1.A题
题意:给定第一行的值表示m列的最大值,第m行的值表示n行的最大值,问是否会行列冲突
思路:挺简单的,不过我在一开始理解题意上用了些时间,按我的理解是输入两组数组,找出每组最大数,若相等则输出possible,否则输出impossible,代码很直接用的C语言
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 int main(){ 3 int r,c,i,j; 4 int s[110],b[110]; 5 while(scanf("%d %d",&r,&c)!=EOF){ 6 for(i=0;i<r;i++){ 7 scanf("%d",&s[i]); 8 } 9 for(j=0;j<c;j++){ 10 scanf("%d",&b[j]); 11 } 12 int max=s[0]; 13 int min=b[0]; 14 for(i=0;i<r;i++){ 15 if(max<=s[i]){ 16 max=s[i]; 17 } 18 } 19 for(j=0;j<c;j++){ 20 if(min<=b[j]){ 21 min=b[j]; 22 } 23 } 24 if(min==max){ 25 printf("possible\n"); 26 } 27 else printf("impossible\n"); 28 } 29 30 31 }
2.G题
题意:复杂字符串中的e
思路:就是记录下e的个数,再双倍输出e其他不变,但要注意数组不要越界,第一次提交就出现了段错误,第二次才正确,看代码
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> char s[1000]; int main(){ //char s[1000]; while(scanf("%s",&s)!=EOF){ int i,m,k=0; m=strlen(s); // printf("%c\n",s[0]); else if(s[0]==‘h‘){ for(i=1;i<m;i++){ if(s[i]==‘e‘){ k++; } } printf("h"); for(i=0;i<k*2;i++){ printf("e"); } printf("y\n"); } } }
3.I题
题意:给定数组a,求公式的最大值
思路:求a数组平方的前缀和以及求a数组后缀和,遍历一遍即可
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
int n, a[1000005];
LL l[1000005], r[1000005];
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) l[i] = l[i - 1] + a[i] * a[i];
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) r[i] = r[i + 1] + a[i];
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) ans = max(ans, l[i] * r[i + 1]);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
4.F题
题意:给定n,求n=m^2-k^2
思路:分三种情况
1.对于n是奇数时,有(x+1)^2-x^2=2x+1
2.对于n是偶数时,有(x+2)^2-x^2=4(x+1)
3.除了上面两种情况,其他都impossible
代码如下:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; LL n; int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%lld", &n); if(n & 1) printf("%lld %lld\n", n / 2 + 1, n / 2); else if(n % 2 == 0 && n % 4) printf("impossible\n"); else printf("%lld %lld\n", (n - 4) / 4 + 2, (n - 4) / 4); return 0; }
5.B题
题解:给定一字符串,最外层数字之间全用+,一层括号用*,两层用+,三层用*,以此类推
思路:每一层括号里的数字之间使用的符号相同,用栈存每一层的数字计算即可,需要手写栈,否则空间不够
代码:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; const long long mod = 1e9 + 7; int n; char s[15]; struct node { int val; node* next; node(int w, node *n){ val = w; next = n; } }; class Stack{ public : int sz; node* head; Stack(){ head = NULL; sz = 0; } bool empty(){ return !sz; } int top(){ if(!empty()) return head->val; return 0; } node *push(int val){ head = new node(val, head); sz++; return head; } void pop(){ if(empty()) return ; node *tp = head; head = head->next; sz--; delete tp; } int size(){ return sz; } }sk[300005]; int change(char s[]){ int res = 0; int len = strlen(s); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) res = res * 10 + s[i] - ‘0‘; return res; } int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%d", &n); int cnt = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ scanf("%s", s); if(s[0] == ‘(‘) cnt++; else if(s[0] == ‘)‘){ if(cnt & 1){ LL ans = 1; while(sk[cnt].size()) ans = ans * sk[cnt].top() % mod, sk[cnt].pop(); cnt--; sk[cnt].push(ans); }else{ LL ans = 0; while(sk[cnt].size()) ans = (ans + sk[cnt].top()) % mod, sk[cnt].pop(); cnt--; sk[cnt].push(ans); } }else{ sk[cnt].push(change(s)); } } LL ans = 0; while(sk[0].size()) ans = (ans + sk[0].top()) % mod, sk[0].pop(); printf("%lld\n", ans); return 0; }
6.C题
题解:可建 k 座桥,建桥后山的高度忽略不计,求从底部(第 r 行)走到顶部(第 1 行)的
路线中最小值最大是多少。
思路:二分答案,用 bfs 跑图即可,因为每一个单元格会重复走,对于走的距离循环来优化 bfs。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; int n, m, k; int mp[1005][1005]; bool vis[1005][1005]; int d[4][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1}; struct node { int x, y; node() {} node(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {} }; int bfs(int val){ memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); queue<node> q[k + 2]; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) vis[n][i] = true, q[mp[n][i] < val ? 1 : 0].push(node(n, i)); for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++){ while(q[i].size()){ node front = q[i].front(); if(front.x == 1) return 1; q[i].pop(); for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++){ int x = front.x + d[j][0], y = front.y + d[j][1]; if(x < 1 || x >= n || y < 1 || y > m) continue; if(!vis[x][y]){ vis[x][y] = true; q[mp[x][y] < val ? i + 1 : i].push(node(x, y)); } } } } return 0; } int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); int l = 0, r = 0; scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &k); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){ scanf("%d", &mp[i][j]); r = max(r, mp[i][j]); } } int ans = l; while(l <= r){ int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if(bfs(mid)) ans = mid, l = mid + 1; else r = mid - 1; } printf("%d\n", ans); return 0; }
7.D题
题解:有一个 n 面的骰子,现在最多可以玩 k 轮,如果在 i(i<=k)轮达到了期望水平(即
期望的骰子分数),那么就会终止,否则继续,问最终游戏的期望分数。
思路:求出第 i 轮的期望分数为 socre1,对于第 i + 1 轮来说,进行第 i + 1 轮
的条件是第 i 轮没有到达期望分数 score1,那么第 i + 1 轮的期望分数为
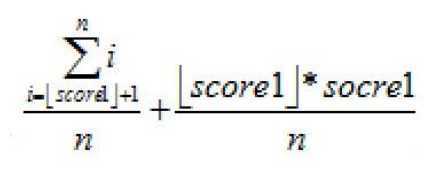
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; int n, k; int p[10005]; int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%d %d", &n, &k); double ans = 0; for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) p[i] = p[i + 1] + i; for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){ if(i == 1){ ans = 1.0 * p[i] / n; }else{ ans = 1.0 * (p[(int)floor(ans) + 1] + floor(ans) * ans) / n; } } printf("%.7lf\n", ans); return 0; }
8.E题
题解:移除最多一半的边使得图没有环。
思路:将所有边分成两部分,第一部分为 u < v,第二部分为 v > u,将小的边
集合删去
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; int n, m; vector<int> v1, v2; int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); for (int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; i++){ scanf("%d %d", &u, &v); if(u < v) v1.push_back(i); else v2.push_back(i); } if(v1.size() > v2.size()){ printf("%d\n", v2.size()); for (auto x : v2) printf("%d\n", x); }else{ printf("%d\n", v1.size()); for (auto x : v1) printf("%d\n", x); } return 0; }
9.H题
题解:
给定起始位置的行(数字 1~11)和列(字母 a~k)和末位置的行和列,求两步(一步的
长度不一定是 1)走到末位置的中间点的数量。
思路:
枚举所有棋的格子,同时满足从起始位置一步到所枚举的格子和所枚举
的格子一步到末位置即答案 + 1
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; char c1, c2; int x, y; bool solve(char sl, int sr, char el, int er){ if(sl == el) return sr != er; if(sl > ‘f‘) sr += sl - ‘f‘; if(el > ‘f‘) er += el - ‘f‘; if(sr == er) return true; if(el - sl == er - sr) return true; return false; } int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%c%d %c%d", &c1, &x, &c2, &y); int ans = 0; for (int i = ‘a‘; i <= ‘k‘; i++){ int num = 11 - abs(‘f‘ - i); for (int j = 1; j <= 11; j++){ if(j > num) break; if(solve(c1, x, i, j) && solve(i, j, c2, y)) ans++; } } printf("%d\n", ans); return 0; }
10.J题
题解:给你 i 到 j 路线长度的平均值(1 <= i, j <= n),求出原始 DAG 路径图
思路:
拓扑排序给你的平均路径图,建立新的拓扑图,设置相邻顶点间的边数
为 1,边值为平均路径。枚举起始点和终点,统计间接到达终点的路数和路径总
长,算出是否要添加一条新的从起始点到终点的直接路径,同时如果有间接路径
时要保证新添的路径长度小于平均值。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; int n, in[105], toposort_v[105], toposort_p[105], num[105][105]; LL dag_ans[105][105]; LL dag_ave[105][105], dag_new[105][105]; int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ scanf("%lld", &dag_ave[i][j]); if(dag_ave[i][j] > 0) in[j]++; } } // toposort to new dag queue<int> q; int cnt = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(!in[i]) q.push(i), toposort_v[++cnt] = i; while(q.size()){ int u = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++){ if(dag_ave[u][v] > 0){ in[v]--; if(in[v] == 0) q.push(v), toposort_v[++cnt] = v; } } } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) toposort_p[toposort_v[i]] = i; // new dag for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ dag_new[i][j] = dag_ave[toposort_v[i]][toposort_v[j]]; } } // orginal ans_dag memset(dag_ans, -1, sizeof(dag_ans)); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){ if(dag_new[i][i + 1] > 0) dag_ans[i][i + 1] = dag_new[i][i + 1], num[i][i + 1] = 1; } for (int len = 2; len <= n; len++){ for (int i = 1; i + len <= n; i++){ int j = i + len; // i -> k -> j ways‘ number and weight LL sum = 0; for (int k = i + 1; k < j; k++){ if(dag_ans[i][k] > 0 && num[k][j] > 0){ num[i][j] += num[k][j]; sum += dag_ans[i][k] * num[k][j] + dag_new[k][j] * num[k][j]; } } // if add a path, ave = (sum + x) / (num[i][j] + 1), x is new path‘s weight LL x = dag_new[i][j] * (num[i][j] + 1) - sum; if((num[i][j] == 0 && dag_new[i][j] > 0) || (num[i][j] && x > 0 && dag_new[i][j] > x)){ // 保证直连的线长度小于间接连得线,所以直连的线小于平均值 dag_ans[i][j] = x; num[i][j]++; } } } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ int x = toposort_p[i], y = toposort_p[j]; printf("%lld%c", dag_ans[x][y], j == n ? ‘\n‘ : ‘ ‘); } } return 0; }
11.K题
题解:
给定 n 件物品和他们的重量以及所有组合重量,求是否存在这 n 件物品的重量
来满足这些组合
思路:
将所有重量存入 multiset 中,每次考虑最大的次大的,必能得到 n 个物
品中一个物品的重量,从 multiset 中删除与此重量有关的所有组合,若找不到,
输出 impossible。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; int n, ans[25]; multiset<int> s; int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0, x; i < (1 << n); i++) scanf("%d", &x), s.insert(x); int cnt = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ if(s.size() < 2) break; cnt++; int x = *prev(s.end()) - *prev(prev(s.end())); ans[i] = x; for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++){ int y = *it; auto p = s.upper_bound(x + y); p = prev(p); if(p == s.end() || p == it || *p != x + y){ printf("impossible\n"); return 0; } s.erase(p); } } if(s.size() != 1 || *s.begin() != 0 || cnt < n) printf("impossible\n"); else for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[i]); return 0; }
12.L题
题解:
两个救生员中最靠近游泳者是监控者。找到两个救生员的坐标,使得救生员监控
的游泳者数量相同,最多有一个游泳的离两个救生员距离相同。
思路:
同 https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/883/H,将所有游泳的根据坐
标排序,用一直线划分成两部分,线的两个无穷远处为端点,若游泳的数量为奇
数,那么此线需经过中间点。设中间点为(x,y)Max 设为无穷大例: n 为偶数 (x -
Max, y - 1), (x + Max, y) n 为奇数 (x - Max, y - 1), (x + Max, y + 1)
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <queue> typedef long long LL; using namespace std; int n; struct node { LL x, y; bool operator <(const node &rhs)const{ return x == rhs.x ? y < rhs.y : x < rhs.x; } }a[100005]; int main() { //freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%lld %lld", &a[i].x, &a[i].y); sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n); int mid = (n + 2) / 2; LL MAX = 10000000000LL; LL x = a[mid].x, y = a[mid].y; if(n & 1){ printf("%lld %lld\n", x - MAX, y - 1); printf("%lld %lld\n", x + MAX, y + 1); }else{ printf("%lld %lld\n", x - MAX, y - 1); printf("%lld %lld\n", x + MAX, y); } return 0; }
2020.3.14--训练联盟周赛 Preliminaries for Benelux Algorithm Programming Contest 2019
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/mxw000120/p/12517114.html