copy from : http://gityuan.com/2016/12/10/input-manager/
基于Android 6.0源码, 分析InputManagerService的启动过程
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/
- InputDispatcher.cpp
- InputReader.cpp
- InputManager.cpp
- EventHub.cpp
- InputListener.cpp
frameworks/native/libs/input/
- InputTransport.cpp
- Input.cpp
- InputDevice.cpp
- Keyboard.cpp
- KeyCharacterMap.cpp
- IInputFlinger.cpp
frameworks/base/services/core/
- java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
- jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
当用户触摸屏幕或者按键操作,首次触发的是硬件驱动,驱动收到事件后,将该相应事件写入到输入设备节点, 这便产生了最原生态的内核事件。接着,输入系统取出原生态的事件,经过层层封装后成为KeyEvent或者MotionEvent ;最后,交付给相应的目标窗口(Window)来消费该输入事件。可见,输入系统在整个过程起到承上启下的衔接作用。
Input模块的主要组成:
Input相关的动态库:
InputManagerService作为system_server中的重要服务,继承于IInputManager.Stub, 作为Binder服务端,那么Client位于InputManager的内部通过IInputManager.Stub.asInterface() 获取Binder代理端,C/S两端通信的协议是由IInputManager.aidl来定义的。
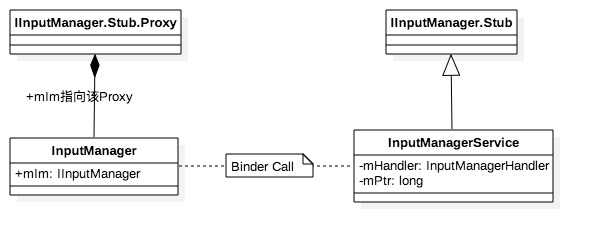
Input模块所涉及的重要类的关系如下:
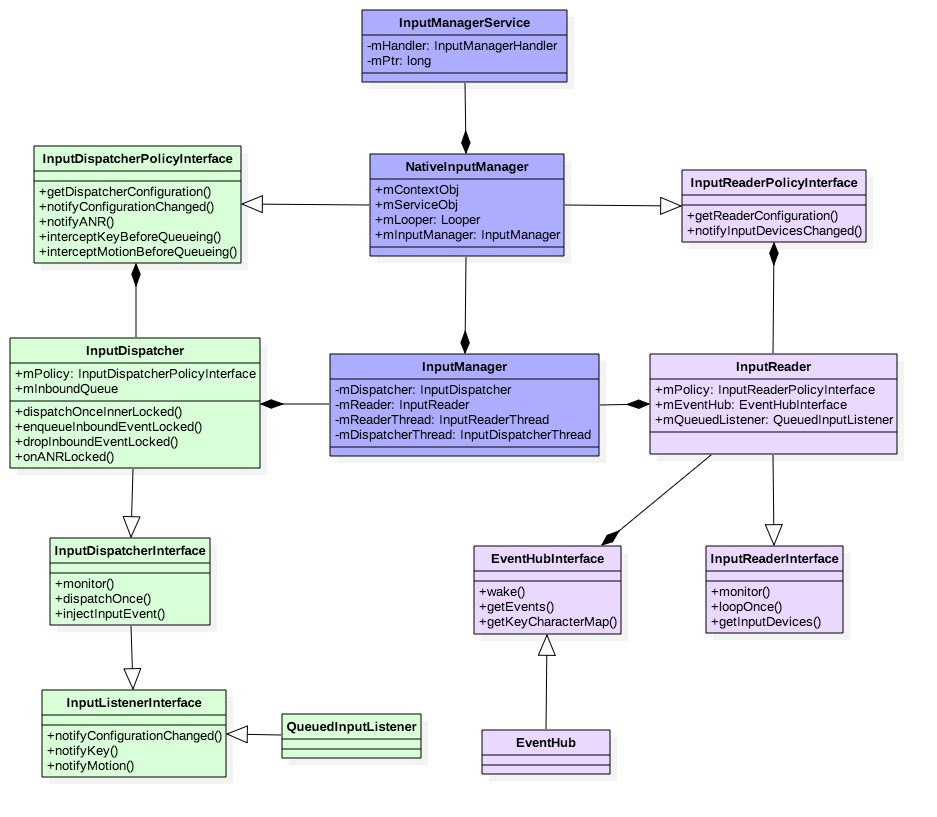
图解:
mPtr指向Native层的NativeInputManager对象;mServiceObj指向Java层的IMS对象;mLooper是指“android.display”线程的Looper;mPolicy都是指NativeInputManager对象;mQueuedListener,数据类型为QueuedInputListener;通过其内部成员变量mInnerListener指向InputDispatcher对象; 这便是InputReader跟InputDispatcher交互的中间枢纽。IMS服务是伴随着system_server进程的启动而启动,整个调用过程:
InputManagerService(初始化)
nativeInit
NativeInputManager
EventHub
InputManager
InputDispatcher
Looper
InputReader
QueuedInputListener
InputReaderThread
InputDispatcherThread
IMS.start(启动)
nativeStart
InputManager.start
InputReaderThread->run
InputDispatcherThread->run
整个过程首先创建如下对象:NativeInputManager,EventHub,InputManager, InputDispatcher,InputReader,InputReaderThread,InputDispatcherThread。 接着便是启动两个工作线程InputReader,InputDispatcher。
private void startOtherServices() {
//初始化IMS对象【见小节2.1】
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager);
...
//将InputMonitor对象保持到IMS对象
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputMonitor());
//[见小节2.9]
inputManager.start();
}
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;
// 运行在线程"android.display"
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());
...
//初始化native对象【见小节2.2】
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());
LocalServices.addService(InputManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
}
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
//获取native消息队列
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
...
//创建Native的InputManager【见小节2.3】
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,
messageQueue->getLooper());
im->incStrong(0);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im); //返回Native对象的指针
}
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject contextObj,
jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper) :
mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
mContextObj = env->NewGlobalRef(contextObj); //上层IMS的context
mServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(serviceObj); //上层IMS对象
...
sp<EventHub> eventHub = new EventHub(); // 创建EventHub对象【见小节2.4】
mInputManager = new InputManager(eventHub, this, this); // 创建InputManager对象【见小节2.5】
}
此处的mLooper是指“android.display”线程的Looper; libinputservice.so库中PointerController和SpriteController对象都继承于于MessageHandler, 这两个Handler采用的便是该mLooper.
[-> EventHub.cpp]
EventHub::EventHub(void) :
mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD), mNextDeviceId(1), mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(0), mClosingDevices(0),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false), mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0), mPendingEventIndex(0), mPendingINotify(false) {
acquire_wake_lock(PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, WAKE_LOCK_ID);
//创建epoll
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
mINotifyFd = inotify_init();
//此处DEVICE_PATH为"/dev/input",监听该设备路径
int result = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY;
//添加INotify到epoll实例
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);
int wakeFds[2];
result = pipe(wakeFds); //创建管道
mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
//将pipe的读和写都设置为非阻塞方式
result = fcntl(mWakeReadPipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
result = fcntl(mWakeWritePipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_WAKE;
//添加管道的读端到epoll实例
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, &eventItem);
...
}
该方法主要功能:
[-> InputManager.cpp]
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
//创建InputDispatcher对象【见小节2.6】
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
//创建InputReader对象【见小节2.7】
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);
initialize();//【见小节2.8】
}
InputDispatcher和InputReader的mPolicy成员变量都是指NativeInputManager对象。
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) :
mPolicy(policy),
mPendingEvent(NULL), mLastDropReason(DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false), mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(NULL),
mDispatchEnabled(false), mDispatchFrozen(false), mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mInputTargetWaitCause(INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE) {
//创建Looper对象
mLooper = new Looper(false);
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = NULL;
//获取分发超时参数
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);
}
该方法主要工作:
[-> InputReader.cpp]
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1),
mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0) {
// 创建输入监听对象
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
refreshConfigurationLocked(0);
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();
}
}
此处mQueuedListener的成员变量mInnerListener便是InputDispatcher对象。 前面【小节2.5】InputManager创建完InputDispatcher和InputReader对象, 接下里便是调用initialize初始化。
[-> InputManager.cpp]
void InputManager::initialize() {
//创建线程“InputReader”
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);
//创建线程”InputDispatcher“
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);
}
InputReaderThread::InputReaderThread(const sp<InputReaderInterface>& reader) :
Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mReader(reader) {
}
InputDispatcherThread::InputDispatcherThread(const sp<InputDispatcherInterface>& dispatcher) :
Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mDispatcher(dispatcher) {
}
初始化的主要工作就是创建两个能访问Java代码的native线程。
到此[2.1-2.8]整个的InputManagerService对象初始化过程并完成,接下来便是调用其start方法。
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public void start() {
// 启动native对象[见小节2.10]
nativeStart(mPtr);
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
//注册触摸点速度和是否显示功能的观察者
registerPointerSpeedSettingObserver();
registerShowTouchesSettingObserver();
mContext.registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings();
updateShowTouchesFromSettings();
}
}, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED), null, mHandler);
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings(); //更新触摸点的速度
updateShowTouchesFromSettings(); //是否在屏幕上显示触摸点
}
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr) {
//此处ptr记录的便是NativeInputManager
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
// [见小节2.11]
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();
...
}
[InputManager.cpp]
status_t InputManager::start() {
result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
...
return OK;
}
该方法的主要功能是启动两个线程:
分层视角:
主要功能:
从整个启动过程,可知有system_server进程中有3个线程跟Input输入系统息息相关,分别是android.display, InputReader,InputDispatcher。
Input事件流程:Linux Kernel -> IMS(InputReader -> InputDispatcher) -> WMS -> ViewRootImpl, 后续再进一步介绍。
最后在列举整个input处理流程中常见的重要对象或结构体,后续input系列文章直接使用以上结构体,可回过来查看。
class InputDevice {
...
private:
InputReaderContext* mContext;
int32_t mId;
int32_t mGeneration;
int32_t mControllerNumber;
InputDeviceIdentifier mIdentifier;
String8 mAlias;
uint32_t mClasses;
Vector<InputMapper*> mMappers;
uint32_t mSources;
bool mIsExternal;
bool mHasMic;
bool mDropUntilNextSync;
typedef int32_t (InputMapper::*GetStateFunc)(uint32_t sourceMask, int32_t code);
int32_t getState(uint32_t sourceMask, int32_t code, GetStateFunc getStateFunc);
PropertyMap mConfiguration;
};
enum DropReason {
DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED = 0, //不丢弃
DROP_REASON_POLICY = 1, //策略
DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH = 2, //应用切换
DROP_REASON_DISABLED = 3, //disable
DROP_REASON_BLOCKED = 4, //阻塞
DROP_REASON_STALE = 5, //过时
};
enum InputTargetWaitCause {
INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE,
INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY, //系统没有准备就绪
INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY, //应用没有准备就绪
};
EventEntry* mPendingEvent;
Queue<EventEntry> mInboundQueue; //需要InputDispatcher分发的事件队列
Queue<EventEntry> mRecentQueue;
Queue<CommandEntry> mCommandQueue;
Vector<sp<InputWindowHandle> > mWindowHandles;
sp<InputWindowHandle> mFocusedWindowHandle; //聚焦窗口
sp<InputApplicationHandle> mFocusedApplicationHandle; //聚焦应用
String8 mLastANRState; //上一次ANR时的分发状态
InputTargetWaitCause mInputTargetWaitCause;
nsecs_t mInputTargetWaitStartTime;
nsecs_t mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime;
bool mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired;
//目标等待的应用
sp<InputApplicationHandle> mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle;
class Connection : public RefBase {
enum Status {
STATUS_NORMAL, //正常状态
STATUS_BROKEN, //发生无法恢复的错误
STATUS_ZOMBIE //input channel被注销掉
};
Status status; //状态
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel; //永不为空
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle; //可能为空
bool monitor;
InputPublisher inputPublisher;
InputState inputState;
//当socket占满的同时,应用消费某些输入事件之前无法发布事件,则值为true.
bool inputPublisherBlocked;
//需要被发布到connection的事件队列
Queue<DispatchEntry> outboundQueue;
//已发布到connection,但还没有收到来自应用的“finished”响应的事件队列
Queue<DispatchEntry> waitQueue;
}
struct EventEntry : Link<EventEntry> {
mutable int32_t refCount;
int32_t type; //时间类型
nsecs_t eventTime; //事件时间
uint32_t policyFlags;
InjectionState* injectionState;
bool dispatchInProgress; //初始值为false, 分发过程则设置成true
};
此处type的可取值为:
enum {
// 内部使用, 正在执行注入操作
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING = -1,
// 事件注入成功
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED = 0,
// 事件注入失败, 由于injector没有权限将聚焦的input事件注入到应用
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED = 1,
// 事件注入失败, 由于没有可用的input target
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED = 2,
// 事件注入失败, 由于超时
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_TIMED_OUT = 3
};
class InputChannel : public RefBase {
// 创建一对input channels
static status_t openInputChannelPair(const String8& name,
sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel);
status_t sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg); //发送消息
status_t receiveMessage(InputMessage* msg); //接收消息
//获取InputChannel的fd的拷贝
sp<InputChannel> dup() const;
private:
String8 mName;
int mFd;
};
sendMessage的返回值:
receiveMessage的返回值:
struct InputTarget {
enum {
FLAG_FOREGROUND = 1 << 0, //事件分发到前台app
FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED = 1 << 1,
FLAG_SPLIT = 1 << 2, //MotionEvent被拆分成多窗口
FLAG_ZERO_COORDS = 1 << 3,
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS = 1 << 8, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE = 1 << 9, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER = 1 << 10, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT = 1 << 11, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT = 1 << 12, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER = 1 << 13, //
FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED = 1 << 14,
//所有分发模式的掩码
FLAG_DISPATCH_MASK = FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER,
};
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel; //目标的inputChannel
int32_t flags;
float xOffset, yOffset; //用于MotionEvent
float scaleFactor; //用于MotionEvent
BitSet32 pointerIds;
};
class InputPublisher {
public:
//获取输入通道
inline sp<InputChannel> getChannel() { return mChannel; }
status_t publishKeyEvent(...); //将key event发送到input channel
status_t publishMotionEvent(...); //将motion event发送到input channel
//接收来自InputConsumer发送的完成信号
status_t receiveFinishedSignal(uint32_t* outSeq, bool* outHandled);
private:
sp<InputChannel> mChannel;
};
class InputConsumer {
public:
inline sp<InputChannel> getChannel() { return mChannel; }
status_t consume(...); //消费input channel的事件
//向InputPublisher发送完成信号
status_t sendFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled);
bool hasDeferredEvent() const;
bool hasPendingBatch() const;
private:
sp<InputChannel> mChannel;
InputMessage mMsg; //当前input消息
bool mMsgDeferred;
Vector<Batch> mBatches; //input批量消息
Vector<TouchState> mTouchStates;
Vector<SeqChain> mSeqChains;
status_t consumeBatch(...);
status_t consumeSamples(...);
static void initializeKeyEvent(KeyEvent* event, const InputMessage* msg);
static void initializeMotionEvent(MotionEvent* event, const InputMessage* msg);
}
class KeyEvent : public InputEvent {
...
protected:
int32_t mAction;
int32_t mFlags;
int32_t mKeyCode;
int32_t mScanCode;
int32_t mMetaState;
int32_t mRepeatCount;
nsecs_t mDownTime; //专指按下时间
nsecs_t mEventTime; //事件发生时间(包括down/up等事件)
}
class MotionEvent : public InputEvent {
...
protected:
int32_t mAction;
int32_t mActionButton;
int32_t mFlags;
int32_t mEdgeFlags;
int32_t mMetaState;
int32_t mButtonState;
float mXOffset;
float mYOffset;
float mXPrecision;
float mYPrecision;
nsecs_t mDownTime; //按下时间
Vector<PointerProperties> mPointerProperties;
Vector<nsecs_t> mSampleEventTimes;
Vector<PointerCoords> mSamplePointerCoords;
};
}
struct NotifyKeyArgs : public NotifyArgs {
nsecs_t eventTime; //事件发生时间
int32_t deviceId;
uint32_t source;
uint32_t policyFlags;
int32_t action;
int32_t flags;
int32_t keyCode;
int32_t scanCode;
int32_t metaState;
nsecs_t downTime; //按下时间
...
};
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Oude/p/12602993.html