聂戴成
201821121012
计算1811
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t fpid;
int count=0;
fpid=fork();
if(fpid<0)
printf("error int fork!");
else if(fpid==0){
printf("Child process,myprocess id is %d\n",getpid());
count++;
}
else{
printf("Parent proess,my process id is %d\n",getpid());
count++;
fpid=fork();
if(fpid<0)
printf("error int fork!");
else if(fpid==0){
printf("Child process,myprocess id is %d\n",getpid());
count++;
}
else{
printf("Parent proess,my process id is %d\n",getpid());
count++;
}
}
printf("Count: %d\n",count);
sleep(300);
return 0;
}
解读:
-ps ef:

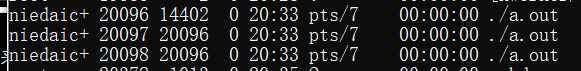
UID:创建进程的用户
PID:系统分配给进程的数字ID
PID分配法:
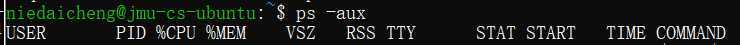

%MEM表示内存占比
VSZ,如果一个程序完全驻留在内存中一共需要会用多少内存;
RSS,表示进程当前实际上占用了多少内存;
STAT,表示当前进程的状态,(S表示处于休眠状态,D表示不可终端的状态,Z表示僵尸进程,X表示死掉的进程);
因为三个进程都被挂起了所以是S,+表示在前台进程组
START,启动这个命令的时间点;
TIME,进程执行起到现在总的CPU占用时间;
COMMAND,表示启动这个进程的命令。
疑问:为什么用不同的命令查看进程,进程的同一个属性有时用不同的字符来表示
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Dlementine/p/12616712.html