装饰模式(Decorator)动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更灵活。
装饰模式中每个对象的实现和对这个对象的使用是分开的。每个装饰对象只需要关心自己的功能,不需要关心如何被添加到对象链当中的。
当系统需要新功能时,是向旧的类中添加新的代码。这些新加的代码通常装饰了原有类的核心职责或主要行为,在主类中加入新的方法、新的逻辑,从而增加了主类的复杂度。而这些新加的东西仅仅是为了满足一些只在某种特定情况下才会执行的特殊行为的需要。对于这种问题,装饰模式提供了一个非常好的解决方案,它把每个要装饰的功能放在单独的类中,并让这个类包装它所需要装饰的对象,因此,当需要执行特殊行为时,客户代码就可以再运行时根据需要有选择地、按顺序地使用装饰功能包装对象。
优点:1.把类中的装饰功能从类中搬移出去,这样简化了原有的类。
2.有效地把类的核心职能和装饰功能区分开了,而且可以去除相关类中重复的装饰逻辑。
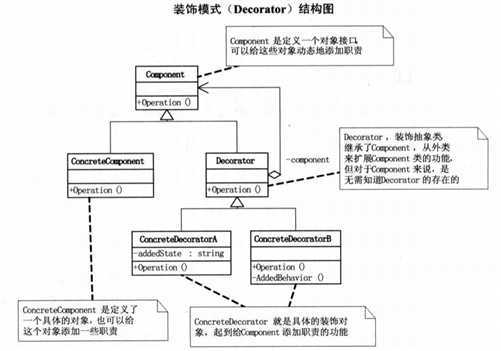
Component是定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加职责。ConcrecteComponent是定义了一个具体的对象,也可以给这个对象添加一些职责。Decorator,装饰抽象类,继承了Component,从外来类来扩展Component类的功能,但对于Component来说,是无需知道Decorator的存在的。至于ConcreateDecorator就是具体的装饰对象,起到给Component添加职责的功能。
// Person类 #ifndef _PERSON_HPP #define _PERSON_HPP class Person{ public: virtual void show(){ } virtual void action(){ } }; #endif
// Girl类 #ifndef _GIRL_HPP #define _GIRL_HPP #include"person.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Girl:public Person{ public: virtual void action(){ cout<< "i am a girl" <<endl; } }; #endif
// Boy类 #ifndef _BOY_HPP #define _BOY_HPP #include"person.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Boy:public Person{ public: virtual void action(){ cout<< "i am a boy" <<endl; } }; #endif
//装饰基类 #ifndef _DECORATOR_HPP #define _DECORATOR_HPP #include"person.hpp" class Decorator : public Person{ public: Decorator(Person* prs):p(prs){ } protected: Person* p; //被装饰的对象 }; #endif
#ifndef _HAT_HPP #define _HAT_HPP #include"person.hpp" // 具体装饰类 Hat类 #include"decorator.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Hat:public Decorator{ public: Hat(Person*p):Decorator(p){ } virtual void show()override{ p->show(); cout << "hat" << endl; } }; #endif
//具体装饰类 Clothes类 #ifndef _ClOTHES_HPP #define _CLOTHES_HPP #include"person.hpp" #include"decorator.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Clothes:public Decorator{ public: Clothes(Person* p):Decorator(p){ } virtual void show(){ p->show(); cout << "Clothes" << endl; } }; #endif
//客户端 #include"person.hpp" #include"hat.hpp" #include"clothes.hpp" #include"girl.hpp" #include"boy.hpp" int main(){ Person* xiaoming = new Boy(); Hat* bhat = new Hat(xiaoming); Clothes* bclothes = new Clothes(bhat); xiaoming->action(); bclothes->show(); Person* xiaohong = new Girl(); Hat*ghat = new Hat(xiaohong); Clothes *gclothes = new Clothes(ghat); xiaohong->action(); gclothes->show(); getchar(); return 0; }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yb-blogs/p/12498587.html