html = get_html(url) soup = BeautifulSoup(html, ‘html.parser‘) #排名 b=soup.find_all(‘div‘,class_=‘tt‘) #片名 v=soup.find_all(‘a‘,class_=‘nn‘) #视频类型 rating_score = soup.find_all(‘span‘, class_=‘jishu‘) curry = [] num =20 for i in range(num): curry.append([i+1,v[i].string, rating_score[i].string]) df = pd.DataFrame(curry,columns = [‘排名‘, ‘片名‘, ‘视频类型\评分‘]) print(df) #将文件保存,使数据可修改 df.to_csv(‘2020搜狗热搜电影数据‘) #读取文件 显示前10行 df = pd.DataFrame(pd.read_csv(‘D:\\jupyy\\2020sougo.csv‘)) df.head(10) #对数据进行筛选切片 df.loc[0:10] #删除无效行和列 df.drop(‘片名‘, axis=1, inplace = True) df.drop(‘序号‘, axis=1, inplace = True) df.head(10) #检查是否有重复值 df.duplicated() #对空值进行处理 df.isnull().sum() #返回0,则表示没有空值 #缺失值处理 df[df.isnull().values==True] #返回无缺失值 #用describe()命令显示描述性统计指标 df.describe() #求最小值 df.min() #求最大值 df.max() #数据分析 X = df.drop("排名",axis=1) predict_model = LinearRegression() predict_model.fit(X,df[‘评分‘]) print("回归系数为:",predict_model.coef_) #绘制排名与评分的回归图 from pylab import * plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘]=[‘SimHei‘]#显示中文 sns.regplot(df.排名,df.评分) # 绘制垂直柱状图 plt.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘]=False #用来正常显示负号 plt.bar(df.排名, df.评分, label="排名与评分柱状图") plt.show() #绘制折线图 def fill(): x = df[‘排名‘] y = df[‘评分‘] plt.xlabel(‘排名‘) plt.ylabel(‘评分‘) plt.plot(x,y) plt.scatter(x,y) plt.title("排名与评分折线图") plt.show() fill() #绘制散点图 def fill0(): plt.scatter(df.排名, df.评分, color=‘green‘, s=25, marker="o") plt.xlabel("排名") plt.ylabel("评分") plt.title("排名与评分-散点图") plt.show() fill0() #绘制排名与评分-箱体图(盒图) def fill2(): plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5)) plt.title(‘绘制排名与评分-箱体图‘) sns.boxplot(x=‘排名‘,y=‘评分‘, data=df) fill2() #绘制部分分布图 sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df, kind=‘kde‘, color=‘lime‘) sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df) sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df, kind=‘reg‘) sns.jointplot(x="排名",y=‘评分‘,data = df, kind=‘hex‘) #绘制一元一次回归方程 def mainly(): colnames = ["序号", "排名", "片名", "评分"] df = pd.read_csv(‘D:\\jupyy\\2020sougo.csv‘,skiprows=1,names=colnames) X = df.排名 Y = df.评分 def King(p, x): k, b = p return k * x + b def own_King(p, x, y): return King(p,x)-y p0 = [0,0] Para = leastsq(own_King, p0, args = (X, Y)) k, b = Para[0] print("k=",k,"b=",b) plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) plt.scatter(X,Y,color="green",label=u"评分分布",linewidth=2) x=np.linspace(0,30,20) y=k*x+b plt.plot(x,y,color="red",label=u"回归方程直线",linewidth=2) plt.title("电影排名和评分关系图") plt.xlabel(‘排名‘) plt.ylabel(‘评分‘) plt.legend() plt.show() mainly() #绘制一元二次回归方程 def man(): colnames = ["序号", "排名", "片名", "评分"] df = pd.read_csv(‘D:\\jupyy\\2020sougo.csv‘,skiprows=1,names=colnames) X = df.排名 Y = df.评分 def aim(p,x): a,b,c=p return a*x*x+b*x+c def error_aim(p,x,y): return aim(p,x)-y p0=[0,0,0] Para=leastsq(error_aim,p0,args=(X,Y)) a,b,c=Para[0] plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) plt.scatter(X,Y,color="b",label=u"评分分布",linewidth=2) x=np.linspace(0,15,20) y=a*x*x+b*x+c plt.plot(x,y,color="r",label=u"拟合直线",linewidth=2) plt.title("影片排名和评分一元二次回归方程关系图") plt.legend() plt.show() man() #数据持久化 def create_file(file_path,msg): #定义一个创建文件夹,将爬取的资源用excel格式打开 Resou =r‘D:\juppy\2020sogo.xlsx‘ df = pd.DataFrame(msg,columns=[‘排名‘,‘片名‘,‘评分‘]) df.to_excel(Resou) print(‘创建完成‘)
四.结论:
经过python对网络爬虫的学习,让自己深刻了解到了python这门语言强大的功能,以及对数据处理的简便与快捷,让数据以更生动
形象具体的方式呈现在我们眼前,同时了解到自身对这门语言的理解还不够透彻,在处理很多方面细节不够到位,让自己认识到更多
的不足,同时加深了对这门语言的热爱。期间看过大量的教学视频,查找了大量的第三方库的使用。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanlsj/p/12704604.html