Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2829 Accepted Submission(s): 1423
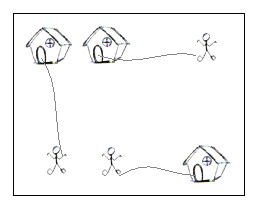
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 110
#define INF 99999999
int n, m;
char map[N][N]; //存储原始字符地图的
int ma[N][N]; //类似边表的可匹配存储
int lx[N], ly[N];
int vtx[N], vty[N];
int match[N];
int slack[N];
int cnt;
int max(int a, int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int min(int a, int b)
{
return a>b?b:a;
}
int hungary(int dd) //匈牙利算法
{
int i;
vtx[dd]=1;
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
if(vty[i])
continue;
else
{
if(lx[dd]+ly[i] == ma[dd][i] )
{
vty[i]=1;
if(match[i]==-1 || hungary(match[i]) )
{
match[i] = dd;
return 1;
}
}
else
slack[i] = min( slack[i], lx[dd] + ly[i]-ma[dd][i] );
}
}
return 0;
}
void km_match() //最大权匹配
{
int i, j;
int temp;
memset(lx, 0, sizeof(lx));
memset(ly, 0, sizeof(ly));
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<cnt; j++)
{
lx[i]=max(lx[i], ma[i][j] );
} //表示当前的i号人,去某一个房子的最大距离
}
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<cnt; j++)
{
slack[j]=INF; //初始无穷大
}
while(1)
{
memset(vtx, 0, sizeof(vtx));
memset(vty, 0, sizeof(vty));
if(hungary(i)) //匈牙利算法
break;
else
{
temp=INF;
for(j=0; j<cnt; j++)
{
if(!vty[j])
{
temp=min(temp, slack[j] );
}
}
for( j=0; j<cnt; j++ )
{
if( vtx[j] )
lx[j] -= temp;
if( vty[j] )
ly[j] += temp;
else
slack[j] -= temp;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j, k, ll;
int ci, cj;
int sum;
while(scanf("%d %d", &n, &m) && n!=0 && m!=0 )
{
memset(match, -1, sizeof(match ));//match数组初始 -1,记录父节点
cnt=0;
for(i=0; i<n; i++ )
{
scanf("%*c"); //每行先取一个回车换行
for(j=0; j<m; j++)
{
scanf("%c", & map[i][j] );
if(map[i][j] == ‘m‘ ) //如果是个人
{
cnt++; //记录 人数, 建图时需要
}
}
}
//四层循环 前两层遍历map寻找m 内两层循环找h
ci=0;
cj=0;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<m; j++)
{
if(map[i][j]==‘m‘) //找到一个人
{
//找到人之后遍历map找 H
for(k=0; k<n; k++)
{
for(ll=0; ll<m; ll++)
{
if(map[k][ll]==‘H‘)
{
ma[ci][cj++] = 100-(abs(k-i)+abs(ll-j));
//大数减边
}
}
}
ci++; //换到下一行存储
cj=0; //cj指针回到0位置
}
}
}
km_match(); //最大权匹配
sum=0;
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
sum+=ma[match[i]][i] ;
}
printf("%d\n", 100*cnt-sum );
}
return 0;
}
28
HDU 1533 Going home,布布扣,bubuko.com
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/yspworld/p/3926311.html