使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数,例如
Myapp.exe -n 10
将生成10个题目。
使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围,例如
Myapp.exe -r 10
将生成10以内(不包括10)的四则运算题目。该参数可以设置为1或其他自然数。该参数必须给定,否则程序报错并给出帮助信息。
生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数,也就是说算术表达式中如果存在形如e1− e2的子表达式,那么e1≥ e2。
生成的题目中如果存在形如e1÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数,除号用的是÷ 。
每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。
例如,23 + 45 = 和45 + 23 = 是重复的题目,6 × 8 = 和8 × 6 = 也是重复的题目。3+(2+1)和1+2+3这两个题目是重复的,由于+是左结合的,1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,也就是3+(1+2),也就是3+(2+1)。但是1+2+3和3+2+1是不重复的两道题,因为1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,而3+2+1等价于(3+2)+1,它们之间不能通过有限次交换变成同一个题目。
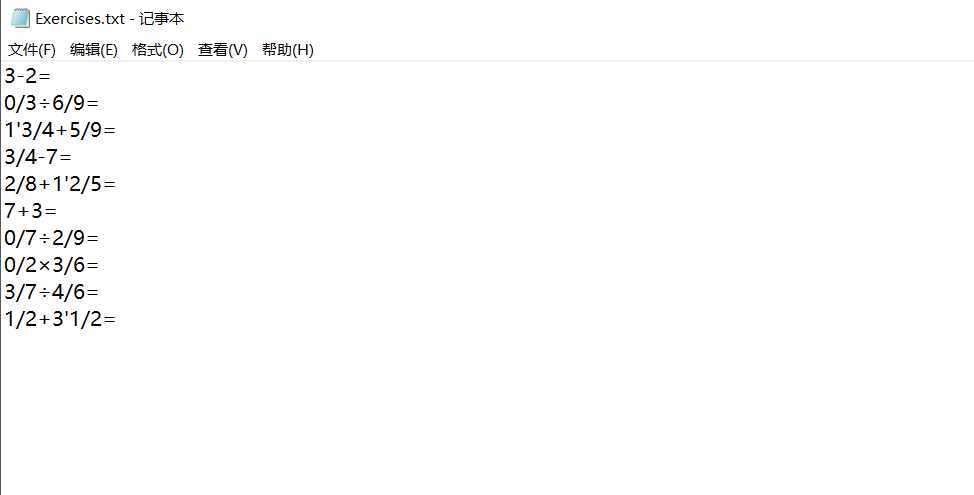
生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件,格式如下:
1.四则运算题目1
2.四则运算题目2
计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件,格式如下:
1.答案1
2.答案2
程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,输入参数如下:
Myapp.exe -e .txt -a .txt
统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
其中“:”后面的数字5表示对/错的题目的数量,括号内的是对/错题目的编号。为简单起见,假设输入的题目都是按照顺序编号的符合规范的题目。
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
60 |
100 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
100 |
120 |
|
Development |
开发 |
600 |
860 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
150 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
40 |
50 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
50 |
60 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
40 |
40 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
160 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
120 |
220 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
90 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
90 |
90 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
60 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
合计 |
1520 |
1920 |
设计实现过程
fomat和caculate都调用translate,fomat调用caculatemain调用fomat,两个类一个主函数,3个其他函数
关键代码
代码思路
1.我们先想到的是把整数化为分数,再化简分子分母,通过生成两个分子和分母实现同时计算
2.我们让假分数带分数,真分数保持不变
3.操作不同文件的输出题目,统计答案
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class A {
public static void main(String args[]){
String[] symbol=new String[]{"+","-","*","/"};
int tot,max;
System.out.println("请输入您要生成的题目数 输入格式:-n 题目数");
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
String st = sc.nextLine();
String[] num=st.split(" ");;
System.out.println("请继续输入您要生成的题目数值范围 输入格式:-r 数值");
Scanner sc1= new Scanner(System.in);
String st1 = sc1.nextLine();
String[] num1=st1.split(" ");
tot=Integer.valueOf(num[1]);
max=Integer.valueOf(num1[1]);
for(int i=0;i<tot;i++){
String[] a= caculate1.format(max);
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
File f=new File("Exercises.txt");//题目写入
fw = new FileWriter(f, true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}if(a[0]!=null) {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println(a[0]);
pw.flush();
try {
fw.flush();
pw.close();
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}FileWriter fn = null;
try {
File f=new File("Answers.txt");//答案写入
fn = new FileWriter(f, true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}if(a[0]!=null) {
PrintWriter pn = new PrintWriter(fn);
pn.println(a[0]+a[1]);
pn.flush();
try {
fn.flush();
pn.close();
fn.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
}}}
import java.util.Random;
public class caculate1 {
public static String[] format(int max){
Random random=new Random();
String exp[]=new String[2];//定义生成的题目
int a= (int) (random.nextInt(max));//分子
int b= (int) (random.nextInt(max));//分母
int c= (int) (random.nextInt(max));//另一个分子
int d= (int) (random.nextInt(max));//另一个分母
int symbol;//运算符
symbol= (int) (random.nextInt(4));
if(b!=0&&d!=0) {//分母均不为0时生成带有分数的计算题,同时计算结果
if(symbol==0) {
int fenzi=a*d+b*c;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]= translate(a,b)+‘+‘+ translate(c,d)+‘=‘;
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);
}
if(symbol==1&&a*d-b*c>=0) {
int fenzi=a*d-b*c;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]= translate(a,b)+‘-‘+ translate(c,d)+‘=‘;
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);
}
if(symbol==1&&a*d-b*c<0) {
int fenzi=b*c-a*d;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]= translate(a,b)+‘-‘+ translate(c,d)+‘=‘;
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);
}
if(symbol==2) {
int fenzi=a*c;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]= translate(a,b)+‘ב+ translate(c,d)+‘=‘;
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);
}
if(symbol==3&&c!=0) {
int fenzi=a*d;
int fenmu=b*c;
exp[0]= translate(a,b)+‘÷‘+ translate(c,d)+‘=‘;
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);
}
}
else {//分母至少一个为0时生成只含有整式的运算式,同时计算结果
b=1; d=1;
if(symbol==0) {
int fenzi=a*d+b*c;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]=a+"+"+c+"=";
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);//计算结果
}
if(symbol==1&&a*d-b*c>=0) {
int fenzi=a*d-b*c;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]=a+"-"+c+"=";
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);//计算结果
}
if(symbol==1&&a*d-b*c<0) {
int fenzi=b*c-a*d;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]=c+"-"+a+"=";
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);//计算结果
}
if(symbol==2) {
int fenzi=a*c;
int fenmu=b*d;
exp[0]=c+"×"+a+"=";
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1]= caculate(fenzi, fenmu);//计算结果
}
if(symbol==3&&c!=0) {
int fenzi = a * d;
int fenmu = b * c;
exp[0] = a + "÷" + c + "=";
System.out.println(exp[0]);
exp[1] = caculate(fenzi, fenmu);//计算结果
}
if(symbol==3&&c==0) {
format(max);
}
}return exp;}
public static String caculate(int a, int b) {// 结果的分数约分,用于计算结果
int y = 1;
for (int i=a;i>=1;i--) {
if(a%i==0&&b%i==0) {
y=i;
break;
}
}
int z=a/y;// 分子
int m=b/y;// 分母
if (z == 0) {
return "0";
}
if(m==1) return z+"";
else return translate(z,m);
}
public static String translate(int a, int b) {//判断假分数,并化假分数为带分数
if(a>=b) {
int c;
c=a/b;
int d;
d=a%b;
{if(d==0) {return c+"";}
return c+"‘"+d+"/"+b;}
}return a+"/"+b;
}-=
}
测试

项目小结
这次的作业依然有很多不足,我们最先想的是如何理解3+2+1!=1+2+3为什么不重复,很是费解,但到最后也没有实现查重,我们代码水平还是很弱,虽然软工不是注重以代码水平,但我知道我们的目标还是要打好代码的基础,同时这次的合作让我们队软件工程这门课程有了进一步的认识时,间紧迫,更要不断地学习,不断沉淀,趁现在时间多好好努力
合作:我的伙伴真的比我强很多,他很多地方都在很耐心很耐心的去教我,这次协作完全是被带飞,同时遇到很多问题我们都能及时沟通反馈
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/bofujiang/p/12617018.html