为了确保整棵树的深度为O(logN),加了额外的平衡条件“任何结点的左右子树高度相差最多1”。
调整规则:如果某一个子树平衡被打破,那么根据新插入的节点的位置可以分为以下几种:(X是被打破平衡的那个子树的根节点)
1.4为外插可用于单旋;2,3为内插可用于双旋。
另一种被广泛使用的平衡二叉搜索树,也是SGI STL唯一实现的搜寻树,作为关联式容器的底层机制之用。RB-tree的平衡条件虽然不同于AVL-tree(都是二叉搜索树),但同样运用了单旋转和双旋转修正操作。RB-tree的规则:
根据规则四:新增节点必须为红色;根据规则三:新增节点的父节点为黑色。
RB-tree的结点设计
//RB-tree特有的颜色定义 typedef bool __rb_tree_color_type; const __rb_tree_color_type __rb_tree_red = false; //红色被定义为0 const __rb_tree_color_type __rb_tree_black = true; //黑色被定义为1 //RB-tree节点基本结构 struct __rb_tree_node_base { typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type; typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr; color_type color; // 节点颜色,非黑即红 base_ptr parent; // 指向父节点,由于RB-tree时常要上溯其父节点 base_ptr left; // 指向左子节点 base_ptr right; // 指向右子节点 // 一直往左走,就能找到红黑树的最小值节点 // 二叉搜索树的性质 static base_ptr minimum(base_ptr x) { while (x->left != 0) x = x->left; return x; } // 一直往右走,就能找到红黑树的最大值节点 // 二叉搜索树的性质 static base_ptr maximum(base_ptr x) { while (x->right != 0) x = x->right; return x; } }; // 真正的节点定义,采用双层节点结构 // 基类中不包含模板参数 template <class Value> struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base { typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type; Value value_field; // 即节点值 };
RB-tree的迭代器
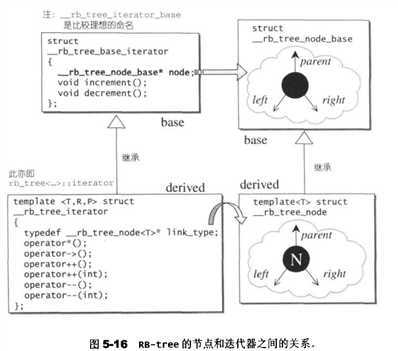
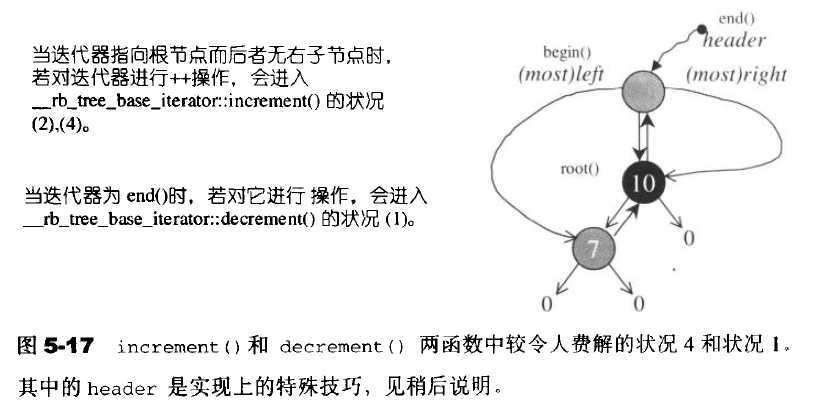
struct __rb_tree_base_iterator { typedef __rb_tree_node_base::base_ptr base_ptr; typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; base_ptr node; // 用来连接红黑树的节点 // 寻找该节点的后继节点上 void increment() { if (node->right != 0) { // 如果存在右子节点 node = node->right; //【情况1】直接跳到右子节点上 while (node->left != 0) // 然后一直往左子树走,直到左子树为空 node = node->left; } else { // 没有右子节点【情况2】 base_ptr y = node->parent; // 找出父节点 while (node == y->right) { // 如果该节点一直为它的父节点的右子节点 node = y; // 就一直往上找,直到不为右子节点为止 y = y->parent; } if (node->right != y) // 若此时该节点不为它的父节点的右子节点 node = y; // 此时的父节点即为要找的后继节点【情况3】 // 否则此时的node即为要找的后继节点【情况4】 // 我们要寻找根节点的下一个节点,而根节点没有右子节点 // 此种情况需要配合rbtree的header节点的特殊设计,后面会讲到 } } // 寻找该节点你的前置节点 void decrement() { if (node->color == __rb_tree_red && // 如果此节点是红节点 node->parent->parent == node) // 且父节点的父节点等于自己 node = node->right; // 则其右子节点即为其前置节点 // 以上情况发生在node为header时,即node为end()时 // 注意:header的右子节点为mostright,指向整棵树的max节点,后面会有解释 else if (node->left != 0) { // 如果存在左子节点 base_ptr y = node->left; // 跳到左子节点上 while (y->right != 0) // 然后一直往右找,知道右子树为空 y = y->right; node = y; // 则找到前置节点 } else { // 如果该节点不存在左子节点 base_ptr y = node->parent; // 跳到它的父节点上 while (node == y->left) { // 如果它等于它的父子节点的左子节点 node = y; // 则一直往上查 y = y->parent; } // 直到它不为父节点的左子节点未知 node = y; // 此时他的父节点即为要找的前驱节点 } } }; template <class Value, class Ref, class Ptr> struct __rb_tree_iterator : public __rb_tree_base_iterator { //...型别声明 // 迭代器的构造函数 __rb_tree_iterator() {} __rb_tree_iterator(link_type x) { node = x; } __rb_tree_iterator(const iterator& it) { node = it.node; } // 提领和成员访问函数,重载了*和->操作符 reference operator*() const { return link_type(node)->value_field; } pointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); } // 前置++和后置++ self& operator++() { increment(); return *this; } self operator++(int) { self tmp = *this; increment(); // 直接调用increment函数 return tmp; } // 前置--和后置-- self& operator--() { decrement(); return *this; } self operator--(int) { self tmp = *this; decrement(); // 直接调用decrement函数 return tmp; } };
RB-tree的数据结构
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc = alloc> class rb_tree { protected: typedef void* void_pointer; typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr; typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node; typedef simple_alloc<rb_tree_node, Alloc> rb_tree_node_allocator; // 专属配置器 typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type; public: // 一些类型声明 typedef Key key_type; typedef Value value_type; typedef value_type* pointer; typedef const value_type* const_pointer; typedef value_type& reference; typedef const value_type& const_reference; typedef rb_tree_node* link_type; typedef size_t size_type; typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; protected: link_type get_node(){return rb_tree_node_allocator::allocate();} void put_node(link_type p){rb_tree_node_allocator::deallocate(p);} link_type create_node() { link_type tmp=get_node();//配置空间 __STL_TRY { construct(&tmp->value_field,x); } __STL_UNWIND(put_node(tmp)); return tmp; } link_type clone_node(link_type x) { link_type tmp=create_node(x->value_field); tmp->color=x->color; tmp->left=0; tmp->right=0; return tmp; } void destroy_node(link_type p) { destroy(&p->value_field); put_node(p); } protected: // RB-tree的数据结构 size_type node_count; // 记录树的节点个数 link_type header; // header节点设计 Compare key_compare; // 节点间的键值大小比较准则 // 以下三个函数用来取得header的成员 link_type& root() const { return (link_type&) header->parent; } link_type& leftmost() const { return (link_type&) header->left; } link_type& rightmost() const { return (link_type&) header->right; } // 以下六个函数用来取得节点的成员 static link_type& left(link_type x) { return (link_type&)(x->left); } static link_type& right(link_type x) { return (link_type&)(x->right); } static link_type& parent(link_type x) { return (link_type&)(x->parent); } static reference value(link_type x) { return x->value_field; } static const Key& key(link_type x) { return KeyOfValue()(value(x)); } static color_type& color(link_type x) { return (color_type&)(x->color); } // 以下六个函数用来取得节点的成员,由于双层设计,导致这里需要两个定义 static link_type& left(base_ptr x) { return (link_type&)(x->left); } static link_type& right(base_ptr x) { return (link_type&)(x->right); } static link_type& parent(base_ptr x) { return (link_type&)(x->parent); } static reference value(base_ptr x) { return ((link_type)x)->value_field; } static const Key& key(base_ptr x) { return KeyOfValue()(value(link_type(x)));} static color_type& color(base_ptr x) { return (color_type&)(link_type(x)->color); } // 求取极大值和极小值,这里直接调用节点结构的函数极可 static link_type minimum(link_type x) { return (link_type) __rb_tree_node_base::minimum(x); } static link_type maximum(link_type x) { return (link_type) __rb_tree_node_base::maximum(x); } public: // RBTree的迭代器定义 typedef __rb_tree_iterator<value_type, reference, pointer> iterator; private: //... void init() { //构造一个空tree header = get_node(); //产生一个节点空间,令header指向它 color(header) = __rb_tree_red; //令header为红色,用来将 //root与header区分开 root() = 0; leftmost() = header; //header的左子节点为自己 rightmost() = header; //header的右子节点为自己 } public: rb_tree(const Compare& comp=Compare()):node_count(0),key_compare(comp){init();} ~rb_tree() { clear(); put_node(hander); } rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>& operator=(const rb_tree<Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare,Alloc>& x); public: Compare key_comp() const { return key_compare; } // 由于红黑树自带排序功能,所以必须传入一个比较器函数 iterator begin() { return leftmost(); } // RBTree的起始节点为左边最小值节点 const_iterator begin() const { return leftmost(); } iterator end() { return header; } // RBTree的终止节点为右边最大值节点 const_iterator end() const { return header; } bool empty() const { return node_count == 0; } // 判断红黑树是否为空 size_type size() const { return node_count; } // 获取红黑树的节点个数 size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1); } // 获取红黑树的最大节点个数,s// 没有容量的概念,故为sizetype最大值 public: pair<iterator,bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);//保持结点值独一无二 iterator insert_equal(const value_type& x);//允许结点值重复 };
RB-tree的构造与内存管理
RB-tree构造方式有两种,一种是以一个现有的RB-tree复制一个新的RB-tree,另一种是产生一棵空树。
rb_tree<int, int, identity<int>, less<int> > itree; rb_tree(const Compare& comp = Compare()) : node_count(0), key_compare(comp) { init(); } void init() { //构造一个空tree header = get_node(); //产生一个节点空间,令header指向它 color(header) = __rb_tree_red; //令header为红色,用来将 //root与header区分开 root() = 0; leftmost() = header; //header的左子节点为自己 rightmost() = header; //header的右子节点为自己 }
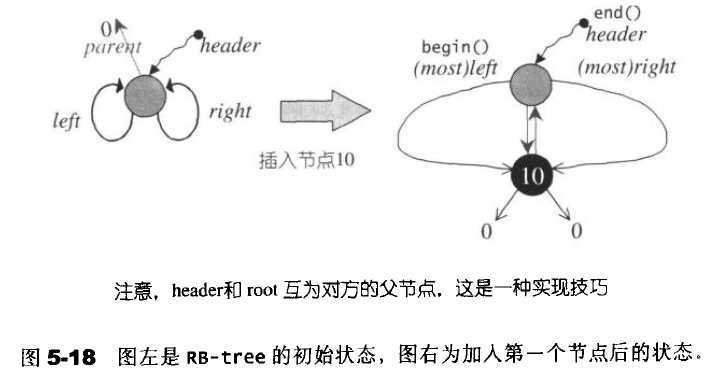
为了控制边界结点,在走到根节点时要特殊处理,为父节点在设计一个根节点hander,在插入结点时不仅要根据RB-tree的特性来维护树,而且还需要hander的正确性,使其父节点指向根节点,左子结点指向最小结点,右子结点指向最大结点。初始状态如下图
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/tianzeng/p/12595061.html