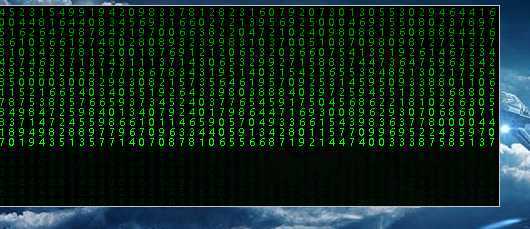
第一种方法:
<canvas id="matrix"></canvas>
JS:
1 $(document).ready(function () {
2 var matrix = document.getElementById("matrix");
3 var context = matrix.getContext("2d");
4 matrix.height = window.innerHeight;
5 matrix.width = window.innerWidth;
6 var drop = [];
7 var font_size = 26; //字体
8 var columns = matrix.width / font_size;
9 for (var i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
10 drop[i] = 1;
11 }
12
13 function drawMatrix() {
14 context.fillStyle = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1)";
15 context.fillRect(0, 0, matrix.width, matrix.height);
16
17 context.fillStyle = "green";
18 context.font = font_size + "px";
19 for (var i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
20 context.fillText(Math.floor(Math.random() * 2), i * font_size, drop[i] * font_size);/*get 0 and 1*/
21 if (drop[i] * font_size > (matrix.height * 2 / 3) && Math.random() > 0.85)/*reset*/
22 drop[i] = 0;
23 drop[i]++;
24 }
25 }
26 setInterval(drawMatrix, 50); //按照指定间隔一直执行方法
27
28
29 });
效果:

第二种方法:
首先看下两个案例:
一:
<canvas id="myCanvasMatrix" width="500" height="200" style="border:1px solid #c3c3c3;"></canvas>
<button type="button" id="puse">puse</button>
<button type="button" id="run">run</button>
$(document).ready(function () {
$(‘#fullpage‘).fullpage({
});
/*
var c2 = document.getElementById("myCanvasMatrix");
var ctx2 = c2.getContext("2d");
其中 ‘ctx2‘ 就等同于下面的 ‘ctx1‘
*/
var ctx1 = $("#myCanvasMatrix").get(0).getContext("2d");
/*
其中$("").get(0)表示获取内部的DOM对象引用
也就是:获取到对象的dom对象后就可以使用对应的dom API
*/
/*
getContext() 方法返回一个用于在画布上绘图的环境。
Canvas.getContext(contextID);
其中contextID参数当前唯一的合法值为‘2d‘,也就是支持了二维绘图
未来可能会支持‘3d‘这个参数哦~
*/
var Matrix = function () {
/*
var my_gradient=ctx1.createLinearGradient(0,0,0,170);
my_gradient.addColorStop(0,"black");
my_gradient.addColorStop(1,"white");
ctx1.fillStyle=my_gradient;
*/
ctx1.fillStyle = ‘rgba(0,0,0,.07)‘;
/*
fillStyle 属性设置或返回用于填充绘画的颜色、渐变或模式。
rgba(R,G,B,A)
其中‘.05‘代表阿尔法透明度
*/
ctx1.fillRect(0, 0, 500, 500);
/*
fillRect() 方法使用 fillStyle 属性所指定的颜色、渐变和模式来填充指定的矩形
*/
ctx1.fillStyle = "#0f0";
ctx1.fillText(‘zhengbin‘, Math.random() * (500), Math.random() * (500));
ctx1.fillText(‘cnblogs‘, Math.random() * (500), Math.random() * (500));
/*
其原理就是不停的产生新的有透明度的背景和要显示的内容,
这样新的背景不停的覆盖旧的显示内容
新的内容就突显了出来
*/
};
runFun();
var id;
function stopFun() {
clearInterval(id);
}
function runFun() {
id = setInterval(Matrix, 50);
/*
setInterval() 定义和用法:
setInterval() 方法可按照指定的周期(以毫秒计)来调用函数或计算表达式。
setInterval() 方法会不停地调用函数,直到 clearInterval() 被调用或窗口被关闭。由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值可用作 clearInterval() 方法的参数。
*/
}
$("button#puse").click(function () {
stopFun();
});
$("button#run").click(function () {
runFun();
});
});
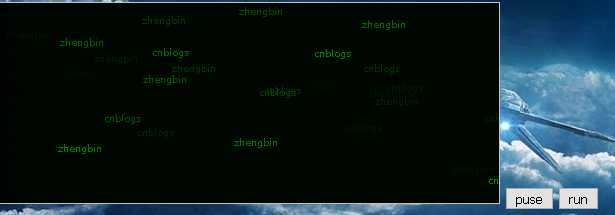
二、
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="500" height="200" style="border:1px solid #c3c3c3;"></canvas>
var YPositions = Array(51).join(0).split(‘‘);
/*
join() 方法用于把数组中的所有元素放入一个字符串
split() 方法用于把一个字符串分割成字符串数组
*/
var c = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx = c.getContext("2d");
var draw = function () {
ctx.fillStyle = ‘rgba(0,0,0,.05)‘;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 500, 500); ctx.fillStyle = "#0f0";
YPositions.map(function (y, index) {
/*
map() 把每个元素通过函数传递到当前匹配集合中,生成包含返回值的新的 jQuery 对象
*/
x = (index * 10);
ctx.fillText(parseInt(Math.random() * 10), x, y);
/*
在(x,y)坐标位产生一个‘a‘字符
index为Ypositions的下标
*/
if (y > 500) {
YPositions[index] = 0;
} else {
YPositions[index] = y + 10;
}
/*
如果新产生的字符已经到了<canvas>的辩解
那么就使产生下一个新字符的位置回归到原点
*/
});
};
setInterval(draw, 30);