1001 害死人不偿命的(3n+1)猜想 (15分)
卡拉兹(Callatz)猜想:
对任何一个正整数 n,如果它是偶数,那么把它砍掉一半;如果它是奇数,那么把 ( 砍掉一半。这样一直反复砍下去,最后一定在某一步得到 n=1。卡拉兹在 1950 年的世界数学家大会上公布了这个猜想,传说当时耶鲁大学师生齐动员,拼命想证明这个貌似很傻很天真的命题,结果闹得学生们无心学业,一心只证 (,以至于有人说这是一个阴谋,卡拉兹是在蓄意延缓美国数学界教学与科研的进展……
我们今天的题目不是证明卡拉兹猜想,而是对给定的任一不超过 1000 的正整数 n,简单地数一下,需要多少步(砍几下)才能得到 n=1?
每个测试输入包含 1 个测试用例,即给出正整数 n 的值。
输出从 n 计算到 1 需要的步数。
35
#include<cstdio> int main(){ int n,count=0; scanf("%d",&n); while(n!=1){ if(n%2==0){ n = n/2; count++; }else{ n = (3*n+1)/2; count++; } } printf("%d",count); return 0; }
给定区间 [−] 内的 3 个整数 A、B 和 C,请判断 A+B 是否大于 C。
输入第 1 行给出正整数 T (≤),是测试用例的个数。随后给出 T 组测试用例,每组占一行,顺序给出 A、B 和 C。整数间以空格分隔。
对每组测试用例,在一行中输出 Case #X: true 如果 A+B>C,否则输出 Case #X: false,其中 X 是测试用例的编号(从 1 开始)。
4
1 2 3
2 3 4
2147483647 0 2147483646
0 -2147483648 -2147483647Case #1: false
Case #2: true
Case #3: true
Case #4: false
#include<cstdio> #include<cmath> int main(){ long long A,B; int DA,DB; scanf("%lld%d%lld%d",&A,&DA,&B,&DB); int PA=0,PB=0; int i=0; while(A!=0){ if(A%10 == DA){ PA = PA + DA*pow(10,i); i++; } A = A/10; } i = 0; while(B!=0){ if(B%10 == DB){ PB = PB + DB*pow(10,i); i++; } B = B/10; } printf("%d\n",PA+PB); return 0; }
要获得一个 C 语言程序的运行时间,常用的方法是调用头文件 time.h,其中提供了 clock() 函数,可以捕捉从程序开始运行到 clock() 被调用时所耗费的时间。这个时间单位是 clock tick,即“时钟打点”。同时还有一个常数 CLK_TCK,给出了机器时钟每秒所走的时钟打点数。于是为了获得一个函数 f 的运行时间,我们只要在调用 f 之前先调用 clock(),获得一个时钟打点数 C1;在 f 执行完成后再调用 clock(),获得另一个时钟打点数 C2;两次获得的时钟打点数之差 (C2-C1) 就是 f 运行所消耗的时钟打点数,再除以常数 CLK_TCK,就得到了以秒为单位的运行时间。
这里不妨简单假设常数 CLK_TCK 为 100。现给定被测函数前后两次获得的时钟打点数,请你给出被测函数运行的时间。
输入在一行中顺序给出 2 个整数 C1 和 C2。注意两次获得的时钟打点数肯定不相同,即 C1 < C2,并且取值在 [。
在一行中输出被测函数运行的时间。运行时间必须按照 hh:mm:ss(即2位的 时:分:秒)格式输出;不足 1 秒的时间四舍五入到秒。
123 457797312:42:59#include<cstdio> int main(){ int c1,c2; scanf("%d%d",&c1,&c2); int ans = c2-c1; if(ans%100>=50){ ans = ans/100+1; }else{ ans = ans/100; } printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n",ans/3600,ans%3600/60,ans%60); return 0; }
划拳是古老中国酒文化的一个有趣的组成部分。酒桌上两人划拳的方法为:每人口中喊出一个数字,同时用手比划出一个数字。如果谁比划出的数字正好等于两人喊出的数字之和,谁就赢了,输家罚一杯酒。两人同赢或两人同输则继续下一轮,直到唯一的赢家出现。
下面给出甲、乙两人的划拳记录,请你统计他们最后分别喝了多少杯酒。
输入第一行先给出一个正整数 N(≤),随后 N 行,每行给出一轮划拳的记录,格式为:
甲喊 甲划 乙喊 乙划
其中喊是喊出的数字,划是划出的数字,均为不超过 100 的正整数(两只手一起划)。
在一行中先后输出甲、乙两人喝酒的杯数,其间以一个空格分隔。
5
8 10 9 12
5 10 5 10
3 8 5 12
12 18 1 13
4 16 12 151 2#include<cstdio> int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); int a1,a2,b1,b2; int faia=0,faib=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a1,&a2,&b1,&b2); if(a1+b1 == a2 && a1+b1 != b2){ faib++; }else if(a1+b1 == b2 && a1+b1 != a2){ faia++; } } printf("%d %d",faia,faib); return 0; }
一个数组A中存有N(>)个整数,在不允许使用另外数组的前提下,将每个整数循环向右移M(≥)个位置,即将A中的数据由(A?0??A?1???A?N−1??)变换为(A?N−M???A?N−1??A?0??A?1???A?N−M−1??)(最后M个数循环移至最前面的M个位置)。如果需要考虑程序移动数据的次数尽量少,要如何设计移动的方法?
每个输入包含一个测试用例,第1行输入N(1)和M(≥);第2行输入N个整数,之间用空格分隔。
在一行中输出循环右移M位以后的整数序列,之间用空格分隔,序列结尾不能有多余空格。
6 2
1 2 3 4 5 65 6 1 2 3 4#include<cstdio> int main(){ int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); int a[110]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); } m = m%n; int count=0; for(int i=n-m;i<n;i++){ printf("%d",a[i]); count++; if(count < n) printf(" "); } for(int i=0;i<n-m;i++){ printf("%d",a[i]); count++; if(count < n) printf(" "); } return 0; }
给定一系列正整数,请按要求对数字进行分类,并输出以下 5 个数字:
每个输入包含 1 个测试用例。每个测试用例先给出一个不超过 1000 的正整数 N,随后给出 N 个不超过 1000 的待分类的正整数。数字间以空格分隔。
对给定的 N 个正整数,按题目要求计算 A?1??~A?5?? 并在一行中顺序输出。数字间以空格分隔,但行末不得有多余空格。
若其中某一类数字不存在,则在相应位置输出 N。
13 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 16 1830 11 2 9.7 98 1 2 4 5 6 7 9 16N 11 2 N 9#include<cstdio> int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); int count[5] = {0}; int ans[5] = {0}; int flag = 1; while(n--){ int temp; scanf("%d",&temp); if(temp%5 == 0 && temp%2==0){ ans[0] = ans[0] + temp; count[0]++; }else if(temp%5 == 1){ ans[1] = ans[1] + flag*temp; flag = -flag; count[1]++; }else if(temp%5 == 2){ ans[2]++; count[2]++; }else if(temp%5 == 3){ count[3]++; ans[3] = ans[3]+temp; }else if(temp%5 == 4){ if(temp > ans[4]){ ans[4] = temp; count[4]++; } } } for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ if(count[i]==0 && i==4){ printf("N"); continue; } if(count[i]==0 && i<4){ printf("N "); continue; } if(i==3){ printf("%.1f ",(double)ans[3]/count[3]); }else if(i==4){ printf("%d",ans[i]); }else{ printf("%d ",ans[i]); } } return 0; }
大家应该都会玩“锤子剪刀布”的游戏:两人同时给出手势,胜负规则如图所示:
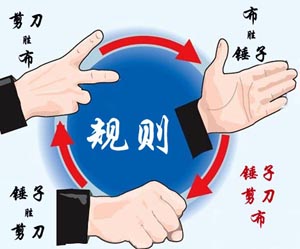
现给出两人的交锋记录,请统计双方的胜、平、负次数,并且给出双方分别出什么手势的胜算最大。
输入第 1 行给出正整数 N(≤),即双方交锋的次数。随后 N 行,每行给出一次交锋的信息,即甲、乙双方同时给出的的手势。C 代表“锤子”、J 代表“剪刀”、B 代表“布”,第 1 个字母代表甲方,第 2 个代表乙方,中间有 1 个空格。
输出第 1、2 行分别给出甲、乙的胜、平、负次数,数字间以 1 个空格分隔。第 3 行给出两个字母,分别代表甲、乙获胜次数最多的手势,中间有 1 个空格。如果解不唯一,则输出按字母序最小的解。
10
C J
J B
C B
B B
B C
C C
C B
J B
B C
J J
5 3 2 2 3 5 B B
#include<cstdio> int change(char c){ if(c==‘B‘){ return 0; }else if(c == ‘C‘){ return 1; }else if(c == ‘J‘){ return 2; } } int main(){ int n; char mp[3]={‘B‘,‘C‘,‘J‘}; scanf("%d",&n); char jia,yi; int jiacondition[3]={0},yicondition[3]={0};//记录甲乙的胜平负次数 int handjia[3]={0},handyi[3]={0};//记录甲乙获胜的手势 while(n--){ getchar(); scanf("%c %c",&jia,&yi); int hjia,hyi; hjia = change(jia); hyi = change(yi); if(hjia == hyi){ jiacondition[1]++; yicondition[1]++; }else if((hjia+1)%3 == hyi){ jiacondition[0]++; yicondition[2]++; handjia[hjia]++; }else if((hyi+1)%3 == hjia){ yicondition[0]++; jiacondition[2]++; handyi[hyi]++; } } printf("%d %d %d\n",jiacondition[0],jiacondition[1],jiacondition[2]); printf("%d %d %d\n",yicondition[0],yicondition[1],yicondition[2]); int id1=0,id2=0; for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ if(handjia[i] > handjia[id1]) id1 = i; if(handyi[i] > handyi[id2]) id2 = i; } printf("%c %c",mp[id1],mp[id2]); return 0; }
The task is really simple: given N exits on a highway which forms a simple cycle, you are supposed to tell the shortest distance between any pair of exits.
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains an integer N (in [3]), followed by N integer distances D?1?? D?2?? ? D?N??, where D?i?? is the distance between the i-th and the (-st exits, and D?N?? is between the N-th and the 1st exits. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The second line gives a positive integer M (≤), with M lines follow, each contains a pair of exit numbers, provided that the exits are numbered from 1 to N. It is guaranteed that the total round trip distance is no more than 1.
For each test case, print your results in M lines, each contains the shortest distance between the corresponding given pair of exits.
5 1 2 4 14 9
3
1 3
2 5
4 13
10
7#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 100010; int dis[MAXN],A[MAXN]; int main(){ int n; int sum=0,query; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&A[i]); sum = sum + A[i]; dis[i] = sum; } int left,right; scanf("%d",&query); for(int i=0;i<query;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&left,&right); if(left >right) swap(left,right); int temp = dis[right-1]-dis[left-1]; printf("%d\n",min(temp,sum-temp)); } return 0; }
Given three integers A, B and C in [−], you are supposed to tell whether A+B>C.
The first line of the input gives the positive number of test cases, T (≤). Then T test cases follow, each consists of a single line containing three integers A, B and C, separated by single spaces.
For each test case, output in one line Case #X: true if A+B>C, or Case #X: false otherwise, where X is the case number (starting from 1).
3
1 2 3
2 3 4
9223372036854775807 -9223372036854775808 0Case #1: false
Case #2: true
Case #3: false
#include<cstdio> int main(){ int T; scanf("%d",&T); int i=1; while(T--){ long long A,B,C; scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&A,&B,&C); long long res = A+B; bool flag; if(A > 0 && B>0 && res <0) flag = true; else if(A < 0 && B < 0 && res>=0) flag = false; else if(res > C) flag = true; else flag = false; if(flag == true){ printf("Case #%d: true\n",i++); }else{ printf("Case #%d: false\n",i++); } } return 0; }
设计函数求一元多项式的导数。(注:x?n??(n为整数)的一阶导数为nx?n−1??。)
以指数递降方式输入多项式非零项系数和指数(绝对值均为不超过 1000 的整数)。数字间以空格分隔。
以与输入相同的格式输出导数多项式非零项的系数和指数。数字间以空格分隔,但结尾不能有多余空格。注意“零多项式”的指数和系数都是 0,但是表示为 0 0。
3 4 -5 2 6 1 -2 012 3 -10 1 6 0#include<cstdio> int main(){ int a[1010]={0}; int e,k,count=0; while(scanf("%d%d",&e,&k)!=EOF){ a[k]=e; } a[0] = 0; for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){ a[i-1] = a[i]*i; a[i]= 0; if(a[i-1]!=0) count++; } if(count==0){ printf("0 0"); }else{ for(int i=1000;i>=0;i--){ if(a[i]!=0){ printf("%d %d",a[i],i); count--; if(count!=0) printf(" "); } } } return 0; }
This time, you are supposed to find A+B where A and B are two polynomials.
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies 2 lines, and each line contains the information of a polynomial:
K N?1?? a?N?1???? N?2?? a?N?2???? ... N?K?? a?N?K????
where K is the number of nonzero terms in the polynomial, N?i?? and a?N?i???? (,) are the exponents and coefficients, respectively. It is given that 1,0.
For each test case you should output the sum of A and B in one line, with the same format as the input. Notice that there must be NO extra space at the end of each line. Please be accurate to 1 decimal place.
2 1 2.4 0 3.2
2 2 1.5 1 0.5
3 2 1.5 1 2.9 0 3.2
#include<cstdio> int main(){ int k; scanf("%d",&k); double p[1010]={}; int n; double a; for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ scanf("%d %lf",&n,&a); p[n] += a; } scanf("%d",&k); for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ scanf("%d %lf",&n,&a); p[n] += a; } int count=0; for(int i=1000;i>=0;i--){ if(p[i]!=0) count++; } printf("%d",count); for(int i=1000;i>=0;i--){ if(p[i]!=0) printf(" %d %.1f",i,p[i]); } return 0; }
This time, you are supposed to find A×B where A and B are two polynomials.
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies 2 lines, and each line contains the information of a polynomial:
K N?1?? a?N?1???? N?2?? a?N?2???? ... N?K?? a?N?K????
where K is the number of nonzero terms in the polynomial, N?i?? and a?N?i???? (,) are the exponents and coefficients, respectively. It is given that 1, 0.
For each test case you should output the product of A and B in one line, with the same format as the input. Notice that there must be NO extra space at the end of each line. Please be accurate up to 1 decimal place.
2 1 2.4 0 3.2
2 2 1.5 1 0.53 3 3.6 2 6.0 1 1.6#include<cstdio> struct{ int exp; double cof; }poly[1001]; int main(){ double ans[2001]={0.0}; int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d %lf",&poly[i].exp,&poly[i].cof); } scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ int exp; double cof; scanf("%d %lf",&exp,&cof); for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ ans[exp+poly[j].exp] += (cof*poly[j].cof); } } int count=0; for(int i=0;i<2001;i++){ if(ans[i]!=0.0) count++; } printf("%d",count); for(int i=2000;i>=0;i--){ if(ans[i]!=0.0) printf(" %d %.1f",i,ans[i]); } return 0; }
算法笔记 第3章 入门篇(1)--入门模拟 配套练习 学习笔记
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/coderying/p/12207776.html