public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的 parent 指针。假设有一 棵 Node 类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的 parent 指针都正确地指向自己的父节点,头节点的 parent 指向 null。只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点 node,请实现返回 node 的后继节点的函数。
在二叉树中,前驱结点和后继结点是按照二叉树中两个结点被中序遍历的先后顺序来划分的。
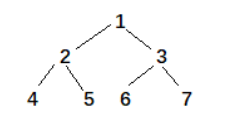
以上面的树形结构为例,中序遍历结果为:4 2 5 1 6 3 7,则 1 的后继结点为 6,前驱结点为 5;
方案:
==这里按自己的理解来比较好==
补充:如果求前驱结点,方案如下:
如果结点有左子树,该结点的前驱就是左子树的最右边结点;
如果结点没有左子树,就一直往上找,直到指向的结点是其父结点的右孩子为止;
public class SuccessorNode {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
// 说明当前结点有右子树,则后继结点为右子树的最左结点
if (node.right != null) {
return getLeftMost(node.right);
} else {
Node parent = node.parent;
// 当前节点是父结点的左孩子则停止;整棵树最右边的节点是没有后继的,例如节点7,最终一直上升到节点1,但是节点1的 parent指向null,所有最后返回
// null表示没有后继;
//一直网上找,直到找到parent.left == node
while (parent != null && parent.left != node) {
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
//这里也兼顾了,找不到的情况,反正找到头,找不到parent.left == node就为空,符合事实
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) {
//为空返回
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
//一路往左
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
}测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(6);
head.parent = null;
head.left = new Node(3);
head.left.parent = head;
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.left.left.parent = head.left;
head.left.left.right = new Node(2);
head.left.left.right.parent = head.left.left;
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.right.parent = head.left;
head.left.right.right = new Node(5);
head.left.right.right.parent = head.left.right;
head.right = new Node(9);
head.right.parent = head;
head.right.left = new Node(8);
head.right.left.parent = head.right;
head.right.left.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left.parent = head.right.left;
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.parent = head.right;
Node test = head.left.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.left.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.right.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.left.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.right; // 10's next is null
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test));
} 程序运行结果为:
1 next: 2
2 next: 3
3 next: 4
4 next: 5
5 next: 6
6 next: 7
7 next: 8
8 next: 9
9 next: 10
10 next: null原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/kristse/p/getpost.html